平衡树初阶——AVL平衡二叉查找树
一、什么是二叉树
1. 什么是树。
计算机科学里面的树本质是一个树状图。树首先是一个有向无环图,由根节点指向子结点。但是不严格的说,我们也研究无向树。所谓无向树就是将有向树的所有边看成无向边形成的树状图。树是一种递归的数据结构,所以我们研究树也是按照递归的方式去研究的。
2.什么是二叉树。
我们给出二叉树的递归定义如下:
(1)空树是一个二叉树。
(2)单个节点是一个二叉树。
(3)如果一棵树中,以它的左右子节点为根形成的子树都是二叉树,那么这棵树本身也是二叉树。
二、BST
1.什么是二叉排序树。
二叉排序树是一种二叉树,它满足树的中序遍历是有序的。
2.BST(Binary Search Tree)。
二叉查找树是一种最普通的二叉排序树,一般称作BST,也称为B-树。在这棵树中,满足在任意一个子树中,都满足左子树 < 根节点 < 右子树,即该树的中序遍历满足从小到大排序的结果。
3.如何构造一个二叉排序树?
很显然,要想构造一个BST,就必须在插入节点时,满足下面的原则:
(1)如果节点为空,则直接插入到该节点。
(2)如果节点不为空,且要插入的值小于等于当前节点的值,那么则将该节点插入到左子树当中。
(3)如果节点不为空,且要插入的值大于当前节点的值,那么则将该节点插入到右子树当中。
4.利用BST的性质对一个数组进行剃重。
由于BST有二叉排序树的性质,我们可以利用这样的性质对一个待定数组进行剃重。原理很简单,只需要在插入的时候如果已经发现了相等的节点的话,那么则不进行插入即可。也就是说,只有该树没有的节点,我们才进行相应的插入操作。
三、BST的相关操作
1.建树(createTree)
BST的建立是基于一个数组进行的,本质上是把数组中的数按顺序插入的树中。可以想象,,每插入一个数,平均时间复杂度为O(logn),所以建树的平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。
2.查找某一个值d(searchTree)
如果我们需要在BST上查找一个值d,那么我们需要从根节点开始,按照下面的思路进行递归查询:
(1)如果当前节点为空,则未找到,返回NULL。
(2)如果当前节点不为空,且当前节点的值等于d,那么则找到,返回当前节点。
(3)如果当前节点不为空,且当前节点的值大于d,那么则递归在左子树中寻找。
(4)如果当前节点不为空,且当前节点的值小于d,那么则递归在右子树中寻找。
可以想象,查找操作的平均时间复杂度为O(logn)
3.删除一个值d(deleteTree)
如果我们想要删除一个值d的节点,那么显然首先需要找到该节点。如果没有找到,则删除操作失败,如果找到,继续下面的操作即可:
(1)如果找到的节点的右子树为空,那么直接用该节点的左节点替换当前节点即可。
(2)如果找到的节点的右子树不为空,且右子树的左子树不为空,则递归找该右子树的左子树。
(3)如果找到的节点的右子树不为空,且右子树的左子树为空,则:
①如果找到的该节点的右节点为空,则返回当前节点,用这个节点去替换需要删除的点即可。
②如果找到的该节点的右子树不为空,则首先用该右子树替换找到的节点,在用找到的节点替换需要删除的节点即可。
显然,删除操作的平均时间复杂度为O(logn)
四、AVL平衡二叉查找树
1.什么是平衡二叉树。
平衡二叉树是一种二叉排序树,并且满足树中任意一个节点的左右子树的高度保持平衡。
2.什么是AVL。
AVL是一种二叉查找树,并且满足树中任意一个节点的左右子树的高度差的绝对值小于等于1,即保持平衡系数不大于1。AVL也称B-BST(Balanced - Binary Search Tree),而AVL的名称只是与这种数据结构的作者有关。
3.引例:为什么会产生AVL
我们为什么需要研究AVL,换句话说,为什么我们要重视BST的平衡性能呢?我们看下面的一个例子。
我们用1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9来进行建树。我们发现,这样建树的结果如下:
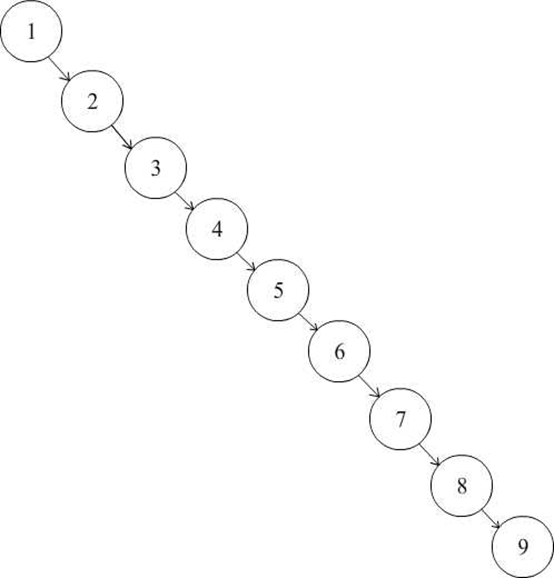
可以看出,这样二叉树实际上退化为了一个链表。在最坏的情况下,插入和删除的时间复杂度都退化为了O(n)。
很显然,树的平衡性越好,这种退化越不明显。所以为了保持BST的高效,我们研究AVL是必要的。
4.如何保持AVL的平衡?
既然要保持左右子树高度差小于等于1,那么我们一定需要在节点里面定义一个新的属性,用来记录该节点为根的树的高度。由于建树的过程是递归的,所以树的高度的更新也是递归完成的。通过更新高度,我们就可以知道什么时候左右子树的高度差大于1了,这个时候产生了失衡。一旦某一个节点开始失衡,那么这个时候必须通过旋转操作使二叉树达到一个新的平衡。
五、AVL的相关操作
1.旋转操作(rotateAvl)
如果在某一个时刻二叉树发生了失衡,我们就需要对二叉树进行相应的旋转使得二叉树重新达到平衡。这个旋转并不是随意的,我们还要保证BST的基本性质,那就是中序遍历必须有序才行。
我们总结二叉树失衡的原因,可以归纳为以下四种情况(其中圆形节点代表失衡有关的节点,方形节点代表子树)
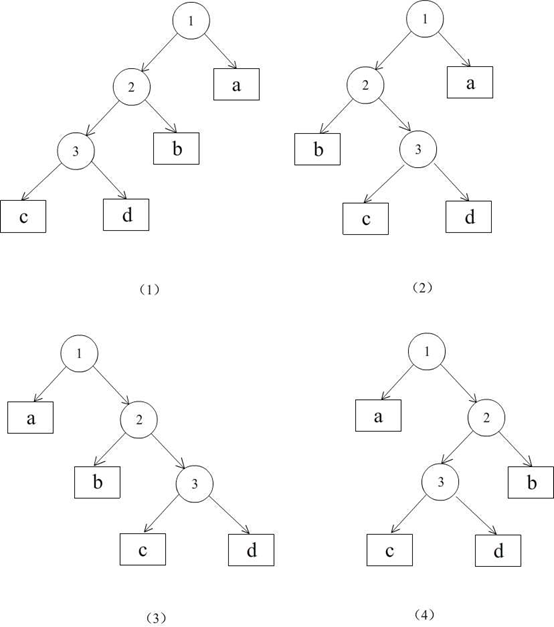
归纳后发现,对于情况(1)(2),都是由于左子树高度大于右子树高度形成的失衡。对于情况(3)(4)则是相反的情况。且情况(1)(3)互为镜像,情况(2)(4)互为镜像。所以我们只以(1)(2)种情况作为例子,(3)(4)情况的道理同出一辙。
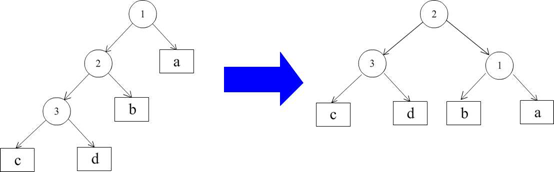
对于情况(1),左子树高度大于右子树高度,而在左子树中,依然是左子树高度大于右子树高度。对于这样的情况,我们需要以1为根进行右转(rightRotate),右转的结果是,2变为新的根,而1则成为2的右节点,2原本的右子树则成为了1的左子树,即,如下图:
对于情况(2),左子树高度大于右子树高度,而在左子树中,左子树高度小于右子树高度。对于这样的情况,我们需要首先需要以2(leftRotate)为根进行左转,左转的结果是3变为1的左子树,而2变为3的左子树,而3原本的左子树成了2的右子树。如下图所示:

之后就转化为了情况(1),故只需要在以1为根进行右转即可。
通过这样的旋转操作,AVL重新达到了平衡。
这个旋转操作的时间复杂度是O(1)的。
2.高度更新操作。
由于高度更新是递归进行的,所以我们选择回溯的阶段进行高度更新。而一个节点的高度应该是左子树高度和右子树高度的最大值再加1。
高度更新在整个AVL中是必要的,不管建树过程中,还是插入操作,或者是删除操作中,我们都需要时时刻刻对高度进行更新,只有正确的更新高度,才能判断二叉树是否失衡。而一旦失衡,我们就需要进行上述的旋转操作,这些是相辅相承的。
高度更新的时间复杂度也是O(1)的。
3.插入操作(insertAvl)
在插入操作中,由于插入的新节点,有可能使原本的二叉树产生了失衡,故应该进行相应的旋转操作。故,这样插入操作能稳定在平均O(logn) 的时间复杂度内。
4.删除操作(deleteAvl)
再删除操作中,由于删除了节点,也有可能是原本平衡的二叉树产生失衡,故也应该进行相应的旋转操作。故,这样删除操作能稳定在O(logn) 的时间复杂度内。
六、代码实现(C/C++)
1.对于节点数据类型的处理:
1 #define Elem int //这样Elem就是节点中数据的类型。
2.节点结构体的二叉链表
1 typedef struct LNode 2 { 3 Elem data; //节点数据域 4 int height; //节点为根的树的高度 5 struct LNode *left,*right; //左子树和右子树 6 struct LNode() //构造函数 7 { 8 height=0; 9 left=right=NULL; 10 } 11 }LNode,*avlTree; 12 //这样定义LNode是节点的类型,avlTree则是节点的指针类型。
3.右旋转子操作,返回旋转之后的根节点指针
1 avlTree _rightRotate(avlTree &r) 2 { 3 int lh=0,rh=0; 4 avlTree t=r->left; 5 r->left=t->right; 6 if(r->left) lh=r->left->height; 7 if(r->right) rh=r->right->height; 8 r->height=max(lh,rh)+1; 9 t->right=r; 10 if(t->left==NULL) t->height=1; 11 else t->height=max(t->left->height,r->height)+1; 12 return t; 13 }
4.左旋转子操作,返回旋转之后的根节点指针
1 avlTree _leftRotate(avlTree &r) 2 { 3 int lh=0,rh=0; 4 avlTree t=r->right; 5 r->right=t->left; 6 if(r->left) lh=r->left->height; 7 if(r->right) rh=r->right->height; 8 r->height=max(lh,rh)+1; 9 t->left=r; 10 if(t->right==NULL) t->height=1; 11 t->height=max(t->height,r->height)+1; 12 return t; 13 }
5.旋转主算法(发生失衡,按照规则进行旋转操作)
1 void rotateAvl(avlTree &root) 2 { 3 int lh=0,rh=0; 4 if(root->left) lh=root->left->height; 5 if(root->right) rh=root->right->height; 6 root->height=max(lh,rh)+1; 7 if(abs(lh-rh)>1) 8 { 9 avlTree tp; 10 int lp=0,rp=0; 11 if(lh>rh) tp=root->left; 12 else tp=root->right; 13 if(tp->left!=NULL) lp=tp->left->height; 14 if(tp->right!=NULL) rp=tp->right->height; 15 if(lh>rh&&lp<rp) root->left=_leftRotate(tp); 16 if(lh<rh&&lp>rp) root->right=_rightRotate(tp); 17 if(lh>rh) root=_rightRotate(root); 18 else root=_leftRotate(root); 19 } 20 }
6.插入操作,向二叉树r插入d。这里用sign标记表示是否进行剃重,如果sign为true则剃重,sign为false则表示可重复。
1 void insertAvl(avlTree &r,Elem d,bool sign) 2 { 3 //递归出口 4 if(r==NULL) { 5 r=new LNode(); 6 r->data=d; 7 r->height++; 8 return; 9 } 10 if(d<=r->data) 11 { 12 if(d==r->data&&sign) return; 13 insertAvl(r->left,d,sign); 14 } 15 else 16 { 17 insertAvl(r->right,d,sign); 18 } 19 rotateAvl(r); //检验失衡并进行旋转 20 }
7. 根据data数组建树。这里用sign标记表示是否进行剃重,如果sign为true则剃重,sign为false则表示可重复。
1 void createAvl(avlTree &root,Elem data[],int n,bool sign) 2 { 3 int i; 4 root=NULL; 5 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 6 { 7 insertAvl(root,data[i],sign); 8 } 9 }
8.查询root里面的数据d所在节点,如果查询成功,则返回该节点。若d数据不存在,则查询失败,返回NULL。
1 avlTree searchAvl(avlTree root,Elem d) 2 { 3 if(root!=NULL) 4 { 5 if(d==root->data) return root; 6 else if(d<root->data) return searchAvl(root->left,d); 7 else searchAvl(root->right,d); 8 } 9 return NULL; 10 }
9.在删除中寻找实际需要删除的点,返回实际点。
1 avlTree _delete(avlTree &root) 2 { 3 avlTree ret=root; 4 if(root->left) ret=_delete(root->left); 5 else if(root->right) 6 { 7 ret=root->right; 8 int t=root->data; 9 root->data=root->right->data; 10 ret->data=t; 11 root->height=1; 12 root->right=NULL; 13 return ret; 14 } 15 else 16 { 17 root=NULL; 18 return ret; 19 } 20 rotateAvl(root); //检验失衡并进行旋转 21 return ret; 22 }
10.删除主操作算法,删除root上的data数据所在节点
1 void deleteAvl(avlTree &root,Elem data) 2 { 3 avlTree ret; 4 if(!root) return; 5 if(root->data!=data) //未找到该节点,首先寻找该节点 6 { 7 if(data<root->data) ret=root->left; 8 else ret=root->right; 9 deleteAvl(ret,data); //递归寻找 10 } 11 else //找到该节点 12 { 13 if(!root->right) //右子树为空 14 { 15 root=root->left; 16 } 17 else //右子树不为空 18 { 19 avlTree t=_delete(root->right); //寻找实际删除的节点 20 root->data=t->data; 21 free(t); 22 } 23 } 24 rotateAvl(root); //检验失衡并进行旋转 25 }
于是我又找到了一份不错的模版总结,仅供参考!
