原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/
题目:
Given a binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example:
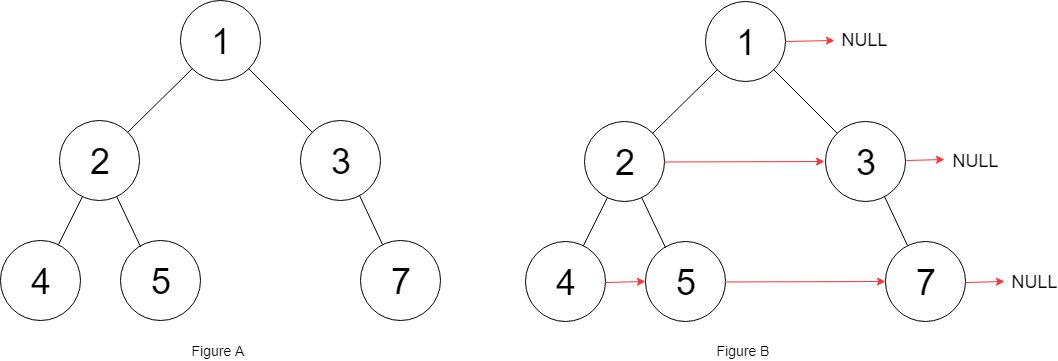
Input: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":4},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":5},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"next":null,"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"val":3},"val":1}
Output: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":{"$id":"5","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"right":null,"val":5},"right":null,"val":4},"next":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"5"},"val":3},"right":{"$ref":"4"},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"6"},"val":1}
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B.
Note:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
题解:
是Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node的进阶版.
Iteration解法相同.
Time Complexity: O(n). Space: O(1).
AC Java:
1 /* 2 // Definition for a Node. 3 class Node { 4 public int val; 5 public Node left; 6 public Node right; 7 public Node next; 8 9 public Node() {} 10 11 public Node(int _val,Node _left,Node _right,Node _next) { 12 val = _val; 13 left = _left; 14 right = _right; 15 next = _next; 16 } 17 }; 18 */ 19 class Solution { 20 public Node connect(Node root) { 21 Node cur = root; 22 while(cur != null){ 23 Node dummyHead = new Node(); //记录下一层的假头 24 Node it = dummyHead; 25 26 while(cur != null){ 27 if(cur.left != null){ 28 it.next = cur.left; 29 it = it.next; 30 } 31 32 if(cur.right != null){ 33 it.next = cur.right; 34 it = it.next; 35 } 36 37 cur = cur.next; //cur 更新到下一层假头的next上面 38 } 39 40 cur = dummyHead.next; 41 } 42 43 return root; 44 } 45 }