#面向对象编程带来的好处之一是代码的重用,实现代码重用的方法之一是通过继承机制。继承完全可以理解成类之间类型和子类型的关系。
#在面向对象程序设计中,当我们定义一个class时,可以从某个现有的class继承,定义的新class称为子类(Subclass),而被继承的class称为基类、父类或者超类(Base class、Super class)。
#继承定义如下:
1 class DerivedClassName(BaseClassName): 2 <statement-1> 3 . 4 . 5 . 6 <statement-N>
#需要注意的是:继承语法class子类名(基类名)时,//基类名写在括号里,基本类时在定义类时,在元组中指明的。
#在Python中,继承有以下特点:
(1)、在继承中,基类的构造方法(__init__()方法)不会被调用,需要在子类的构造方法中专门调用。
(2)、在调用基类的方法时需要加上基类的类名前缀,并带上self参数变量。区别于在类中调用普通函数时不需要带self参数。
(3)、在Python中,首先查找对应类型的方法,如果在子类中找不到对应的方法,才到基类中逐个查找。
#例如:
1 #! /usr/bin/python3 2 #-*-coding:UTF-8-*- 3 #继承 4 5 class Animal(object): 6 def run(self): 7 print('Animal is running.')
#上面定义了一个名为Animal的类,类中定义了一个run()方法直接输出(没有显式定义__init__()方法,会调用默认的构造方法)。在编写Dog和Cat类时,可以直接从Animal类继承,定义如下:
1 class Animal(object): 2 def run(self): 3 print('Animal is running.') 4 5 class Dog(Animal): 6 pass 7 8 class Cat(Animal): 9 pass
#在这段代码中,对于Dog来说,Animal就是他的父类;对于Animal来说,Dog就是他的子类。Cat和Dog类似。
#继承最大的好处时子类获得了父类全部非私有的功能。由于在Animal中定义了非私有的run()方法,因此作为Animal的子类,Dog和Cat什么方法都没有定义,自动拥有父类中的run()方法,执行以下代码:
1 #! /usr/bin/python3 2 #-*-coding:UTF-8-*- 3 #继承 4 5 class Animal(object): 6 def run(self): 7 print('Animal is running.') 8 9 class Dog(Animal): 10 pass 11 12 class Cat(Animal): 13 pass 14 15 dog=Dog() 16 dog.run() 17 18 cat=Cat() 19 cat.run()
#程序执行结果如下:
1 D:Pythonworkspace>python 继承.py 2 Animal is running. 3 Animal is running.
#由执行结果看到,子类中没有定义任何方法,但都成功执行了run()方法。
#当然,子类可以拥有一些自己的方法,比如在Dog类中增加一个eat方法:
1 class Dog(Animal): 2 def eat(self): 3 print('Eating.') 4 5 pass
#程序执行结果如下:
1 D:Pythonworkspace>python 继承.py 2 Animal is running. 3 Eating.
#由执行结果看到,既执行了父类的方法,又执行了dog自己定义的方法。
#子类不能继承父类中的私有方法,也不能调用父类的私有方法,父类定义如下:
1 #! /usr/bin/python3 2 #-*-coding:UTF-8-*- 3 #继承 4 5 class Animal(object): 6 def run(self): 7 print('Animal is running.') 8 9 def __run(self): 10 print('this is a private method.')
#子类定义不变,执行如下调用语句:
1 dog=Dog() 2 dog.run() 3 dog.__run()
#程序执行结果如下:
1 D:Pythonworkspace>python 继承.py 2 Animal is running. 3 Traceback (most recent call last): 4 File "继承.py", line 18, in <module> 5 dog.__run() 6 AttributeError: 'Dog' object has no attribute '__run'
#由执行结果看到,子类不能调用父类的私有方法,子类虽然继承了父类,但是调用父类的私有方法相当于从外部调用类中的方法,因而不能调用成功。
#对于父类中扩展的非私有方法,子类可以拿来即用,如在父类Animal中增加一个jump方法:
1 #! /usr/bin/python3 2 #-*-coding:UTF-8-*- 3 #继承 4 5 class Animal(object): 6 def run(self): 7 print('Animal is running.') 8 9 def jump(sel): 10 print('Animal is jumpping.') 11 12 def __run(self): 13 print('I am a private method.')
#上面我们增加了一个非私有的jump()方法,子类Dog和Cat保持原样,执行如下调用:
1 dog=Dog() 2 dog.run() 3 dog.jump() 4 #dog.__run() 5 6 cat=Cat() 7 cat.run() 8 cat.jump() 9 cat.__run()
#程序执行结果如下:
1 D:Pythonworkspace>python 继承.py 2 Animal is running. 3 Animal is jumpping. 4 Animal is running. 5 Animal is jumpping. 6 Traceback (most recent call last): 7 File "继承.py", line 29, in <module> 8 cat.__run() 9 AttributeError: 'Cat' object has no attribute '__run'
#由执行结果看到,子类可以立即获取父类增加的非私有方法。
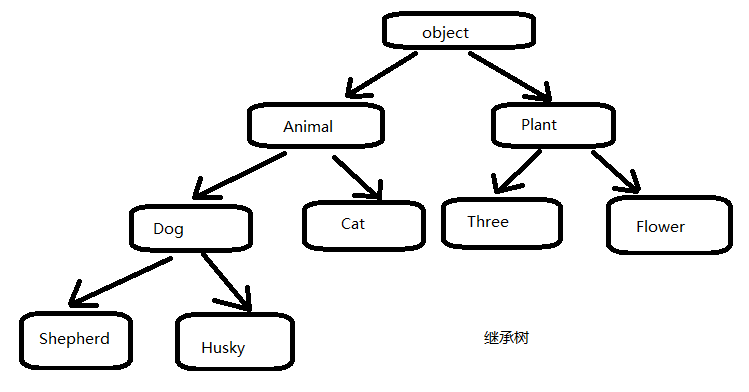
#继承可以一级一级继承下来,就好比爷爷到爸爸再到儿子的关系。所有类最终都可以追溯到根类object,这些继承关系看上去就像一颗倒着的树,如下图所示:

#例如如下:
1 #! /usr/bin/python3 2 #-*-coding:UTF-8-*- 3 #class的继承 4 5 class Animal(object): 6 def run(self): 7 print('Animal is running.') 8 9 def eat(self): 10 print('this is good food.') 11 12 class BigDog(Animal): 13 pass 14 15 class BigCat(Animal): 16 pass 17 18 class SmallDog(BigDog): 19 pass 20 21 class SmallCat(BigCat): 22 pass 23 24 25 dog=BigDog() 26 dog.run() 27 28 cat=BigCat() 29 cat.run() 30 31 32 bigdog=BigDog() 33 bigdog.eat() 34 35 bigcat=BigCat() 36 bigcat.eat()
#程序执行结果如下:
1 D:Pythonworkspacedatatime20171129>python class的继承.py 2 Animal is running. 3 Animal is running. 4 this is good food. 5 this is good food.
#由输出结果看到,SmallDog和SmallCat虽然和Animal没有直接的联系,但是也通过BigDog和BigCat继承了Animal的eat()方法