原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/find-eventual-safe-states/
题目:
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. If we reach a node that is terminal (that is, it has no outgoing directed edges), we stop.
Now, say our starting node is eventually safe if and only if we must eventually walk to a terminal node. More specifically, there exists a natural number K so that for any choice of where to walk, we must have stopped at a terminal node in less than K steps.
Which nodes are eventually safe? Return them as an array in sorted order.
The directed graph has N nodes with labels 0, 1, ..., N-1, where N is the length of graph. The graph is given in the following form: graph[i] is a list of labels j such that (i, j) is a directed edge of the graph.
Example: Input: graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]] Output: [2,4,5,6] Here is a diagram of the above graph.
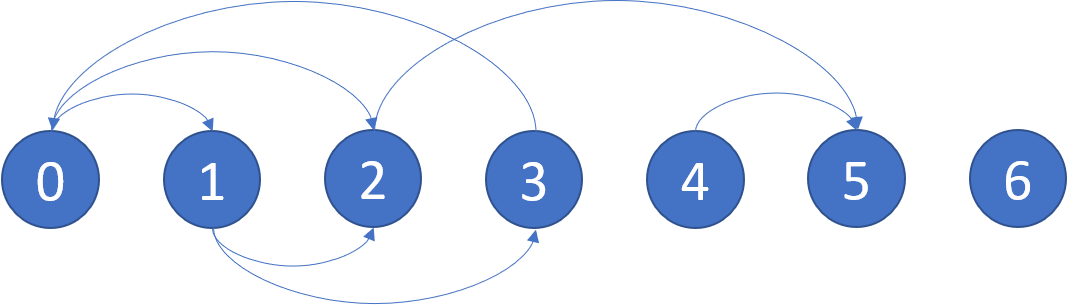
Note:
graphwill have length at most10000.- The number of edges in the graph will not exceed
32000. - Each
graph[i]will be a sorted list of different integers, chosen within the range[0, graph.length - 1].
题解:
If a node has no outgoing degree, then it must be safe.
Put these nodes into queue.
When polling cur node, from its incoming edge, decrease source node out degree by 1. If source node out degree becomes 0, then it is safe too, put it into queue.
Perform this unitl queue is empty. All the nodes coming out of queue are safe.
Time Complexity: O(V+E+VlogV). Construct rgraph takes O(V+E). Treverse takes O(V+E). Sort takes O(VlogV).
Space: O(V+E).
AC Java:
1 class Solution { 2 public List<Integer> eventualSafeNodes(int[][] graph) { 3 int N = graph.length; 4 List<List<Integer>> rgraph = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); 5 6 for(int i = 0; i<N; i++){ 7 rgraph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); 8 } 9 10 LinkedList<Integer> que = new LinkedList<Integer>(); 11 int [] outDegrees = new int[N]; 12 13 for(int i = 0; i<N; i++){ 14 outDegrees[i] = graph[i].length; 15 16 if(graph[i].length == 0){ 17 que.add(i); 18 continue; 19 } 20 21 for(int target : graph[i]){ 22 rgraph.get(target).add(i); 23 } 24 } 25 26 List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 27 while(!que.isEmpty()){ 28 int cur = que.poll(); 29 res.add(cur); 30 for(int source : rgraph.get(cur)){ 31 outDegrees[source]--; 32 if(outDegrees[source] == 0){ 33 que.add(source); 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 38 Collections.sort(res); 39 return res; 40 } 41 }