线程与进程
- java默认2个线程,main,gc
- 真实的线程时底层C++调用的,并不是java
- cup核心数,就是并行的线程数
- 单核CUP,要多线程并行,就是用并发实现宏观并行
- 线程状态
- New
- running
- blocked
- waiting
- time_waiting
- terminal
- wait与sleep
- 来自不同的类
- 都会释放cup,但wait释放锁,即释放资源,sleep不释放
- wait只在同步代码块,sleep任意
- 线程是一个资源类,没有任何附属操作,OOP编程
- 资源类包含属性,方法
- 资源类方法同步
- 启动线程操作资源类
锁
-
Syncronized与Lock
- Lock可判断锁状态,终止等待
- Lock必须手动释放,否则死锁
- Lock可控制是否是公平锁,默认非公平锁
- 线程获取锁本来是先来后到,但若是非公平锁,则允许线程插队
- Lock适合锁大量代码块
-
可重入锁
-
不区分读写操作时使用
-
公平,非公平,可插队(默认)
-
线程进入资源类方法1时加获取锁,方法2调用方法2,又要获取锁,也可获取,因为是重入锁
public synchronized void get(){} public synchronized void get2(){} // 两个线程调用同一个对象的get1,get2,一个线程会被阻塞,应为锁的是this,即锁是同一个对象,只能给一个线程, public synchronized void get(){get2)} public synchronized void get2(){} // 线程调用get(),由于是一个线程调用get,get2,可重入此时起作用,否则就是自己锁死自己 // 也可理解威武 -
sync ,reentLock都是可重入
-
-
可重入读写锁
- 使用时调用读锁,或写锁使用
- 写锁(独占锁),即写的时候其它不能写,其它不能读
- 读锁(共享锁),读的时候其它不能写,其它可以读
- 无锁,无限制
- 读操作与写操作分离时使用
-
可重入读锁
-
可重入写锁
集合安全
List<Integer> 1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> l = new Vector<>(); // 同步sync
List<Integer> l = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()); // 同步sync
List<Integer> l = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); // Lock锁 JUC里面的
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>(); // 就是hashmap的键
Set<Integer> s= Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<>());// 同步sync
Set<Integer> s= new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();// Lock 锁 JUC里面的
// -----------------------------
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String,String>(16,0.75f);
Map<String,String> map2 = new Hashtable<>();// 同步sync
Map<String,String> map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<>());// 同步sync
Map<String,String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();//分段Lock锁,锁定某一段 JUC里面的
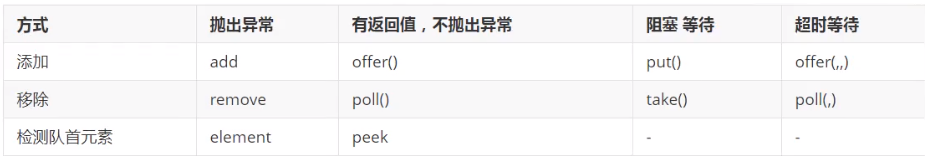
阻塞队列
//BlockingQueue 实现类都是用了Lock的,即线程安全的
BlockingQueue<Integer> q = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(10);
BlockingQueue<Integer> q = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Integer>();
// 同步队列,只能存放一个元素
BlockingQueue<Integer> q = new SynchronousQueue<Integer>();
