Vector
1.可变长的动态数组
2.需包含头文件#include<vector> (当然,如果用了万能头文件#include<bits/stdc++.h>则可忽略)
3.支持随机访问迭代器:
- 根据下标随机访问某个元素,时间复杂度O(1)
- 在尾部添加速度很快
- 在中间插入慢
4.所有STL算法都能对vector操作。
下面是关于vector使用的代码:
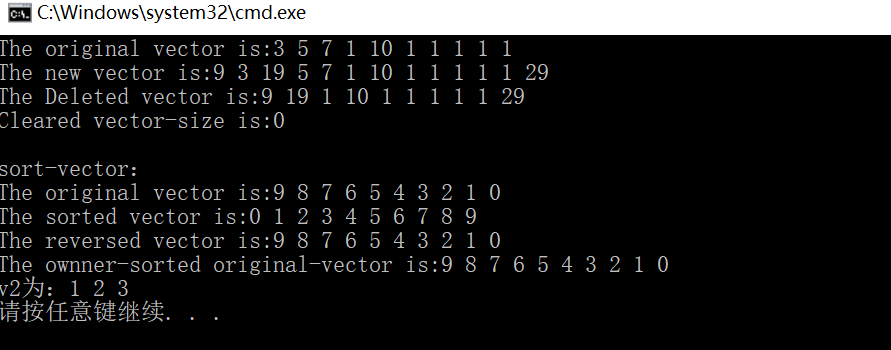
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 void fun(int &n) //配套for_each输出vector容器 6 { 7 cout<<n<<" "; 8 } 9 //自己设计比较函数,对元素进行降序排列。 10 bool cmp(const int &a,const int &b) 11 { 12 if(a!=b) return a>b; 13 } 14 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 15 { 16 vector<int> v(10); //定义一个vector容器 17 vector<int>::iterator i; //vector<int>::iterator i--迭代器定义 18 //对vector赋值 19 for(int j=0;j<v.size();++j) 20 v[j]=1; 21 v[0]=3;v[1]=5;v[2]=7; 22 v.at(4)=10; 23 //输出vector的值 24 cout<<"The original vector is:"; 25 for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),fun); 26 //相当于for(vector<int>::iterator i=v.begin();i!=v.end();++i) 27 //fun函数用来输出 28 //STL中的功能,便于输(tou)出(lan) :) 29 cout<<" "; 30 31 //向vector中插入元素 32 v.insert(v.begin(),9); //在v[0]插入9 33 v.insert(v.begin()+2,19); //在v[2]插入19 34 v.insert(v.end(),29); //在最后一个位置v[10+2+1]插入29 35 //输出 36 cout<<"The new vector is:"; 37 for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),fun); 38 cout<<endl; 39 40 //删除 41 v.erase(v.begin()+1); 42 v.erase(v.begin()+2,v.begin()+4); 43 cout<<"The Deleted vector is:"; 44 for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),fun); 45 46 //清空 v 47 v.clear(); 48 cout<<endl<<"Cleared vector-size is:"<<v.size()<<endl; 49 cout<<endl; 50 51 //开始排序 52 cout<<"sort-vector:"<<endl; 53 for (int j = 0; j < 10; ++j) 54 { 55 v.push_back(9-j); 56 } 57 cout<<"The original vector is:"; 58 for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),fun); 59 cout<<endl; 60 sort(v.begin(),v.end()); //排序,默认升序. 61 cout<<"The sorted vector is:"; 62 for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),fun); 63 cout<<endl; 64 //将vector逆转 65 reverse(v.begin(),v.end()); 66 cout<<"The reversed vector is:"; 67 for (i = v.begin(); i != v.end(); ++i) 68 { 69 cout<<*i<<" "; 70 } 71 cout<<endl; 72 //用自定义的排序规则,按从大到小排序 73 sort(v.begin(),v.end(),cmp); 74 cout<<"The ownner-sorted original-vector is:"; 75 for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),fun); 76 cout<<endl; 77 78 int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5}; //定义一个数组,并用vector复制 79 vector<int> v2(a,a+3); //构造函数并复制 a中的前3个数字 80 cout<<"v2为:"; 81 for_each(v2.begin(),v2.end(),fun); 82 return 0; 83 }
编译结果如下: