1、可见性(Visibility)
可见性是指,当一个线程修改了某一个全局共享变量的数值,其他线程是否能够知道这个修改。
显然,在串行程序来说可见性的问题是不存在的。因为你在任何一个地方操作修改了某个变量,那么在后续的程序里面,读取这个变量的数值,一定是修改后的数值。
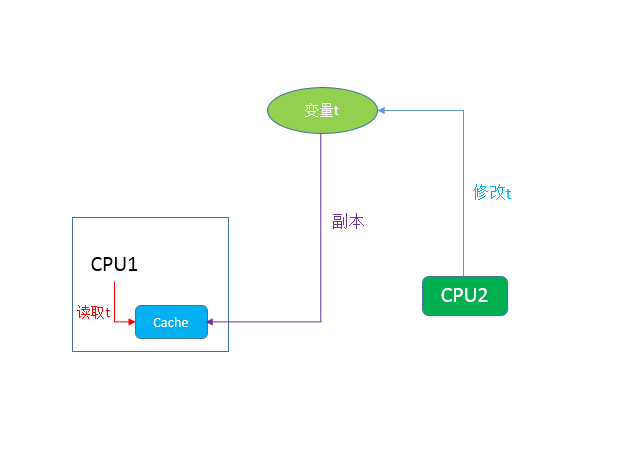
但是,这个问题在并行程序里面就不见得了。在并行程序里面,如果一个线程修改了某一个全局变量,那么其他线程未必可以马上知道这个变动。下面的图1展示了可见性问题的一种。如果在CPU1和CPU2上各运行一个线程,他们共享变量t,由于编译器优化或者应该优化的缘故,在CPU1上的线程将变量t进行了优化,将其缓存在Cache中或者寄存器里面。这种情况下,如果在CPU2上的那个线程修改了线程t 的实际数值,那么CPU1上的线程可能并无法意识到这个改动,依然会读取cache中或者寄存器里面的数据。因此,就产生了可见性问题。外在表现就是,变量t 的数值被CPU2上的线程修改,但是CPU1上的线程依然会读到一个旧的数据。
2、原子性(Atomicity)
原子性,指的是一个操作是不可中断的。即使是在多个线程一起执行的时候,一个操作一旦开始,就不会被其他线程打断。
3、Java内存模型的抽象结构( JMM )
在Java中,所有实例域、静态域和数组元素都存储在堆内存中,堆内存在线程之间共享(本章用“共享变量”这个术语代指实例域,静态域和数组元素)。局部变量(Local Variables),方法定义参数(Java语言规范称之为Formal Method Parameters)和异常处理器参数(ExceptionHandler Parameters)不会在线程之间共享,它们不会有内存可见性问题,也不受内存模型的影响。
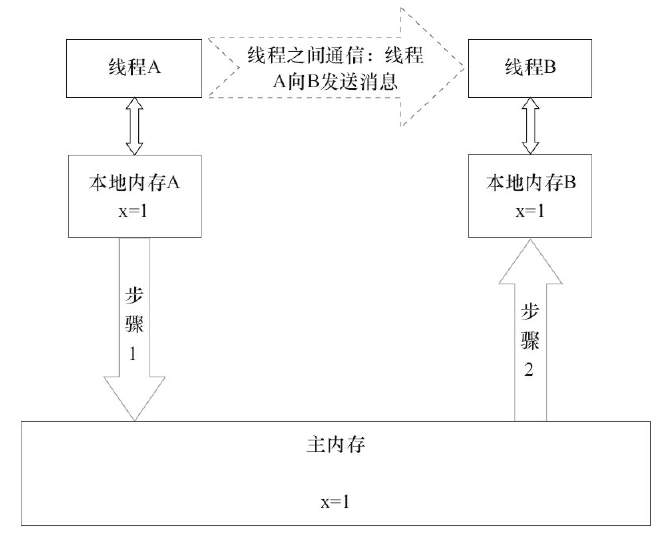
Java线程之间的通信由Java内存模型(本文简称为JMM)控制,JMM决定一个线程对共享变量的写入何时对另一个线程可见。从抽象的角度来看,JMM定义了线程和主内存之间的抽象关系:线程之间的共享变量存储在主内存(Main Memory)中,每个线程都有一个私有的本地内存(Local Memory),本地内存中存储了该线程以读/写共享变量的副本。本地内存是JMM的一个抽象概念,并不真实存在。它涵盖了缓存、写缓冲区、寄存器以及其他的硬件和编译器优化。Java内存模型的抽象示意如图所示。
图3-1 Java内存模型的抽象结构示意图
从图3-1来看,如果线程A与线程B之间要通信的话,必须要经历下面2个步骤。
1)线程A把本地内存A中更新过的共享变量刷新到主内存中去。
2)线程B到主内存中去读取线程A之前已更新过的共享变量。
下面通过示意图(见图3-2)来说明这两个步骤。
图3-2 线程之间的通信图
如图3-2所示,本地内存A和本地内存B由主内存中共享变量x的副本。假设初始时,这3个内存中的x值都为0。线程A在执行时,把更新后的x值(假设值为1)临时存放在自己的本地内存A中。当线程A和线程B需要通信时,线程A首先会把自己本地内存中修改后的x值刷新到主内存中,此时主内存中的x值变为了1。随后,线程B到主内存中去读取线程A更新后的x值,此时线程B的本地内存的x值也变为了1。
从整体来看,这两个步骤实质上是线程A在向线程B发送消息,而且这个通信过程必须要经过主内存。JMM通过控制主内存与每个线程的本地内存之间的交互,来为Java程序员提供内存可见性保证。
4、volatile
4.1使用volatile以后,做了如下事情
- 每次修改volatile变量都会同步到主存中。
- 每次读取volatile变量的值都强制从主存读取最新的值(强制JVM不可优化volatile变量,如JVM优化后变量读取会使用cpu缓存而不从主存中读取)
4.2 volatile解决的是多线程间共享变量的可见性问题,而保证不了多线程间共享变量原子性问题。对于多线程的i++,++i,依然还是会存在多线程问题,volatile是无法解决的.如下:使用一个线程i++,另一个i--,最终得到的结果不为0。
4.2.1 多线程下的i++问题
一个线程对count进行times次的加操作,一个线程对count进行times次的减操作。count最后的结果,不为0.
