实验十四 Swing图形界面组件
实验时间 20178-11-29
一、知识部分
1.模型-视图-控制器模式
模型:储存内容
视图:显示内容
控制器:处理用户输入
2.布局管理
2-1.流布局管理器(FlowLayout)
JPanel对象的默认布局管理器为FlowLayout,组件加入JPanel中总是处于中央,一行可以排列多个组件,如果一行的空间容纳不下所有的组件则换行。当顶层窗口缩放时,JPanel中组件的大小不会随之缩放。
2-2.边框布局管理器(BorderLayout)
是JFrame的内容窗格的默认布局管理器,可以选择将空间放在内容窗格的东、南、西、北、中。 且将组件加入其中时,组件会充满其对应的整个区域,如果在这个方位再加入一个组件,会覆盖原本存在的组件。当顶层窗口缩放时,东南西北的组件不会随之变化,中部的组件会等比例变化。
如果要在某方法并排加入几个组件,则可以先将组件加入JPanel中,再放入边框布局管理器。
BorderLayout的常量定义为字符串
frame.add(new JButton("Yes"),BorderLayout.SOUTH);
2-3.网格布局(Grid Layout)
布局类似于表格,每个单元大小一致,当顶层窗口缩放时组件大小也随之变化,但是尺寸比例保持一致。
frame.SetLayout(new GridLayout(4,4));//形成4x4的网格
frame.add(new JButton("1"));
GridLayout(int r,int c) 参数之一可以为0,但是不能同时为0
GridLayout(int r,int c,int hgap,int vgap) hgap表示单元之间的水平间距,vgap表示单元之间的垂直间距
3.文本输入
3-1.扩展于JTextComponent的JTextField和JTextArea
JTextField和JTextArea都用于文本输入,其中JTextField接收单行文本的输入,而JTextArea可接收多行文本的输入。
列数为文本域的宽度,如果希望文本域最多能输入N个字符,则将宽度设置为N
JTextField text = new JTextField("Input Here",20);
第二个构造函数可以指定文本区显示的行数和列数。如果需要设置滚动条,则需要将文本区加入JScrollPane中,再讲JScrollPane插入容器。
JTextArea area = new TextArea(4,10);
JScrollPane pane = new JScrollPane(area);
panel.add(pane);
3-2.扩展于JTextField的JPasswordField
接受单行输入,输入字符被特殊字符掩盖
3-3.JLabel
没有任何修饰,不能响应用户输入,只是容纳文本的组件。可以设置标签的显示文字、图标以及对其方式
其中对其方式是SwingConstants里的常量,如LEFT/RIGHT/CENTER等
JLabel label = new JLabel("User Name:",SwingConstants.RIGHT);
4.选择组件
4-1.JCheckBox
复选框自动带有标签和图标,在构造时可以提供,当用户选中复选框时会触发动作事件。
JCheckBox box = new JCheckBox("Bold");
box.setSelected(true);
4-2.单选钮(JRadioButton)
自带标签和图标。单选钮只能多选其一,要打到这种效果需要把所有的单选钮加入ButtonGroup的对象里,从而使得新按钮被按下时,取消前一个选中的按钮的状态。ButtonGroup直接扩展于Object类,所以单选钮需加入容器中进行布局,ButtonGroup和容器(如JPanel)是相互独立的。
选中时触发动作事件。
4-3.边框(Border)
任何继承自JComponent的组件都可以使用边框(void setBorder(Border b))。常用的方法是将组件放入容器中,然后容器使用边框。是通过调用BorderFactory的静态方法构建边框。
同时可以为边框设置标题:
Border etch = BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder();
Border title = BorderFactory.createTitleBorder(etch,"Title");
panel.setBorder(title);
4-4.组合框
JComboBox< T>是泛型类,构建时需注意。
组合框不仅有下拉选择的功能,还具有文本框编辑的功能。
获得当前选中内容:
combo.getItemAt(combo.getSelectedIndex());
//Object getItemAt(int index)
当用户从组合框中选中一个选项时,组合框就会产生一个动作事件。
4-5.滑动条(JSlider)
滑动条在构造时默认是横向,如果需要纵向滑动条:
JSlider s = new JSlider(SwingConstants.VERTICAL,min,max,initialValue);
当滑动条滑动时,会触发ChangeEvent,需要调用addChangeListener()并且安装一个实现了ChangeListener接口的对象。这个接口只有一个StateChanged方法
//得到滑动条的当前值
ChangeListener listen = event ->{
JSlider s = (JSlider)event.getSource();
int val = s.getValue();
...
};
如果需要显示滑动条的刻度,则setPaintTicks(true);
如果要将滑动条强制对准刻度,则setSnapToTicks(true);
如果要为滑动条设置标签,则需要先构建一个Hashtable< Integer,Component>,将数字与标签对应起来,再调用setLabelTable(Dictionary label);
5.复杂的布局管理
5-1.GridBagLayout(网格组布局)
即没有限制的网格布局,行和列的尺寸可以改变,且单元格可以合并
过程:
1)建议一个GridBagLayout对象,不需要指定行列数
2)将容器setLayout为GBL对象
3)为每个组件建立GridBagConstraints对象,即约束组件的大小以及排放方式
4)通过add(component,constraints)增加组件
使用帮助类来管理约束会方便很多。
5-2.不使用布局管理器
frame.setLayout(null);
JButton btn = new JButton("Yes");
frame.add(btn);
btn.setBounds(10,10,100,30);
//void setBounds(int x,int y,int width,int height)//x,y表示左上角的坐标,width/height表示组件宽和高,Component类的方法
5-3.组件的遍历顺序(焦点的顺序):从左至右从上到下
component.setFocusable(false);//组件不设置焦点
6.菜单
分为JMenuBar/JMenu/JMenuItem,当选择菜单项时会触发一个动作事件,需要注册监听器监听
7.对话框
对话框分为模式对话框和无模对话框,模式对话框就是未处理此对话框之前不允许与其他窗口交互。
7-1.JOptionPane
提供了四个用静态方法(showxxxx)显示的对话框:
构造对话框的步骤:
1)选择对话框类型(消息、确认、选择、输入)
2)选择消息类型(String/Icon/Component/Object[]/任何其他对象)
3)选择图标(ERROR_MESSAGE/INFORMATION_MESSAGE/WARNING_MESSAGE/QUESTION_MESSAGE/PLAIN_MESSAGE)
4)对于确认对话框,选择按钮类型(DEFAULT_OPTION/YES_NO_OPTION/YES_NO_CANCEL_OPTION/OK_CANCEL_OPTION)
5)对于选项对话框,选择选项(String/Icon/Component)
6)对于输入对话框,选择文本框或组合框
确认对话框和选择对话框调用后会返回按钮值或被选的选项的索引值
7-2.JDialog类
可以自己创建对话框,需调用超类JDialog类的构造器
public aboutD extends JDialog
{
public aboutD(JFrame owner)
{
super(owner,"About Text",true);
....
}
}
构造JDialog类后需要setVisible才能时窗口可见
if(dialog == null)
dialog = new JDialog();
dialog.setVisible(true);
7-3.文件对话框(JFileChooser类)
7-4.颜色对话框(JColorChooser类)
二、实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握GUI布局管理器用法;
(2) 掌握各类Java Swing组件用途及常用API;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第12章示例程序,测试程序并进行组内讨论。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第12章示例程序,测试程序并进行组内讨论。
测试程序1
l 在elipse IDE中运行教材479页程序12-1,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握各种布局管理器的用法;
l 理解GUI界面中事件处理技术的用途。
l 在布局管理应用代码处添加注释;

测试程序2
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材486页程序12-2,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握各种文本组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
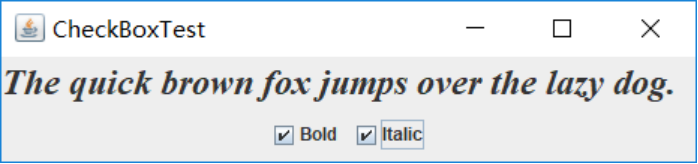
测试程序3
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材489页程序12-3,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握复选框组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
普通字体:

加粗:

斜体和加粗:
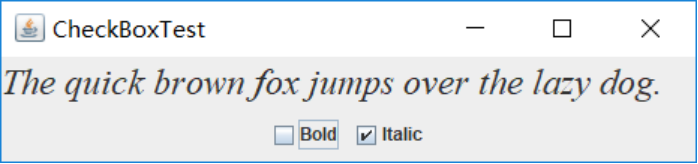
斜体:
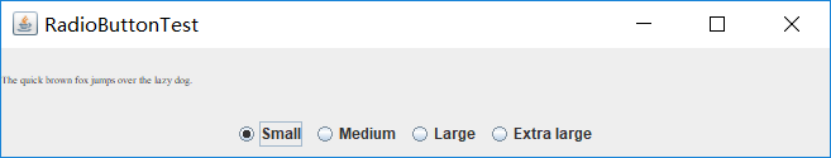
测试程序4
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材491页程序12-4,运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握单选按钮组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
samll:
medium:
large:
extra large:

单选钮,只能选中一个
测试程序5
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材494页程序12-5,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握边框的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
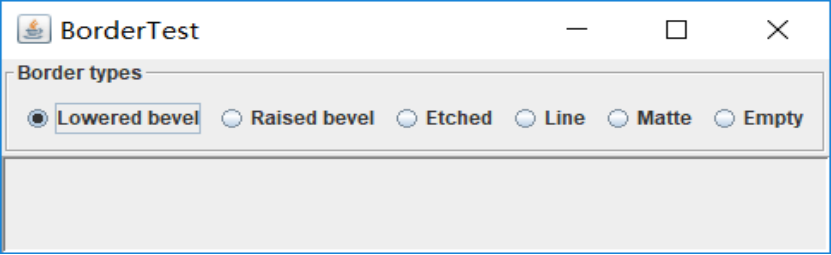

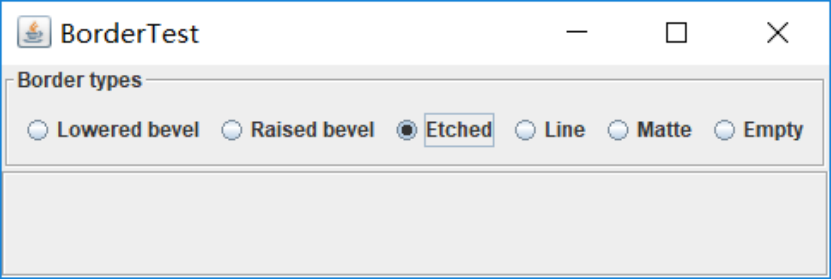


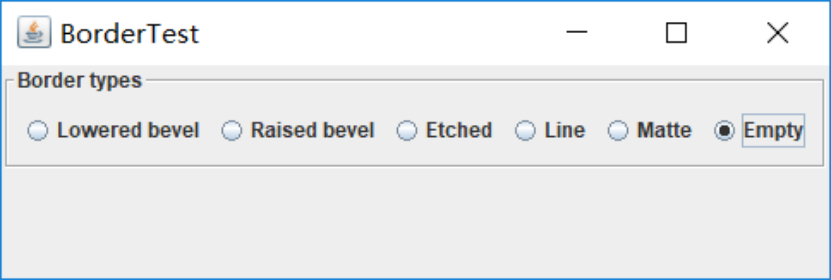
测试程序6
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材498页程序12-6,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握组合框组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。


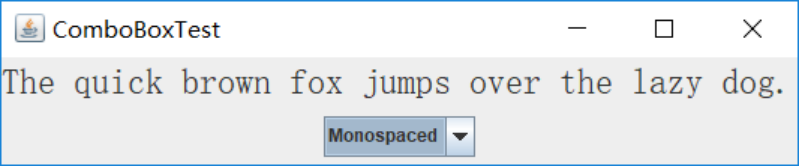
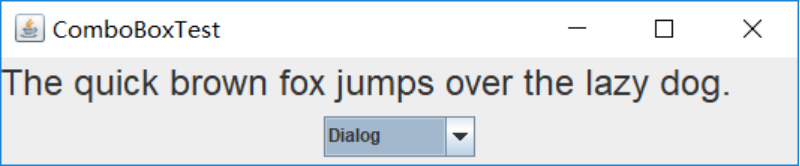
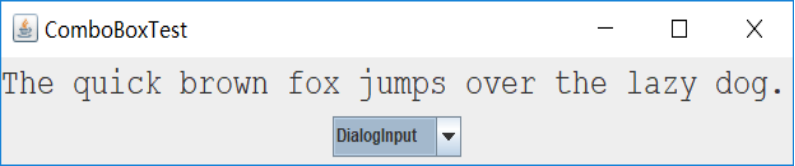
测试程序7
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材501页程序12-7,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握滑动条组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