BlockingQueue<Integer> q = (BlockingQueue<Integer>) new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Integer>();
线程池
- 节约资源
- 控制最大并发数
// 本质就是ThreadPoolExecutor(7各参数)
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 推荐手动创建
ExecutorService s = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2, // 一直开着的上数量
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(),// 最大线程数,一般就是CUP核心数
3, // 等待
TimeUnit.SECONDS, // 单位
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3),// 等待队列 最多同时开启max+cap个线程
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), // 默认线程工厂
// 拒绝策略,有四种
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() //线程超过max+cap,又来任务,抛出异常
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() //线程超过max+cap,线程池不受理,来源线程执行
//new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() //线程超过max+cap,又来任务,不抛出异常,但丢弃任务
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() //线程超过max+cap,又来任务,尝试与第一个任务竞争,竞争失败,不抛异常,但还丢弃任务
函数式接口,简化编程模型
-
Function:转换型接口,给定一个类型,转为另一个
-
可以用lambda
-
Function<String,Integer> f = str->{return str.length();}; System.out.print(function.apply("abc"));
-
-
Predicate:断定型接口
-
只能返回boolean类型
Predicate<String> p = str->{return str.isEmpty();};
-
-
Supplier:供给型接口,用于产生数据
- 没有参数,只有返回值
-
Consumer:消费型接口,用于处理传入的数据
- 没有返回值
Stream流计算
- 数据------》存储,计算
- 集合,mysql用于存储
- 计算都是流
List<String> l = new ArrayList<>();
l.stream()
.filter(str->{return str.length()>=2;}) // 断定型
.map(str->{return str.toLowerCase();}) // 转换型
.sorted((str1,str2)->str1.compareTo(str2)) // 排序
.limit(1) // 只输出1个
.forEach(System.out::println);
ForkJoin
- 并行执行任务
- 大量数据使用
- forkjoinpool
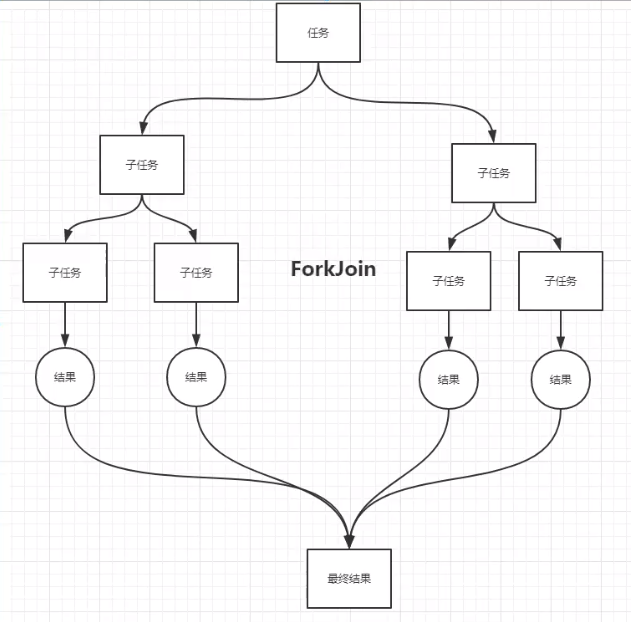
class ForkJoinDemo extends RecursiveTask<Long>{
private Long start;
private Long end;
private Long temp=100000L; // 临界值
public ForkJoinDemo(){
}
public ForkJoinDemo(Long start, Long end){
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
protected Long compute() {
if(end-start < temp){
Long sum = 0L;
for(Long i = start; i <= end; i++){
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}else{
Long mid = (start + end)/2;