Treap树
核心是 利用随机数的二叉排序树的各种操作复杂度平均为O(lgn)
Treap模板:
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <ctime> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <cstdlib> 7 #include <cmath> 8 #include <utility> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <queue> 11 #include <map> 12 #include <set> 13 #define max(x,y) ((x)>(y)?(x):(y)) 14 #define min(x,y) ((x)>(y)?(y):(x)) 15 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 16 #define MAXN 100005 17 18 using namespace std; 19 20 int cnt=1,rt=0; //节点编号从1开始 21 22 struct Tree 23 { 24 int key, size, pri, son[2]; //保证父亲的pri大于儿子的pri 25 void set(int x, int y, int z) 26 { 27 key=x; 28 pri=y; 29 size=z; 30 son[0]=son[1]=0; 31 } 32 }T[MAXN]; 33 34 void rotate(int p, int &x) 35 { 36 int y=T[x].son[!p]; 37 T[x].size=T[x].size-T[y].size+T[T[y].son[p]].size; 38 T[x].son[!p]=T[y].son[p]; 39 T[y].size=T[y].size-T[T[y].son[p]].size+T[x].size; 40 T[y].son[p]=x; 41 x=y; 42 } 43 44 void ins(int key, int &x) 45 { 46 if(x == 0) 47 T[x = cnt++].set(key, rand(), 1); 48 else 49 { 50 T[x].size++; 51 int p=key < T[x].key; 52 ins(key, T[x].son[!p]); 53 if(T[x].pri < T[T[x].son[!p]].pri) 54 rotate(p, x); 55 } 56 } 57 58 void del(int key, int &x) //删除值为key的节点 59 { 60 if(T[x].key == key) 61 { 62 if(T[x].son[0] && T[x].son[1]) 63 { 64 int p=T[T[x].son[0]].pri > T[T[x].son[1]].pri; 65 rotate(p, x); 66 del(key, T[x].son[p]); 67 } 68 else 69 { 70 if(!T[x].son[0]) 71 x=T[x].son[1]; 72 else 73 x=T[x].son[0]; 74 } 75 } 76 else 77 { 78 T[x].size--; 79 int p=T[x].key > key; 80 del(key, T[x].son[!p]); 81 } 82 } 83 84 int find(int p, int &x) //找出第p小的节点的编号 85 { 86 if(p == T[T[x].son[0]].size+1) 87 return x; 88 if(p > T[T[x].son[0]].size+1) 89 find(p-T[T[x].son[0]].size-1, T[x].son[1]); 90 else 91 find(p, T[x].son[0]); 92 } 93 94 int find_NoLarger(int key, int &x) //找出值小于等于key的节点个数 95 { 96 if(x == 0) 97 return 0; 98 if(T[x].key <= key) 99 return T[T[x].son[0]].size+1+find_NoLarger(key, T[x].son[1]); 100 else 101 return find_NoLarger(key, T[x].son[0]); 102 }
View Code
相关题目:POJ 3481 1442 2352
Splay Tree(伸展树)
核心就是 过程Splay(x, y),即将x节点转移到y节点的子节点上面(其中y是x的祖先)。
利用其中双旋的优势能够保证查询复杂度均摊为O(lgn)
一开始理解有些困难,其实实际上不做深入的理解就是,双旋的过程就是一个建立相对平衡的二叉树的一个过程。
》对于二叉树,最极端的情况就是线性插入,使得整棵二叉树退化为一条链。比如你查询链的最后一个节点,之后再次查询第一个节点。
1)若只是单旋通过Splay(x, 0)将最后一个节点移动到根节点,需要O(n)复杂度,而查询第一个节点时又需要O(n)复杂度,来来往往就退化成一条链了。
2)若是双旋Splay(x, 0)将最后一个节点移动到根节点上时,移动过程中建立起了相对平衡的二叉树,需要O(n),也就是查询第一个节点时,大概是需要O(lgn)复杂度。这就降低了复杂度。可以证明,总的每个操作的均摊复杂度是O(lgn)。
具体证明可以参见 杨思雨《伸展树的基本操作与应用》
I 用于维护单调队列 :(以key为维护对象保证单调)
常用版:(支持相同值)