测试程序8
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材512页程序12-8,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握菜单的创建、菜单事件监听器、复选框和单选按钮菜单项、弹出菜单以及快捷键和加速器的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
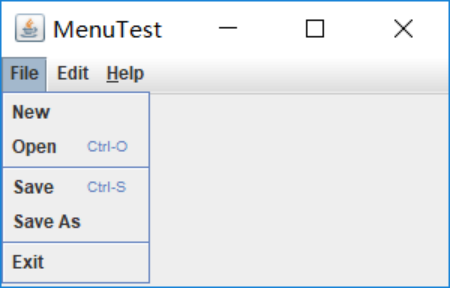
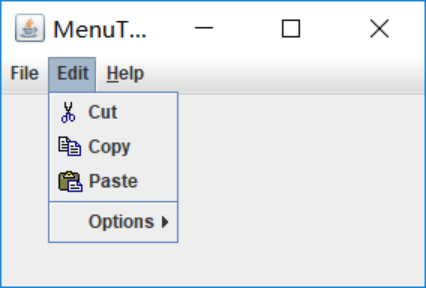

测试程序9
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材517页程序12-9,结合运行结果理解程序;
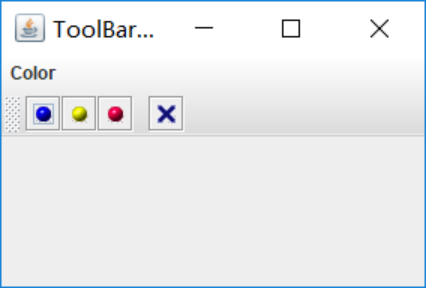
l 掌握工具栏和工具提示的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
初始:
将鼠标放置在四个按钮上都会有对应的提示(如图):
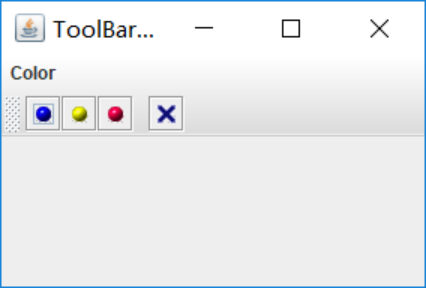
测试程序10
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材524页程序12-10、12-11,结合运行结果理解程序,了解GridbagLayout的用法。
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材533页程序12-12,结合程序运行结果理解程序,了解GroupLayout的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
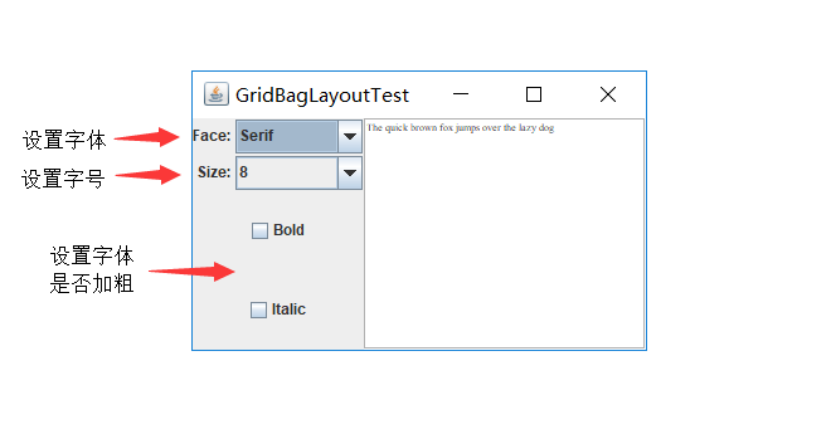
测试程序11
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材539页程序12-13、12-14,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握定制布局管理器的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
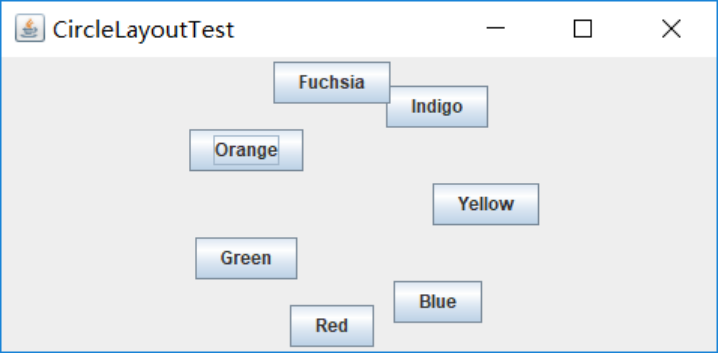
测试程序12
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材544页程序12-15、12-16,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握选项对话框的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
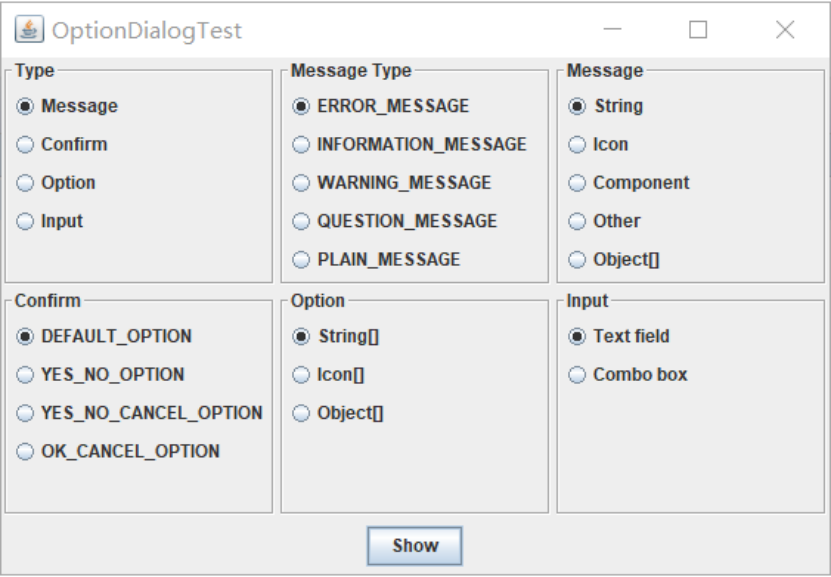
测试程序13
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材552页程序12-17、12-18,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握对话框的创建方法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

