原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-binary-search-tree-from-preorder-traversal/
题目:
Return the root node of a binary search tree that matches the given preorder traversal.
(Recall that a binary search tree is a binary tree where for every node, any descendant of node.left has a value < node.val, and any descendant of node.right has a value > node.val. Also recall that a preorder traversal displays the value of the node first, then traverses node.left, then traverses node.right.)
Example 1:
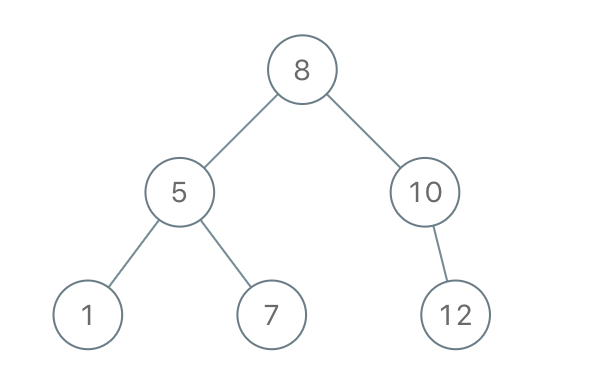
Input: [8,5,1,7,10,12]
Output: [8,5,10,1,7,null,12]
Note:
1 <= preorder.length <= 100- The values of
preorderare distinct.
题解:
The first element should be root. As BST, root left subtree should be smaller than root value, right subtree should be bigger than root value.
Could use root value as pivot and find out array corresponding to left subtree, also array corresponding to right subtree.
Time Complexity: O(nlogn). Each level of tree, it takes O(n) time, tree height should be O(logn).
Space: O(logn).
AC Java:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder) { 12 if(preorder == null || preorder.length == 0){ 13 return null; 14 } 15 16 return dfs(preorder, 0, preorder.length-1); 17 } 18 19 private TreeNode dfs(int[] preorder, int l, int r){ 20 if(l > r){ 21 return null; 22 } 23 24 TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[l]); 25 int biggerIndex = l+1; 26 while(biggerIndex<=r && preorder[biggerIndex]<preorder[l]){ 27 biggerIndex++; 28 } 29 30 root.left = dfs(preorder, l+1, biggerIndex-1); 31 root.right = dfs(preorder, biggerIndex, r); 32 return root; 33 } 34 }
For each node, it should be lower and higher bound.
For current value, if it is not within the bound, return null.
Otherwise, use this value to construct a node and return it. Move the index.
Time Complexity: O(n).
Space: O(logn). Regardless res.
AC Java:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 int i = 0; 12 13 public TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder) { 14 if(preorder == null || preorder.length == 0){ 15 return null; 16 } 17 18 return dfs(preorder, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE); 19 } 20 21 private TreeNode dfs(int [] preorder, int min, int max){ 22 if(i>=preorder.length){ 23 return null; 24 } 25 26 if(preorder[i]<min || preorder[i]>max){ 27 return null; 28 } 29 30 TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[i]); 31 i++; 32 root.left = dfs(preorder, min, root.val); 33 root.right = dfs(preorder, root.val, max); 34 return root; 35 } 36 }
Iteration method. Use stack to store TreeNode.
When encountering new value, first peek the top of stack, assign it to top. Then while stack top is smaller than new value, keep popping and update top.
If actually it doesn't pop, then new value node is top left child. Otherwise, new value node is last popped node's right child.
Time Complexity: O(n).
Space: O(logn). Stack space, regardless res.
AC Java:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder) { 12 if(preorder == null || preorder.length == 0){ 13 return null; 14 } 15 16 TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]); 17 Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<TreeNode>(); 18 stk.push(root); 19 for(int i = 1; i<preorder.length; i++){ 20 TreeNode cur = new TreeNode(preorder[i]); 21 TreeNode top = stk.peek(); 22 23 while(!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek().val<preorder[i]){ 24 top = stk.pop(); 25 } 26 27 if(top.val < preorder[i]){ 28 top.right = cur; 29 }else{ 30 top.left = cur; 31 } 32 33 stk.push(cur); 34 } 35 36 return root; 37 } 38 }