1 Struct Tree{ 2 3 int key, size, fa, son[2]; 4 5 } 6 7 void PushUp(int x); 8 9 void Rotate(int x, int p); //0左旋 1右旋 10 11 void Splay(int x, int To) //将x节点插入到To的子节点中 12 13 int find(int key) //返回值为key的节点 若无返回0 若有将其转移到根处 14 15 int prev() //返回比根值小的最大值 若无返回0 若有将其转移到根处 16 17 int succ() //返回比根值大的最小值 若无返回0 若有将其转移到根处 18 19 void Insert(int key) //插入key 并且将该节点转移到根处 20 21 void Delete(int key) //删除值为key的节点 若有重点只删其中一个 x的前驱移动到根处 22 23 int GetPth(int p) //获得第p小的节点 并将其转移到根处 24 25 int GetRank(int key) //获得值<=key的节点个数 并将其转移到根处 若<key只需将<=换为<
模板:
1 int cnt=1, rt=0; 2 3 struct Tree 4 { 5 int key, size, fa, son[2]; 6 void set(int _key, int _size, int _fa) 7 { 8 key=_key; 9 size=_size; 10 fa=_fa; 11 son[0]=son[1]=0; 12 } 13 }T[MAXN]; 14 15 inline void PushUp(int x) 16 { 17 T[x].size=T[T[x].son[0]].size+T[T[x].son[1]].size+1; 18 } 19 20 inline void Rotate(int x, int p) //0左旋 1右旋 21 { 22 int y=T[x].fa; 23 T[y].son[!p]=T[x].son[p]; 24 T[T[x].son[p]].fa=y; 25 T[x].fa=T[y].fa; 26 if(T[x].fa) 27 T[T[x].fa].son[T[T[x].fa].son[1] == y]=x; 28 T[x].son[p]=y; 29 T[y].fa=x; 30 PushUp(y); 31 PushUp(x); 32 } 33 34 void Splay(int x, int To) //将x节点插入到To的子节点中 35 { 36 while(T[x].fa != To) 37 { 38 if(T[T[x].fa].fa == To) 39 Rotate(x, T[T[x].fa].son[0] == x); 40 else 41 { 42 int y=T[x].fa, z=T[y].fa; 43 int p=(T[z].son[0] == y); 44 if(T[y].son[p] == x) 45 Rotate(x, !p), Rotate(x, p); //之字旋 46 else 47 Rotate(y, p), Rotate(x, p); //一字旋 48 } 49 } 50 if(To == 0) rt=x; 51 } 52 53 int find(int key) //返回值为key的节点 若无返回0 若有将其转移到根处 54 { 55 int x=rt; 56 while(x && T[x].key != key) 57 x=T[x].son[key > T[x].key]; 58 if(x) Splay(x, 0); 59 return x; 60 } 61 62 int prev() //返回比根值小的最大值 若无返回0 若有将其转移到根处 63 { 64 int x=T[rt].son[0]; 65 if(!x) return 0; 66 while(T[x].son[1]) 67 x=T[x].son[1]; 68 Splay(x, 0); 69 return x; 70 } 71 72 int succ() //返回比根值大的最小值 若无返回0 若有将其转移到根处 73 { 74 int x=T[rt].son[1]; 75 if(!x) return 0; 76 while(T[x].son[0]) 77 x=T[x].son[0]; 78 Splay(x, 0); 79 return x; 80 } 81 82 void Insert(int key) //插入key 并且将该节点转移到根处 83 { 84 if(!rt) 85 T[rt = cnt++].set(key, 1, 0); 86 else 87 { 88 int x=rt, y=0; 89 while(x) 90 { 91 y=x; 92 x=T[x].son[key > T[x].key]; 93 } 94 T[x = cnt++].set(key, 1, y); 95 T[y].son[key > T[y].key]=x; 96 Splay(x, 0); 97 } 98 } 99 100 void Delete(int key) //删除值为key的节点 若有重点只删其中一个 x的前驱移动到根处 101 { 102 int x=find(key); 103 if(!x) return; 104 int y=T[x].son[0]; 105 while(T[y].son[1]) 106 y=T[y].son[1]; 107 int z=T[x].son[1]; 108 while(T[z].son[0]) 109 z=T[z].son[0]; 110 if(!y && !z) 111 { 112 rt=0; 113 return; 114 } 115 if(!y) 116 { 117 Splay(z, 0); 118 T[z].son[0]=0; 119 PushUp(z); 120 return; 121 } 122 if(!z) 123 { 124 Splay(y, 0); 125 T[y].son[1]=0; 126 PushUp(y); 127 return; 128 } 129 Splay(y, 0); 130 Splay(z, y); 131 T[z].son[0]=0; 132 PushUp(z); 133 PushUp(y); 134 } 135 136 int GetPth(int p) //获得第p小的节点 并将其转移到根处 137 { 138 if(!rt) return 0; 139 int x=rt, ret=0; 140 while(x) 141 { 142 if(p == T[T[x].son[0]].size+1) 143 break; 144 if(p>T[T[x].son[0]].size+1) 145 { 146 p-=T[T[x].son[0]].size+1; 147 x=T[x].son[1]; 148 } 149 else 150 x=T[x].son[0]; 151 } 152 Splay(x, 0); 153 return x; 154 } 155 156 int GetRank(int key) //获得值<=key的节点个数 并将其转移到根处 若<key只需将<=换为< 157 { 158 if(!rt) return 0; 159 int x=rt, ret=0, y; 160 while(x) 161 { 162 y=x; 163 if(T[x].key <= key) 164 { 165 ret+=T[T[x].son[0]].size+1; 166 x=T[x].son[1]; 167 } 168 else 169 x=T[x].son[0]; 170 } 171 Splay(y, 0); 172 return ret; 173 }