ForkJoinDemo f1 = new ForkJoinDemo(start,mid);
f1.fork(); //任务压入队列
ForkJoinDemo f2 = new ForkJoinDemo(mid+1,end);
f2.fork();
return f1.join()+f2.join();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 1 加到10亿
// 方法一 for循环累加
// 方法二
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask<Long> submit = pool.submit(new ForkJoinDemo(1L,10_0000_0000L));// 提交任务
System.out.println(submit.get());
// 方法三 最快
LongStream.range(0L,10_0000_0000L).parallel().reduce(0,Long::sum);
}
}
异步回调
public static void main(String args[]) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println("com1执行");// 耗时操作
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get()); // null
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("com2执行");
return 2; // 有返回值
});
completableFuture2.whenComplete((t,u)->{
System.out.println("t=>"+t); // 正常执行的返回结果
System.out.println("u=>"+u); // 错误信息
}).exceptionally((e)->{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());//
return 500; // 出错了返回的结果
});
System.out.println(completableFuture2.get());
}
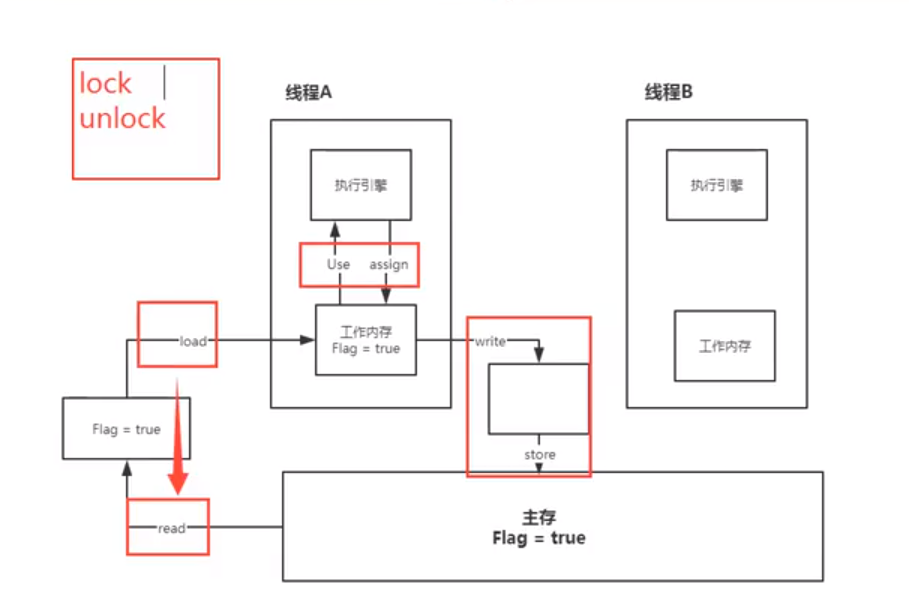
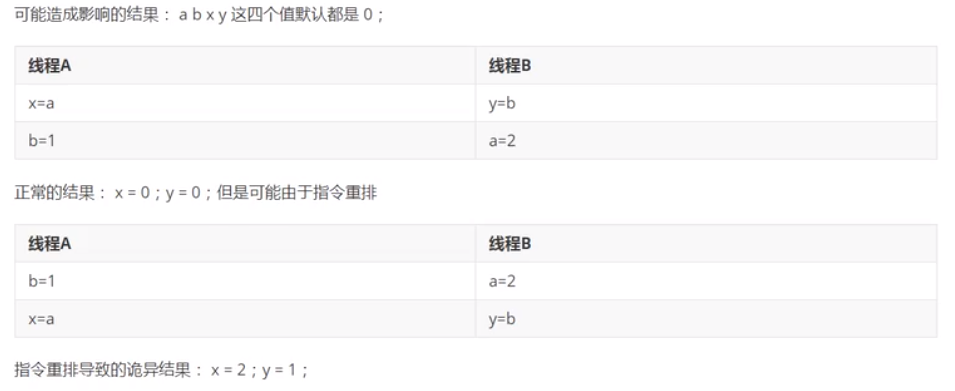
JMM
不存在的东西,是一种约定
- 线程解锁前,把共享变量立刻刷新回主存
- 加锁前,读取主存最新值到工作内存
- 加锁,解锁是同一把锁
- 8种指令成对出现
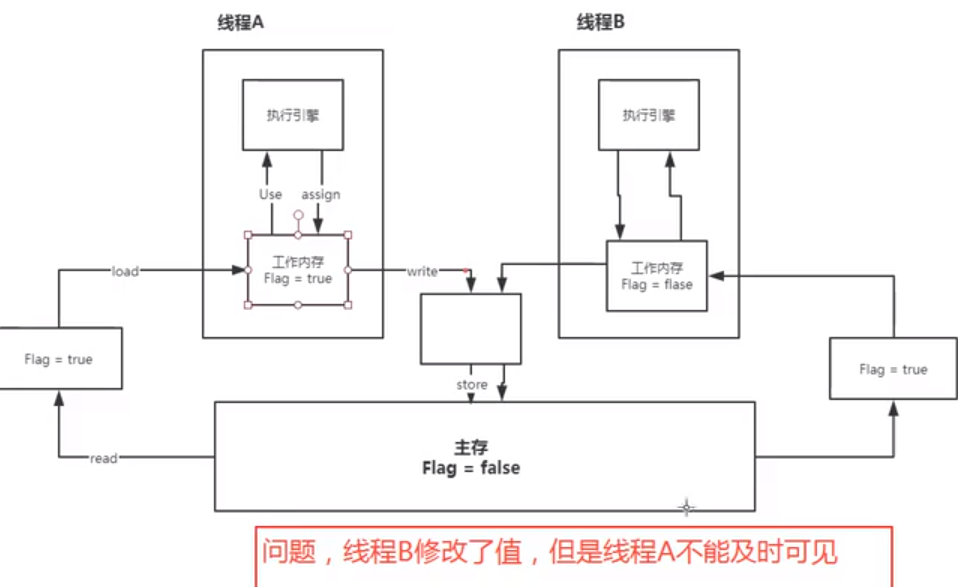
程序不知道主存中的值被修改了。
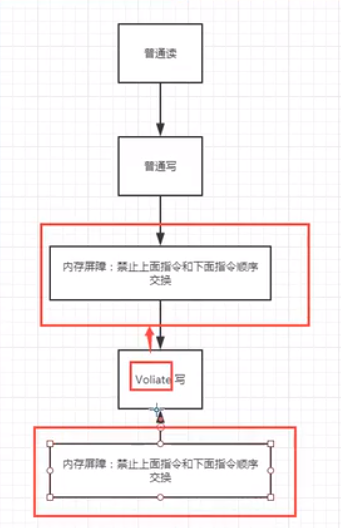
Volatile
-
可见性,上述例子中flag 设置为volatile即可,
-
不保证原子性,在不使用锁的时候,使用原子类可解决原子性问题
- 这些原子类与操作系统有关系,在内存中修改值
- Unsafe类,特殊的存在,java的后门,通过它可以操作内存
-
禁止指令重排
-
你的程序,计算机并不是按照你写的执行
-
源码-》编译器优化重排-》指令并行重排-》内存系统重排-》执行
-
-
-
单例模式
https://blog.dean0731.top/post/8
CAS
AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(2020);
// 比较并交换 cup的并发原语,即能直接操作内存
num.compareAndSet(2020,2021);
System.out.println(num.get());
num.getAndIncrement();
- 比较工作内存与主存中的值,是期望的,执行操作,如果不是,一直循环
- 循环耗时
- 一次只能一个共享变量
- ABA问题
原子引用
带版本号的原子操作
自旋锁
CAS实现自旋锁
class SpinLock{
AtomicReference<Thread> f = new AtomicReference<>();
public void lock(){
// f 可以说就是当前线程, f为空, f就变为当前线程, 其他线程来拿锁的时候不为空,一直循环
while(!f.compareAndSet(null,Thread.currentThread())){
}
}
public void unlock(){
// 释放锁,
f.compareAndSet(Thread.currentThread(),null);
}
}
死锁
排查死锁
- jsp -l 可查看运行中的java程序
- jstack 进程号 查看该程序的堆栈信息