public class VolatileTest { private static volatile int count = 0; private static final int times = 10000; public static void main(String[] args) { long curTime = System.nanoTime(); Thread decThread = new DecThread(); decThread.start(); System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i++"); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { count++; } System.out.println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--"); // 等待decThread结束 while (decThread.isAlive()) ; long duration = System.nanoTime() - curTime; System.out.println("Result: " + count); System.out.format("Duration: %.2fs ", duration / 1.0e9); } private static class DecThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--"); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { count--; } System.out .println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--"); } } }
4.2.2 程序的运行结果
Start thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i-- Start thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++ End thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++ End thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i-- Result: -6240 Duration: 0.00s
4.2.3 i++和++i并非原子操作
原因是i++和++i并非原子操作,我们若查看字节码,会发现
void f1() { i++; } 的字节码如下
void f1(); Code: 0: aload_0 1: dup 2: getfield #2; //Field i:I 5: iconst_1 6: iadd 7: putfield #2; //Field i:I 10: return
可见i++执行了多部操作,从变量i中读取读取i的值->值+1 ->将+1后的值写回i中,这样在多线程的时候执行情况就类似如下了
Thread1 Thread2 r1 = i; r3 = i; r2 = r1 + 1; r4 = r3 + 1; i = r2; i = r4;
这样会造成的问题就是 r1, r3读到的值都是 0,最后两个线程都将 1 写入 i, 最后 i等于 1,但是却进行了两次自增操作。
可知加了volatile和没加volatile都无法解决非原子操作的线程同步问题。
5、使用循环CAS,实现i++原子操作
5.1 关于Java并发包的介绍
Java提供了java.util.concurrent.atomic包来提供线程安全的基本类型包装类。这些包装类都是是用CAS来实现,i++的原子性操作。以AtomicInteger为例子,讲一下 public final int getAndIncrement(){} 方法的实现。
public final int getAndIncrement() { for (;;) { int current = get(); int next = current + 1; if (compareAndSet(current, next)) return current; } }
5.2 使用循环CAS,来实现i++的原子性操作
public class AtomicIntegerTest { private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0); private static final int times = 10000; AtomicInteger atomicInteger; public static void main(String[] args) { long curTime = System.nanoTime(); Thread decThread = new DecThread(); decThread.start(); System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i++"); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { // 进行自加的操作 count.getAndIncrement(); } System.out.println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i++"); // 等待decThread结束 while (decThread.isAlive()) ; long duration = System.nanoTime() - curTime; System.out.println("Result: " + count); System.out.format("Duration: %.2fs ", duration / 1.0e9); } private static class DecThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--"); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { // 进行自减的操作 count.getAndDecrement(); } System.out .println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--"); } } }
Start thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++ Start thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i-- End thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i-- End thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++ Result: 0 Duration: 0.00s
6、使用锁机制,实现i++原子操作
6.1 使用锁机制,实现i++原子操作
package com.baowei.yuanzi; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class LockTest { private static int count = 0; private static final int times = 10000; // 使用Lock实现,多线程的数据同步 public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static void main(String[] args) { long curTime = System.nanoTime(); Thread decThread = new DecThread(); decThread.start(); System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i++"); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { // 进行自加的操作 try { lock.lock(); count++; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } System.out.println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i++"); // 等待decThread结束 while (decThread.isAlive()) ; long duration = System.nanoTime() - curTime; System.out.println("Result: " + count); System.out.format("Duration: %.2fs ", duration / 1.0e9); } private static class DecThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--"); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { // 进行自减的操作 try { lock.lock(); count--; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } System.out .println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--"); } } }
6.2 程序的运行结果
Start thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i-- Start thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++ End thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++ End thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i-- Result: 0 Duration: 0.04s
7、使用synchronized,实现i++原子操作
7.1 使用synchronized,实现i++原子操作
package com.baowei.yuanzi; public class SynchronizedTest { private static int count = 0; private static final int times = 1000000; public static void main(String[] args) { long curTime = System.nanoTime(); Thread decThread = new DecThread(); decThread.start(); System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i++"); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { // 进行自加的操作 synchronized (SynchronizedTest.class) { count++; } } System.out.println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i++"); // 等待decThread结束 while (decThread.isAlive()) ; long duration = System.nanoTime() - curTime; System.out.println("Result: " + count); System.out.format("Duration: %.2fs ", duration / 1.0e9); } private static class DecThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--"); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { // 进行自减的操作 synchronized (SynchronizedTest.class) { count--; } } System.out .println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--"); } } }
7.2 程序的运行结果
Start thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++ Start thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i-- End thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i-- End thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++ Result: 0 Duration: 0.03s
8、参考的资料
8.1 Java 高并发程序设计(21页)
8.2 http://www.cnblogs.com/zemliu/p/3298685.html
8.3 Java 并发编程的艺术 ( The Art of Java Concurrency Programming ) (22-23 页)
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Bwz_Learning」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zbw18297786698/article/details/53420780