View Code
完全版:(支持相同值,支持区间删除,支持懒惰标记)
1 Struct Tree{ 2 3 int key, num, size, fa, son[2]; 4 5 } 6 7 void PushUp(int x); 8 9 void PushDown(int x); 10 11 int Newnode(int key, int fa); //新建一个节点并返回 12 13 void Rotate(int x, int p); //0左旋 1右旋 14 15 void Splay(int x, int To); //将x节点移动到To的子节点中 16 17 int GetPth(int p, int To); //返回第p小的节点 并移动到To的子节点中 18 19 int Find(int key); //返回值为key的节点 若无返回0 若有将其转移到根处 20 21 int Prev(); //返回根节点的前驱 22 23 int Succ(); //返回根结点的后继 24 25 void Insert(int key); //插入key值 26 27 void Delete(int key); //删除值为key的节点 28 29 int GetRank(int key); //获得值<=key的节点个数 30 31 void Delete(int l, int r); //删除值在[l, r]中的节点
模板:
1 int cnt, rt; 2 int Add[MAXN]; 3 4 struct Tree{ 5 int key, num, size, fa, son[2]; 6 }T[MAXN]; 7 8 inline void PushUp(int x) 9 { 10 T[x].size=T[T[x].son[0]].size+T[T[x].son[1]].size+T[x].num; 11 } 12 13 inline void PushDown(int x) 14 { 15 if(Add[x]) 16 { 17 if(T[x].son[0]) 18 { 19 T[T[x].son[0]].key+=Add[x]; 20 Add[T[x].son[0]]+=Add[x]; 21 } 22 if(T[x].son[1]) 23 { 24 T[T[x].son[1]].key+=Add[x]; 25 Add[T[x].son[1]]+=Add[x]; 26 } 27 Add[x]=0; 28 } 29 } 30 31 inline int Newnode(int key, int fa) //新建一个节点并返回 32 { 33 ++cnt; 34 T[cnt].key=key; 35 T[cnt].num=T[cnt].size=1; 36 T[cnt].fa=fa; 37 T[cnt].son[0]=T[cnt].son[1]=0; 38 return cnt; 39 } 40 41 inline void Rotate(int x, int p) //0左旋 1右旋 42 { 43 int y=T[x].fa; 44 PushDown(y); 45 PushDown(x); 46 T[y].son[!p]=T[x].son[p]; 47 T[T[x].son[p]].fa=y; 48 T[x].fa=T[y].fa; 49 if(T[x].fa) 50 T[T[x].fa].son[T[T[x].fa].son[1] == y]=x; 51 T[x].son[p]=y; 52 T[y].fa=x; 53 PushUp(y); 54 PushUp(x); 55 } 56 57 void Splay(int x, int To) //将x节点移动到To的子节点中 58 { 59 while(T[x].fa != To) 60 { 61 if(T[T[x].fa].fa == To) 62 Rotate(x, T[T[x].fa].son[0] == x); 63 else 64 { 65 int y=T[x].fa, z=T[y].fa; 66 int p=(T[z].son[0] == y); 67 if(T[y].son[p] == x) 68 Rotate(x, !p), Rotate(x, p); //之字旋 69 else 70 Rotate(y, p), Rotate(x, p); //一字旋 71 } 72 } 73 if(To == 0) rt=x; 74 } 75 76 int GetPth(int p, int To) //返回第p小的节点 并移动到To的子节点中 77 { 78 if(!rt || p > T[rt].size) return 0; 79 int x=rt; 80 while(x) 81 { 82 PushDown(x); 83 if(p >= T[T[x].son[0]].size+1 && p <= T[T[x].son[0]].size+T[x].num) 84 break; 85 if(p > T[T[x].son[0]].size+T[x].num) 86 { 87 p-=T[T[x].son[0]].size+T[x].num; 88 x=T[x].son[1]; 89 } 90 else 91 x=T[x].son[0]; 92 } 93 Splay(x, 0); 94 return x; 95 } 96 97 int Find(int key) //返回值为key的节点 若无返回0 