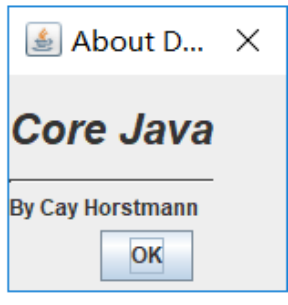
测试程序14
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材556页程序12-19、12-20,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握对话框的数据交换用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
代码:
package dataExchange; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a menu whose File->Connect action shows a password dialog. */ public class DataExchangeFrame extends JFrame { public static final int TEXT_ROWS = 20; public static final int TEXT_COLUMNS = 40; private PasswordChooser dialog = null; private JTextArea textArea; public DataExchangeFrame() { // construct a File menu JMenuBar mbar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(mbar); JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("File"); mbar.add(fileMenu); // add Connect and Exit menu items JMenuItem connectItem = new JMenuItem("Connect"); connectItem.addActionListener(new ConnectAction()); fileMenu.add(connectItem); // The Exit item exits the program JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); exitItem.addActionListener(event -> System.exit(0)); fileMenu.add(exitItem); textArea = new JTextArea(TEXT_ROWS, TEXT_COLUMNS); add(new JScrollPane(textArea), BorderLayout.CENTER); pack(); } /** * The Connect action pops up the password dialog. */ private class ConnectAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { // if first time, construct dialog if (dialog == null) dialog = new PasswordChooser(); // set default values dialog.setUser(new User("yourname", null)); // pop up dialog if (dialog.showDialog(DataExchangeFrame.this, "Connect")) { // if accepted, retrieve user input User u = dialog.getUser(); textArea.append("user name = " + u.getName() + ", password = " + (new String(u.getPassword())) + " "); } } } }
package dataExchange; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class DataExchangeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new DataExchangeFrame(); frame.setTitle("DataExchangeTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
package dataExchange; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Component; import java.awt.Frame; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JDialog; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JPasswordField; import javax.swing.JTextField; import javax.swing.SwingUtilities; /** * A password chooser that is shown inside a dialog */ public class PasswordChooser extends JPanel { private JTextField username; private JPasswordField password; private JButton okButton; private boolean ok; private JDialog dialog; public PasswordChooser() { setLayout(new BorderLayout()); // construct a panel with user name and password fields JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2)); panel.add(new JLabel("User name:")); panel.add(username = new JTextField("")); panel.add(new JLabel("Password:")); panel.add(password = new JPasswordField("")); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER); // create Ok and Cancel buttons that terminate the dialog okButton = new JButton("Ok"); okButton.addActionListener(event -> { ok = true; dialog.setVisible(false); }); JButton cancelButton = new JButton("Cancel"); cancelButton.addActionListener(event -> dialog.setVisible(false)); // add buttons to southern border JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel.add(okButton); buttonPanel.add(cancelButton); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); } /** * Sets the dialog defaults. * @param u the default user information */ public void setUser(User u) { username.setText(u.getName()); } /** * Gets the dialog entries. * @return a User object whose state represents the dialog entries */ public User getUser() { return new User(username.getText(), password.getPassword()); } /** * Show the chooser panel in a dialog * @param parent a component in the owner frame or null * @param title the dialog window title */ public boolean showDialog(Component parent, String title) { ok = false; // locate the owner frame Frame owner = null; if (parent instanceof Frame) owner = (Frame) parent; else owner = (Frame) SwingUtilities.getAncestorOfClass(Frame.class, parent); // if first time, or if owner has changed, make new dialog if (dialog == null || dialog.getOwner() != owner) { dialog = new JDialog(owner, true); dialog.add(this); dialog.getRootPane().setDefaultButton(okButton); dialog.pack(); } // set title and show dialog dialog.setTitle(title); dialog.setVisible(true); return ok; } }
package dataExchange; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Component; import java.awt.Frame; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JDialog; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JPasswordField; import javax.swing.JTextField; import javax.swing.SwingUtilities; /** * A password chooser that is shown inside a dialog */ public class PasswordChooser extends JPanel { private JTextField username; private JPasswordField password; private JButton okButton; private boolean ok; private JDialog dialog; public PasswordChooser() { setLayout(new BorderLayout()); // construct a panel with user name and password fields JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2)); panel.add(new JLabel("User name:")); panel.add(username = new JTextField("")); panel.add(new JLabel("Password:")); panel.add(password = new JPasswordField("")); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER); // create Ok and Cancel buttons that terminate the dialog okButton = new JButton("Ok"); okButton.addActionListener(event -> { ok = true; dialog.setVisible(false); }); JButton cancelButton = new JButton("Cancel"); cancelButton.addActionListener(event -> dialog.setVisible(false)); // add buttons to southern border JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel.add(okButton); buttonPanel.add(cancelButton); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); } /** * Sets the dialog defaults. * @param u the default user information */ public void setUser(User u) { username.setText(u.getName()); } /** * Gets the dialog entries. * @return a User object whose state represents the dialog entries */ public User getUser() { return new User(username.getText(), password.getPassword()); } /** * Show the chooser panel in a dialog * @param parent a component in the owner frame or null * @param title the dialog window title */ public boolean showDialog(Component parent, String title) { ok = false; // locate the owner frame Frame owner = null; if (parent instanceof Frame) owner = (Frame) parent; else owner = (Frame) SwingUtilities.getAncestorOfClass(Frame.class, parent); // if first time, or if owner has changed, make new dialog if (dialog == null || dialog.getOwner() != owner) { dialog = new JDialog(owner, true); dialog.add(this); dialog.getRootPane().setDefaultButton(okButton); dialog.pack(); } // set title and show dialog dialog.setTitle(title); dialog.setVisible(true); return ok; } }
运行结果:
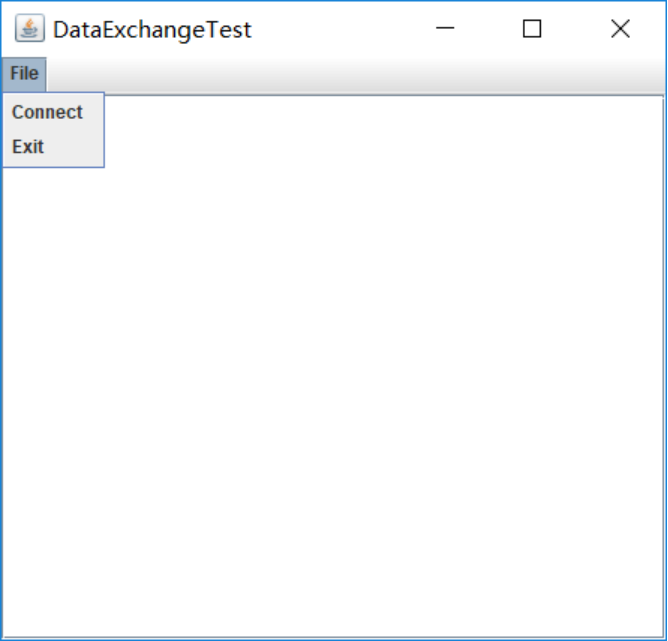

