| 软件工程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/informationsecurity1812 |
|---|---|
| 作业要求 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/informationsecurity1812/homework/11155 |
| 作业目标 | 论文查重算法设计+单元测试+JProfiler+PSP表格+Git管理 |
代码链接(Java)
-
GitHub链接,若有帮助,可以点个Star~
-
可运行的Jar包已发布至仓库的release包内
计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
整体流程
- MainApplication.main()会接收到三个参数,接着执行process方法
- 将两个等待对比的文本内容分别转换为字符串
- SimilarTextCalculator.getSimilarity(),对比这两个字符串
- 将结果输出到指定路径文件
工程分包的截图
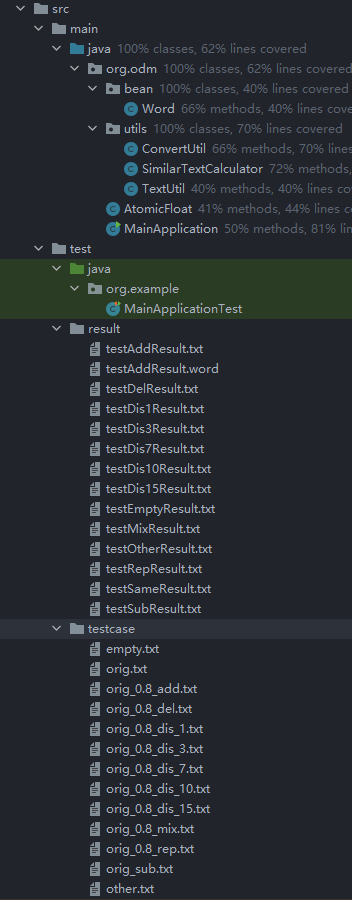
项目内的主要的类
- MainApplication : 主程序,入口
- AtomicFloat :可原子操作的Float类
- SimilarTextCalculator : 相似文本计算工具类
- ConvertUtil :转换工具类,实现字符串与文本文件的互转
- TextUtil:文本处理工具类,执行文本分词等操作
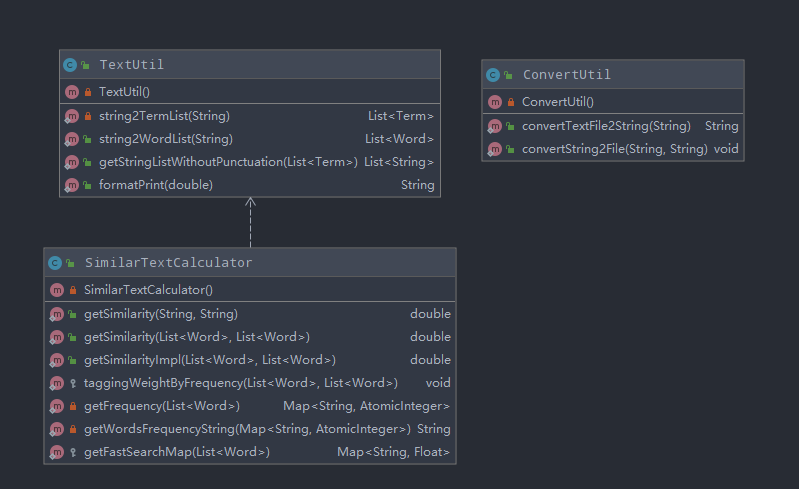
类、函数之间的关系通过IDEA自带生成的UML图直观地呈现
org.odm 包内的UML图
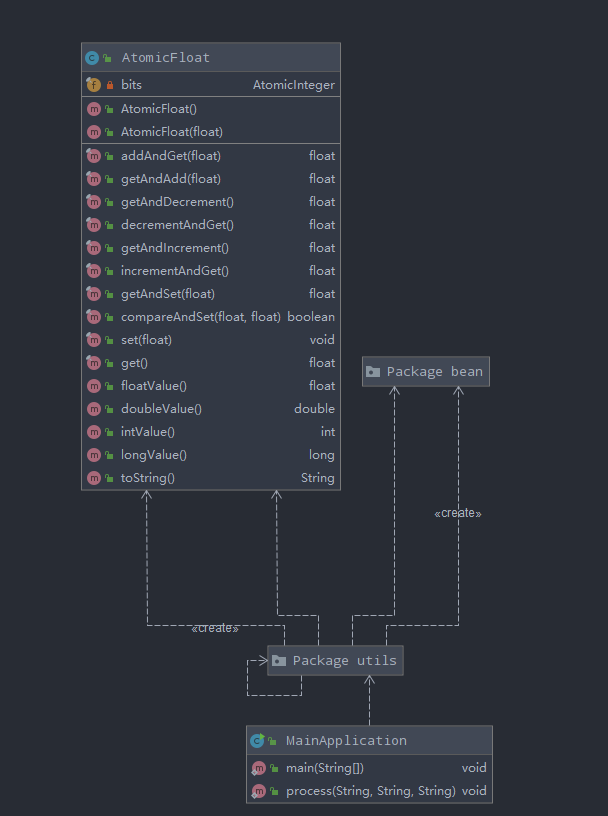
utils包内的UML图
实际命令行运行效果

算法的关键
基于一个概念——余弦距离,也称为余弦相似度,是用向量空间中两个向量夹角的余弦值作为衡量两个个体间差异的大小的度量。余弦值越接近1,就表明夹角越接近0度,也就是两个向量越相似,这就叫"余弦相似性"。
独到之处
复杂文本情况下,速度可以维持在2s内,简单情况下如文本高度相同,速度可以达到20ms,同时识别准确率也很不错。计算速度和准确度达到了相对均衡。
文本相似度算法—余弦相似度算法
计算公式
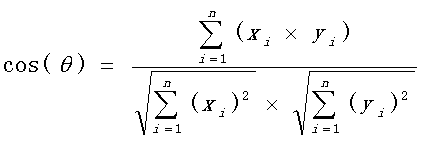
- 余弦值越接近 1 ,也就是两个向量越相似,这就叫"余弦相似性"
- 余弦值越接近 0 ,也就是两个向量越不相似,也可以说这两个字符串越不相似
实际例子
用余弦相似度算法计算文本的相似性。
为了简单起见,先从句子着手。
句子A:这顶帽子尺寸大了。那顶尺寸合适。
句子B:这顶帽子尺寸不小,那顶更合适。
基本计算的思路是:如果这两句话的用词越相似,它们的内容就应该越相似。
因此,可以从词频入手,计算它们的相似程度。
第一步,分词
句子A:这顶/帽子/尺寸/大了。那顶/尺寸/合适。
句子B:这顶/帽子/尺寸/不/小,那顶/更/合适。
第二步,计算词频
句子A:这顶(1),帽子(1),尺寸(2),大了(1),那顶(1),合适(1),不(0),小(0),更(0)
句子B:这顶(1),帽子(1),尺寸(1),大了(0),那顶(1),合适(1),不(1),小(1),更(1)
第三步,写出词频向量
句子A:(1,1,2,1,1,1,0,0,0)
句子B:(1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1)
第四步:运用上面的公式:计算如下:
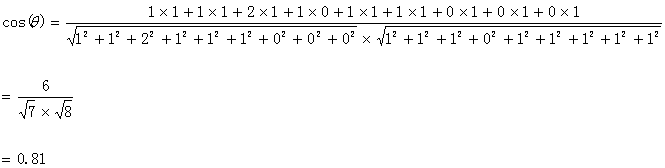
计算结果中夹角的余弦值为0.81,非常接近于1。
所以,上面的句子A和句子B是基本相似的
算法总结
- 分词:分词当然要按一定规则,不然随便分那也没有意义,那这里通过采用HanLP中文自然语言处理中标准分词进行分词。
- 统计词频:就统计上面词出现的次数。
- 通过每一个词出现的次数,变成一个向量,通过向量公式计算相似率。
计算模块的单元测试展示(白盒)
展示单元测试代码(12种情况)
public class MainApplicationTest {
@BeforeClass
public static void beforeTest(){
System.out.println("测试即将开始");
}
@AfterClass
public static void afterTest(){
System.out.println("测试结束");
}
/**
* 测试 文本为空文本的情况
*/
@Test
public void testForEmpty(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/empty.txt","src/test/result/testEmptyResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试 输入的对比文本路径参数为错误参数的情况
*/
@Test
public void testForWrongOriginArgument(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/123.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_add.txt","src/test/result/testAddResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试 输出文件路径参数为错误参数的情况
*/
@Test