若有将其转移到根处 98 { 99 if(!rt) return 0; 100 int x=rt; 101 while(x) 102 { 103 PushDown(x); 104 if(T[x].key == key) break; 105 x=T[x].son[key > T[x].key]; 106 } 107 if(x) Splay(x, 0); 108 return x; 109 } 110 111 int Prev() //返回根节点的前驱 非重点 112 { 113 if(!rt || !T[rt].son[0]) return 0; 114 int x=T[rt].son[0]; 115 while(T[x].son[1]) 116 { 117 PushDown(x); 118 x=T[x].son[1]; 119 } 120 Splay(x, 0); 121 return x; 122 } 123 124 int Succ() //返回根结点的后继 非重点 125 { 126 if(!rt || !T[rt].son[1]) return 0; 127 int x=T[rt].son[1]; 128 while(T[x].son[0]) 129 { 130 PushDown(x); 131 x=T[x].son[0]; 132 } 133 Splay(x, 0); 134 return x; 135 } 136 137 void Insert(int key) //插入key值 138 { 139 if(!rt) 140 rt=Newnode(key, 0); 141 else 142 { 143 int x=rt, y=0; 144 while(x) 145 { 146 PushDown(x); 147 y=x; 148 if(T[x].key == key) 149 { 150 T[x].num++; 151 T[x].size++; 152 break; 153 } 154 T[x].size++; 155 x=T[x].son[key > T[x].key]; 156 } 157 if(!x) 158 x=T[y].son[key > T[y].key]=Newnode(key, y); 159 Splay(x, 0); 160 } 161 } 162 163 void Delete(int key) //删除值为key的节点1个 164 { 165 int x=Find(key); 166 if(!x) return; 167 if(T[x].num>1) 168 { 169 T[x].num--; 170 PushUp(x); 171 return; 172 } 173 int y=T[x].son[0]; 174 while(T[y].son[1]) 175 y=T[y].son[1]; 176 int z=T[x].son[1]; 177 while(T[z].son[0]) 178 z=T[z].son[0]; 179 if(!y && !z) 180 { 181 rt=0; 182 return; 183 } 184 if(!y) 185 { 186 Splay(z, 0); 187 T[z].son[0]=0; 188 PushUp(z); 189 return; 190 } 191 if(!z) 192 { 193 Splay(y, 0); 194 T[y].son[1]=0; 195 PushUp(y); 196 return; 197 } 198 Splay(y, 0); 199 Splay(z, y); 200 T[z].son[0]=0; 201 PushUp(z); 202 PushUp(y); 203 } 204 205 int GetRank(int key) //获得值<=key的节点个数 206 { 207 if(!Find(key)) 208 { 209 Insert(key); 210 int tmp=T[T[rt].son[0]].size; 211 Delete(key); 212 return tmp; 213 } 214 else 215 return T[T[rt].son[0]].size+T[rt].num; 216 } 217 218 void Delete(int l, int r) //删除值在[l, r]中的所有节点 l!=r 219 { 220 if(!Find(l)) Insert(l); 221 int p=Prev(); 222 if(!Find(r)) Insert(r); 223 int q=Succ(); 224 if(!p && !q) 225 { 226 rt=0; 227 return; 228 } 229 if(!p) 230 { 231 T[rt].son[0]=0; 232 PushUp(rt); 233 return; 234 } 235 if(!q) 236 { 237 Splay(p, 0); 238 T[rt].son[1]=0; 239 PushUp(rt); 240 return; 241 } 242 Splay(p, q); 243 T[p].son[1]=0; 244 PushUp(p); 245 PushUp(q); 246 }
View Code
相关题目:HNOI 2002 POJ3481 POJ2352 POJ1442
NOI2004 郁闷的出纳员
II 用于维护序列: (以序列下标为对象维护,相当于对区间操作)(能够完成线段树的操作及其不能完成的操作)
