原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/the-maze/
题目:
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball's start position, the destination and the maze, determine whether the ball could stop at the destination.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
Example 1:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4) Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4) Output: true Explanation: One possible way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.
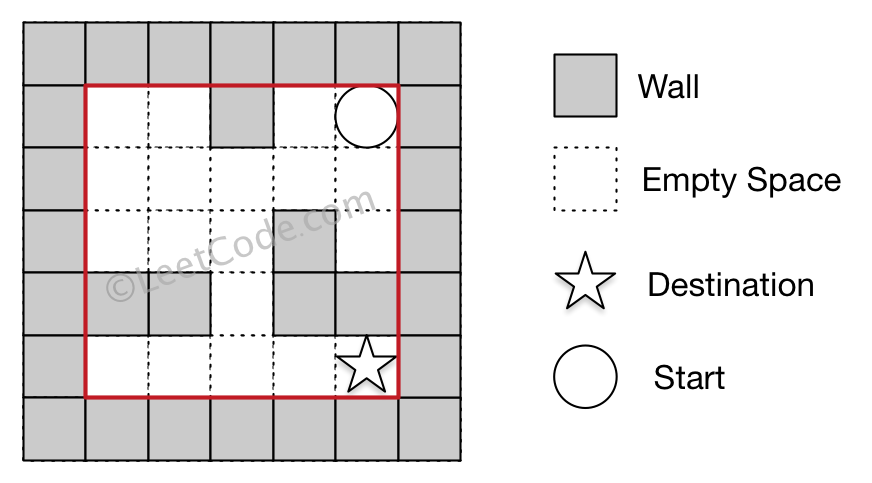
Example 2:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4) Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (3, 2) Output: false Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination.
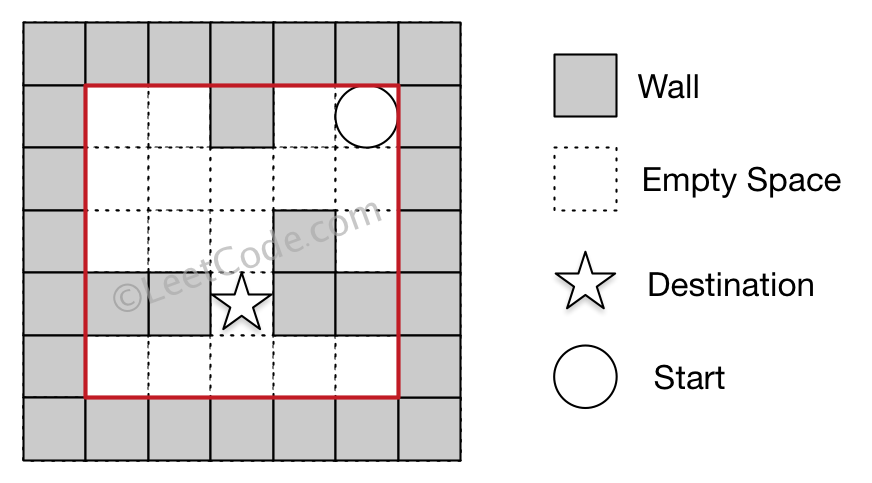
Note:
- There is only one ball and one destination in the maze.
- Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and both the width and height of the maze won't exceed 100.
题解:
Starting from start index, perform BFS on 4 directions. For each direction, only stops when hitting the boundary or wall.
Then check if hitting position is visited before. If not, mark it as visited, add it to queue.
Time Complexity: O(m*n). m = maze.length. n = maze[0].length.
Space: O(m*n).
AC Java:
1 class Solution { 2 int [][] dirs = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0,-1}, {0,1}}; 3 4 public boolean hasPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) { 5 if(maze == null || maze.length == 0 || maze[0].length == 0){ 6 return false; 7 } 8 9 int m = maze.length; 10 int n = maze[0].length; 11 if(start[0]<0 || start[0]>=m || start[1]<0 || start[1]>=n || 12 destination[0]<0 || destination[0]>=m || destination[1]<0 || destination[1]>=n){ 13 return false; 14 } 15 16 17 LinkedList<int []> que = new LinkedList<>(); 18 boolean [][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; 19 que.add(start); 20 visited[start[0]][start[1]] = true; 21 while(!que.isEmpty()){ 22 int [] cur = que.poll(); 23 if(cur[0] == destination[0] && cur[1] == destination[1]){ 24 return true; 25 } 26 27 for(int [] dir : dirs){ 28 int r = cur[0]; 29 int c = cur[1]; 30 while(r+dir[0]>=0 && r+dir[0]<m && c+dir[1]>=0 && c+dir[1]<n && maze[r+dir[0]][c+dir[1]]==0){ 31 r += dir[0]; 32 c += dir[1]; 33 } 34 35 if(!visited[r][c]){ 36 visited[r][c] = true; 37 que.add(new int[]{r, c}); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 42 return false; 43 } 44 }
Could also use DFS. DFS state needs maze, current starting point, destinaiton point, visited matrix and current moving direction.
If starting point == destinaiton point, return true.
Otherwise, for each of 4 directions, calculae the stop point.
If the stop point hasn't been visited before, mark it as visited and continue DFS from that point. If any of 4 dirs, dfs result from that point return true, then return true.
Time Complexity: O(m*n).
Space: O(m*n).
AC Java:
1 class Solution { 2 int [][] dirs = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1,0}, {0,-1}, {0,1}}; 3 public boolean hasPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) { 4 if(maze == null || maze.length == 0 || maze[0].length == 0){ 5 return false; 6 } 7 8 int m = maze.length; 9 int n = maze[0].length; 10 boolean [][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; 11 visited[start[0]][start[1]] = true; 12 13 for(int [] dir : dirs){ 14 if(dfs(maze, start, destination, dir, visited)){ 15 return true; 16 } 17 } 18 19 return false; 20 } 21 22 private boolean dfs(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] dest, int [] dir, boolean [][] visited){ 23 int m = maze.length; 24 int n = maze[0].length; 25 26 int r = start[0]; 27 int c = start[1]; 28 29 if(r == dest[0] && c ==dest[1]){ 30 return true; 31 } 32 33 while(r+dir[0]>=0 && r+dir[0]<m && c+dir[1]>=0 && c+dir[1]<n && maze[r+dir[0]][c+dir[1]]==0){ 34 r += dir[0]; 35 c += dir[1]; 36 } 37 38 if(visited[r][c]){ 39 return false; 40 } 41 42 visited[r][c] = true; 43 for(int [] nextDir : dirs){ 44 if(dfs(maze, new int[]{r,c}, dest, nextDir, visited)){ 45 return true; 46 } 47 } 48 49 return false; 50 } 51 }