public void testForWrongOutputArgument(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/result/testAWrongArgumentResult");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试20%文本添加情况:orig_0.8_add.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForAdd(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_add.txt","src/test/result/testAddResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试20%文本删除情况:orig_0.8_del.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForDel(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_del.txt","src/test/result/testDelResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试20%文本乱序情况:orig_0.8_dis_1.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForDis1(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_dis_1.txt","src/test/result/testDis1Result.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试20%文本乱序情况:orig_0.8_dis_3.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForDis3(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_dis_3.txt","src/test/result/testDis3Result.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试20%文本乱序情况:orig_0.8_dis_7.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForDis7(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_dis_7.txt","src/test/result/testDis7Result.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试20%文本乱序情况:orig_0.8_dis_10.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForDis10(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_dis_10.txt","src/test/result/testDis10Result.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试20%文本乱序情况:orig_0.8_dis_15.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForDis15(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_dis_15.txt","src/test/result/testDis15Result.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试20%文本格式错乱情况:orig_0.8_mix.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForMix(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_mix.txt","src/test/result/testMixResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试20%文本错别字情况:orig_0.8_rep.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForRep(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_rep.txt","src/test/result/testRepResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试相同文本:orig.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForSame(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/result/testSameResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试文本的子集文本:orig_sub.txt
*/
@Test
public void testForSub(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_sub.txt","src/test/result/testSubResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
说明测试的方法,构造测试数据的思路
- 单元测试,利用各种不同情况的文本,与原文本进行相似度的计算,在控制台输出计算的结果,以及输入错误的文件路径参数。
- 测试的文本涵盖了不同情况:在原文本上进行添加、删除、错别字、打乱顺序、格式错乱,节选文本原片段等
测试结果
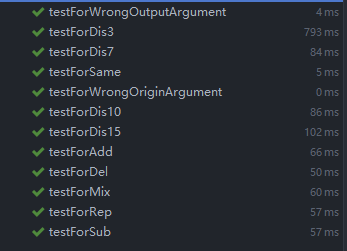
