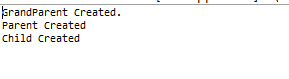
1、运行 TestInherits.java 示例,观察输出,注意总结父类与子类之间构造方法的调用关系修改Parent构造方法的代码,显式调用GrandParent的另一个构造函数,注意这句调用代码是否是第一句,影响重大!
结论:
通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
TestInherits.java
class Grandparent {
public Grandparent() {
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string) {
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent {
public Parent() {
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
public Child() {
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Child c = new Child();
}
}
实验截图:
2、请自行编写代码测试以下特性(动手动脑):
在子类中,若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字。
程序源代码:
class father
{
void output()
{
System.out.println("father created.");
}
}
class son extends father
{
void output()
{
super.output();
System.out.println("son created.");
}
}
public class OverrideTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
son s=new son();
s.output();
}
}
程序结果截图:

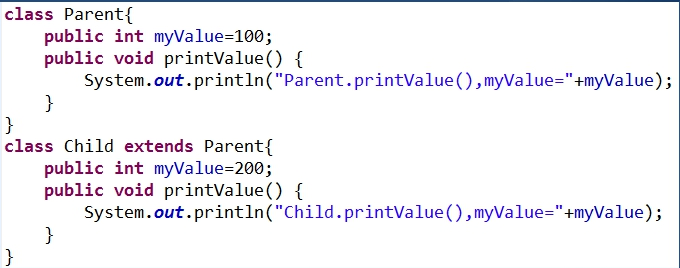
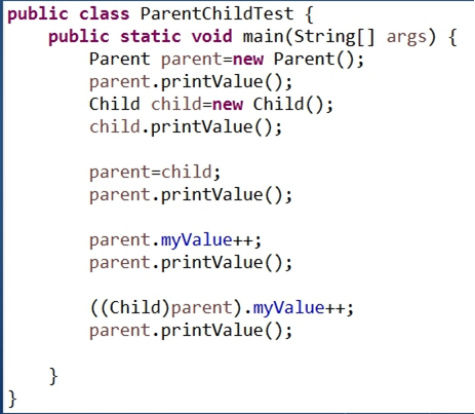
3、运行以下测试代码
1. 左边的程序运行结果是什么?
2. 你如何解释会得到这样的输出?
3. 计算机是不会出错的,之所以得
到这样的运行结果也是有原因的,
那么从这些运行结果中,你能总
结出Java的哪些语法特性?
(1)运行结果
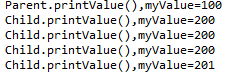
(2)解释:
第一个调用Parent类的printValue()输出Parent类myValue的值
第二个调用Child类的printValue()输出Child类myValue的值
第三个将child赋值给parent,即输出child中的myValue的值
第四个因为parent已经被child赋值,parent.printValue()与第三次输出一样,而parent.myValue++中调用的是父类Parent类中的myValue值
第五个将parent转化为child类自增
(3)改或编写一些代码进行测试,验证自己的想法
代码:
parent.myValue++;
System.out.println(parent.myValue++);
parent.printValue();
结果:
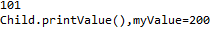
(4)总结:
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
这个特性实际上就是面向对象“多态”特性的具体表现。
如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。
如果子类被当作父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的!
牢记:在实际开发中,要避免在子类中定义与父类同名 的字段。不要自找麻烦!——但考试除外,考试 中出这种题还是可以的。