测试程序15
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材564页程序12-21、12-22、12-23,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握文件对话框的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
代码:
运行结果:
点击File中的Open后:
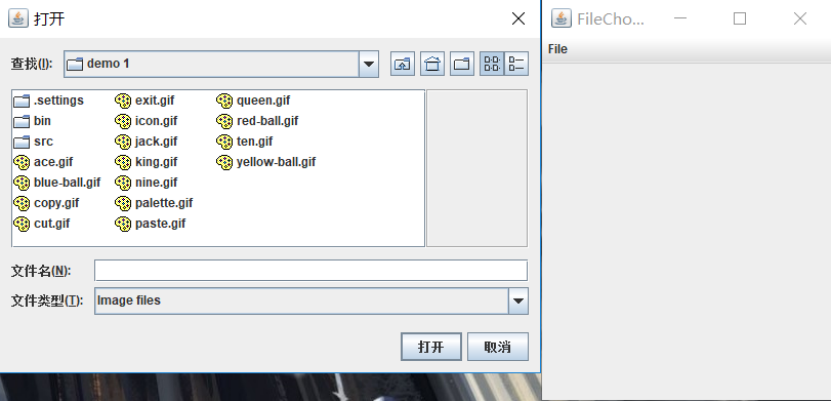
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材570页程序12-24,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 了解颜色选择器的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
运行结果:
三个按钮分别代表三种模式(详解在书上p570),这里选的Modal模式:

共有五种标题(样本,HSV,HSL,RGB,CMYK)对话框

实验2:组内讨论反思本组负责程序,理解程序总体结构,梳理程序GUI设计中应用的相关组件,整理相关组件的API,对程序中组件应用的相关代码添加注释。
负责程序:12-19。
该程序主要是进行了数据的交换,使用对话框最通常的目的是获取用户的输人信息。在前面已经看到,构造对话框对象非常简单;首先初始化数据,然后调用 set Visible(true)就会在屏幕上显示对话框。
 (图1)
(图1)
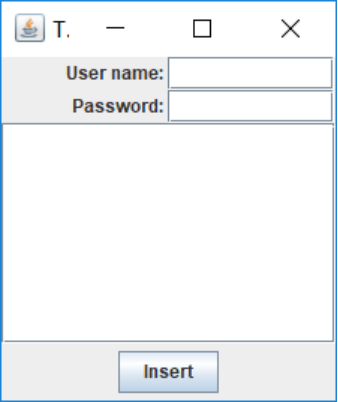
图2所示的对话框,可以用来获得用户名和用户密码以便连接某些在线服务。
 (图2)
(图2)
对话框应该提供设置默认数据的方法。例如,示例程序中的 Passwordchooser类提供了一个 setuser方法,用来将默认值放到下面的字段中:
public vold setuser(User u)
{
username, settext(u, getname ());
}
一但设置了默认值(如果需要)就可以调用 setvisible(true)让对话框显示在屏幕上。然后用户输入信息,点击OK或者 Cancel按钮。这两个按钮的事件处理器都会调用set Visible( false)终止对 set Visible(true)的调用。另外,用户也可以选择关闭对话框。如果没有为对话框安装窗口监听器,就会执行默认的窗口结東操作,即对话框变为不可见,这也中止了对 setvisible(true)的调用。
重要的问题是在用户解除这个对话框之前,一直调用 setvisible(true)阻塞。这样易于实现模式对话框。希望知道用户是接收对话框,还是取消对话框。在示例代码中设置了OK标志,在对话框显示之前是 false。只有OK按钮的事件处理器可以将它设置为tnue。这样,就可以获得对话框中的用户输入。
实验3:组间协同学习:在本班课程QQ群内,各位同学对实验1中存在的问题进行提问,提问时注明实验1中的测试程序编号,负责对应程序的小组需及时对群内提问进行回答。
实验总结:
本章我们主要学习了一些用户界面组件的一些用法,通过本章的学习我们对于用户界面的构造有了更细致的了解,学习了一些简单的用户界面的一些组件的使用,在本次的实验中我们小组遇到了很多问题,通过小组内的讨论和学习成功的将问题解决了。希望在今后的学习中我们能有更多的进步。