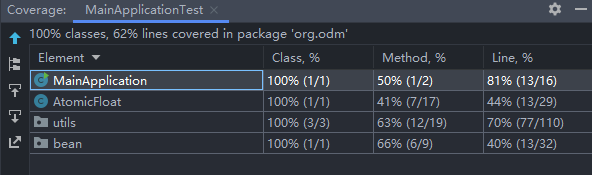
测试覆盖率截图
计算模块部分异常处理说明
IOException以及FileNotFoundException,异常的场景是文件的写入和读取以及文件不存在仍要操作,可能会导致这些异常,所以要提前规避。
如下:
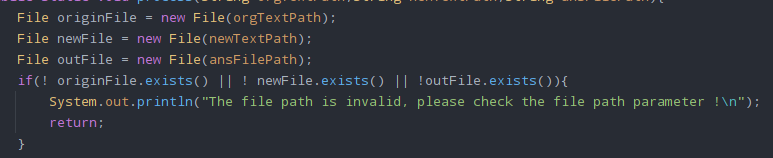
对应的测试
/**
* 测试 文本为空文本的情况
*/
@Test
public void testForEmpty(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/empty.txt","src/test/result/testEmptyResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试 输入的对比文本路径参数为错误参数的情况
*/
@Test
public void testForWrongOriginArgument(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/123.txt","src/test/testcase/orig_0.8_add.txt","src/test/result/testAddResult.txt");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
/**
* 测试 输出文件路径参数为错误参数的情况
*/
@Test
public void testForWrongOutputArgument(){
try {
MainApplication.process("src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/testcase/orig.txt","src/test/result/testAWrongArgumentResult");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 如果抛出异常,证明测试失败,没有通过,没通过的测试计数在Failures中
Assert.fail();
}
}
测试结果
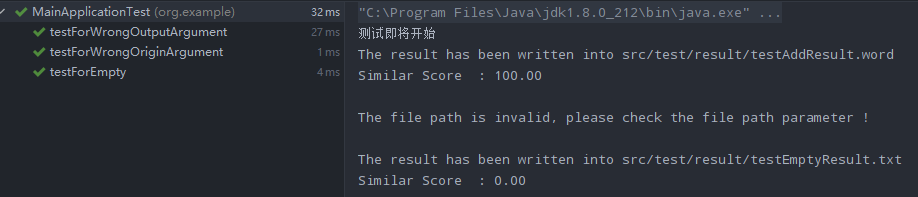
计算模块接口部分的性能改进
执行单元测试,对各种情况进行测试的同时使用 JProfiler对性能进行监控
-
类的内存消耗
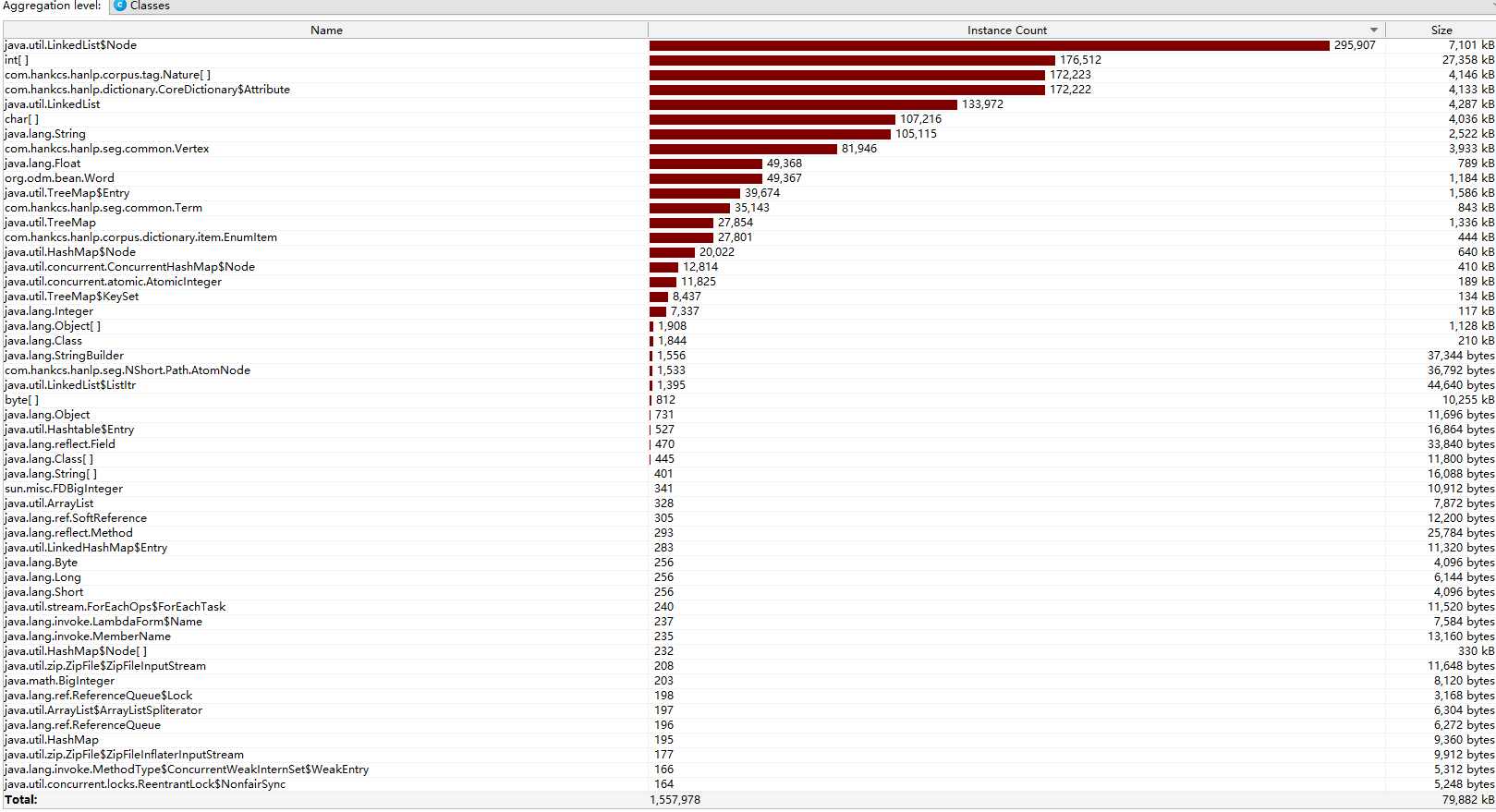
-
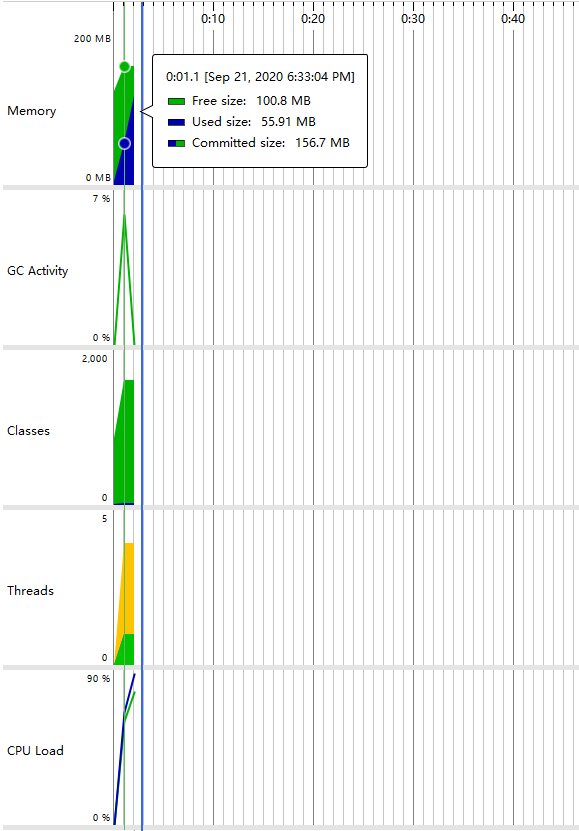
CPU Load(运行时间:1.1 s,满足要求)
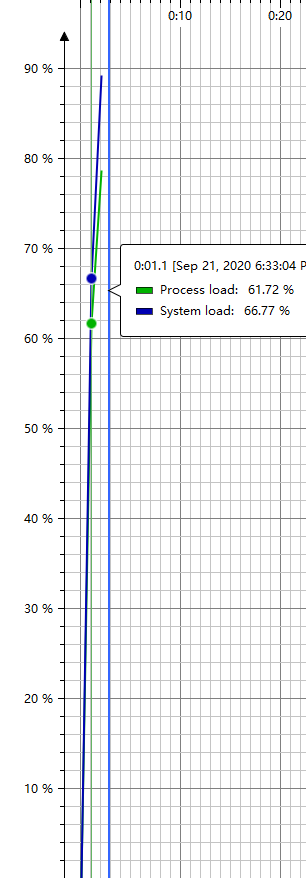
- 堆内存情况
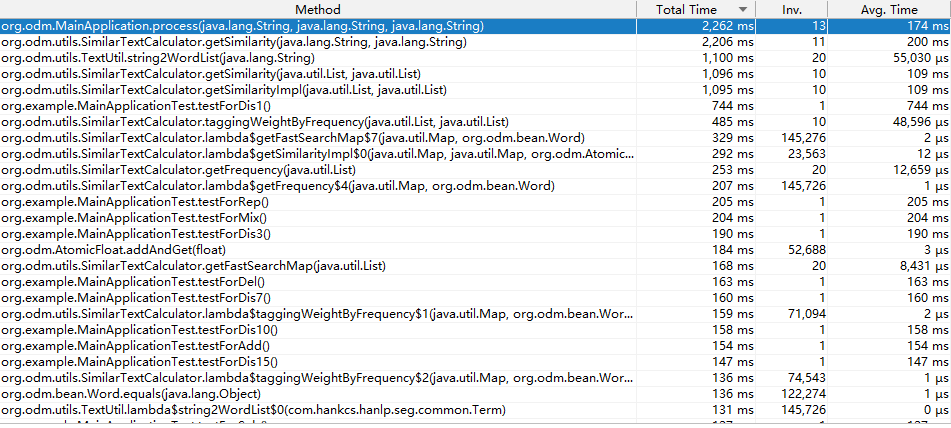
- 耗时操作情况
由图可以看出,改进前的程序中时间平均耗时最大的方法——Hanlp的分词操作
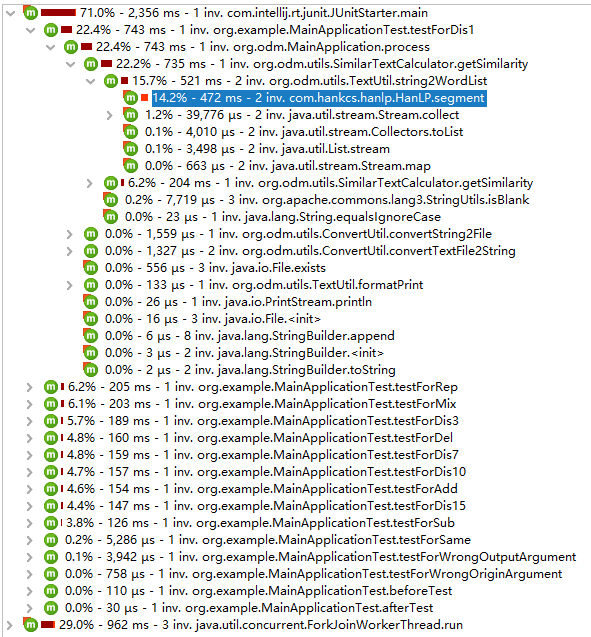
改进耗时的地方
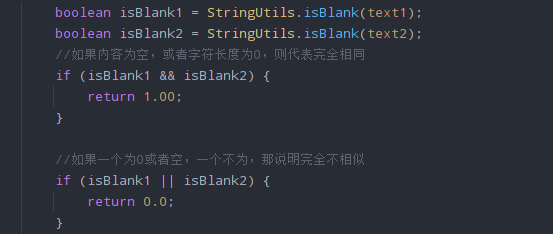
摸索了大概20分钟,最后发现由于最耗时的地方是在于分词操作的函数,而如果一味提高速度就会损失精度,所以无法从Hanlp的分词函数动刀。故只好从其他耗时地方(对象创建等)入手,例子如下:
代码质量检查Code Quantity Analysis
使用了Github 上对公开项目托管的静态代码检查工具——Codacy
修复了一些issue后,现在已经是一个干净的项目了,截图如下:
PSP表格
| PSP 各个阶段 | 自己预估的时间(分钟) | 实际的记录(分钟) |
|---|---|---|
| 计划: 明确需求和其他因素,估计以下的各个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 45 |
| 开发 (包括下面 8 项子任务) | (以下都填预估值) | 218 |
| · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术、新工具的时间) | 20 | 30 |
| · 生成设计文档 (整体框架的设计,各模块的接口,用时序图,快速原型等方法) | 15 | 5 |
| · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档,或者自己复审) | 15 | 20 |
| · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定或选择合适的规范) | 5 | 3 |
| · 具体设计(用伪代码,流程图等方法来设计具体模块) | 20 | 30 |
| · 具体编码 | 60 | 75 |
| · 代码复审 | 15 | 20 |
| · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 35 |
| 报告 | 75 | 95 |
| 测试报告(发现了多少bug,修复了多少) | 15 | 20 |
| 计算工作量 (多少行代码,多少次签入,多少测试用例,其他工作量) | 10 | 15 |
| 事后总结, 并提出改进计划 (包括写文档、博客的时间) | 50 | 60 |
| 总共花费的时间 (分钟) | 290 | 358 |
看来还是对自己太自信了~未来尽量实际追上计划吧
总结
- Java的项目不常写,于是按照了平时写android的分包和设计类的关系
- 性能方面的话,用了比较主流的Hanlp的分词和余弦计算,所以速度和精度达到了均衡;学会了用JProfiler监控性能
- 单元测试的话,感觉挺方便的,但是这次的结果都是不可预计的,所以得用白盒测试。使用了断言Assert.fail()。
- 异常处理部分,处理了主要的 IOException 和 FileNotFoundException
- PSP,还是高估了自己的能力,从一开始的一头雾水到最后解决了,还是看出自己的很多不足。