1 Struct Tree{ 2 3 int key, sum, size, fa, son[2]; 4 5 } 6 7 支持操作: 8 9 void PushUp(int x); 10 11 void PushDown(int x); 12 13 int MakeTree(int l, int r, int a[]); //新建一个子树返回根节点 14 15 void Rotate(int x, int p); //0左旋 1右旋 16 17 void Splay(int x, int To); //将x节点移动到To的子节点中 18 19 int Select(int p, int To); //将第p个数移动到To的子节点中 并返回该节点 20 21 int Find(int key); //返回值为key的节点 若无返回0 若有将其转移到根处 22 23 int Prev(); //返回根节点的前驱 24 25 int Succ(); //返回根结点的后继 26 27 void Insert(int p, int l, int r, int a[]) //将a[l .. r]的数插入到下标为p后面 28 29 void Delete(int l, int r); //删除区间[l, r]中的节点 30 31 int Query(int l, int r); //返回[l, r]的和 32 33 待补充。。 34 35 Size Balance Tree 36 37 和上述两种二叉树比起来,SBT可能是最像真正平衡二叉树吧。 38 39 SBT能够保证树的高度在lgn,这样对于插入,删除操作都能够准确保证时间复杂度在O(lgn) 40 41 Maintain操作事实上理解起来也是挺简单的,至于证明参见CQF神牛的 《SBT》
模版:
1 int cnt, rt; 2 3 struct Tree 4 { 5 int key, size, son[2]; 6 }T[MAXN]; 7 8 inline void PushUp(int x) 9 { 10 T[x].size=T[T[x].son[0]].size+T[T[x].son[1]].size+1; 11 } 12 13 inline int Newnode(int key) 14 { 15 ++cnt; 16 T[cnt].key=key; 17 T[cnt].size=1; 18 T[cnt].son[0]=T[cnt].son[1]=0; 19 return cnt; 20 } 21 22 void Rotate(int p, int &x) 23 { 24 int y=T[x].son[!p]; 25 T[x].son[!p]=T[y].son[p]; 26 T[y].son[p]=x; 27 PushUp(x); 28 PushUp(y); 29 x=y; 30 } 31 32 void Maintain(int &x, int p) //维护SBT的!p子树 33 { 34 if(T[T[T[x].son[p]].son[p]].size > T[T[x].son[!p]].size) 35 Rotate(!p, x); 36 else if(T[T[T[x].son[p]].son[!p]].size > T[T[x].son[!p]].size) 37 Rotate(p, T[x].son[p]), Rotate(!p, x); 38 else return; 39 Maintain(T[x].son[0], 0); 40 Maintain(T[x].son[1], 1); 41 Maintain(x, 0); 42 Maintain(x, 1); 43 } 44 45 inline int Prev() //返回比根值小的最大值 若无返回0 46 { 47 int x=T[rt].son[0]; 48 if(!x) return 0; 49 while(T[x].son[1]) 50 x=T[x].son[1]; 51 return x; 52 } 53 54 inline int Succ() //返回比根值大的最小值 若无返回0 55 { 56 int x=T[rt].son[1]; 57 if(!x) return 0; 58 while(T[x].son[0]) 59 x=T[x].son[0]; 60 return x; 61 } 62 63 void Insert(int key, int &x) 64 { 65 if(!x) x=Newnode(key); 66 else 67 { 68 T[x].size++; 69 Insert(key, T[x].son[key > T[x].key]); 70 Maintain(x, key > T[x].key); 71 } 72 } 73 74 bool Delete(int key, int &x) //删除值为key的节点 key可以不存在 75 { 76 if(!x) return 0; 77 if(T[x].key == key) 78 { 79 if(!T[x].son[0]) 80 { 81 x=T[x].son[1]; 82 return 1; 83 } 84 if(!T[x].son[1]) 85 { 86 x=T[x].son[0]; 87 return 1; 88 } 89 int y=Prev(); 90 T[x].size--; 91 return Delete(T[x].key, T[x].son[0]); 92 } 93 else 94 if(Delete(key, T[x].son[key > T[x].key])) 95 { 96 T[x].size--; 97 return 1; 98 } 99 } 100 101 int GetPth(int p, int &x) //返回第p小的节点 102 { 103 if(!x) return 0; 104 if(p == T[T[x].son[0]].size+1) 105 return x; 106 if(p > T[T[x].son[0]].size+1) 107 return GetPth(p-T[T[x].son[0]].size-1, T[x].son[1]); 108 else 109 return GetPth(p, T[x].son[0]); 110 } 111 112 int GetRank(int key, int &x) //找出值<=key的节点个数 113 { 114 if(!x) return 0; 115 if(T[x].key <= key) 116 return T[T[x].son[0]].size+1+GetRank(key, T[x].son[1]); 117 else 118 return GetRank(key, T[x].son[0]); 119 }
View Code
相关题目:POJ 3481
上述题均为用于测试平衡树基本操作的题目。
提高题:
在文章的最后贴上一个二叉树专题训练https://vjudge.net/contest/84416;jsessionid=E73DCD38F70FF141A029A2DB5958B2F1
喜欢的点个赞并订阅我们,我们将会提供最优质的文章供大家学习参考,欢迎大家一起学习QAQ