前提:
1、项目中引入MySQL的JAR包,POM参考如下配置:
<!-- mysql-connector-java --> <!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.38</version> </dependency>
示例:
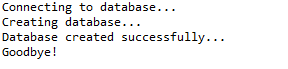
一、创建数据库

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Creating database..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "CREATE DATABASE STUDENTS"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("Database created successfully..."); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException se2) { } // nothing we can do try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
二、选择数据库

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample2 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:

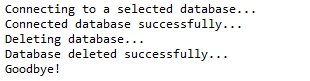
三、删除数据库

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample3 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Deleting database..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "DROP DATABASE STUDENTS"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("Database deleted successfully..."); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
四、创建表

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample4 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Creating table in given database..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "CREATE TABLE REGISTRATION " + "(id INTEGER not NULL, " + " first VARCHAR(255), " + " last VARCHAR(255), " + " age INTEGER, " + " PRIMARY KEY ( id ))"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("Created table in given database..."); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:

五、删除表

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample5 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Deleting table in given database..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "DROP TABLE REGISTRATION "; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("Table deleted in given database..."); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:

六、插入记录

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample6 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Inserting records into the table..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "INSERT INTO Registration " + "VALUES (100, 'Zara', 'Ali', 18)"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); sql = "INSERT INTO Registration " + "VALUES (101, 'Mahnaz', 'Fatma', 25)"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); sql = "INSERT INTO Registration " + "VALUES (102, 'Zaid', 'Khan', 30)"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); sql = "INSERT INTO Registration " + "VALUES(103, 'Sumit', 'Mittal', 28)"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("Inserted records into the table..."); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:

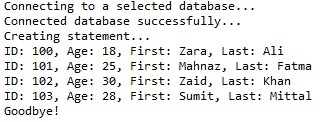
七、查询表记录

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample7 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Creating statement..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration"; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); // STEP 5: Extract data from result set while (rs.next()) { // Retrieve by column name int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); } rs.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
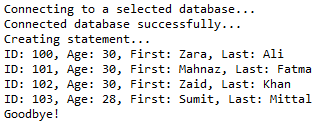
八、更新表记录

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample8 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Creating statement..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "UPDATE Registration " + "SET age = 30 WHERE id in (100, 101)"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // Now you can extract all the records // to see the updated records sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration"; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { // Retrieve by column name int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); } rs.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
九、删除记录

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample9 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Creating statement..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "DELETE FROM Registration " + "WHERE id = 101"; stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // Now you can extract all the records // to see the remaining records sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration"; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { // Retrieve by column name int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); } rs.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
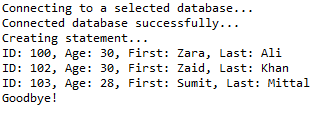
十、Where子句

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample10 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Creating statement..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); // Extract records without any condition. System.out.println("Fetching records without condition..."); String sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration"; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { // Retrieve by column name int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); } // Select all records having ID equal or greater than 101 System.out.println("Fetching records with condition..."); sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration" + " WHERE id >= 101 "; rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { // Retrieve by column name int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); } rs.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
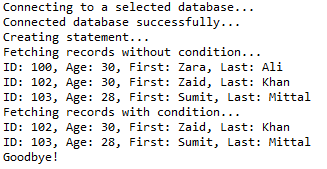
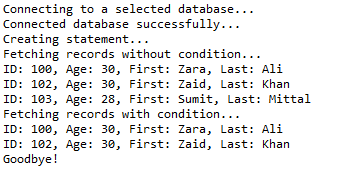
十一、Like子句

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample11 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Creating statement..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); // Extract records without any condition. System.out.println("Fetching records without condition..."); String sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration"; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { // Retrieve by column name int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); } // Select all records having ID equal or greater than 101 System.out.println("Fetching records with condition..."); sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration" + " WHERE first LIKE '%za%' "; rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { // Retrieve by column name int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); } rs.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
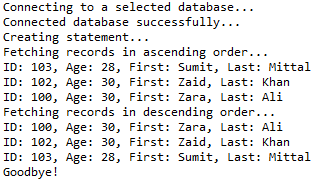
十二、排序

//STEP 1. Import required packages import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample12 { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/STUDENTS?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials static final String USER = "root"; static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // STEP 2: Register JDBC driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection System.out.println("Connecting to a selected database..."); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); System.out.println("Connected database successfully..."); // STEP 4: Execute a query System.out.println("Creating statement..."); stmt = conn.createStatement(); // Extract records in ascending order by first name. System.out.println("Fetching records in ascending order..."); String sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration" + " ORDER BY first ASC"; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { // Retrieve by column name int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); } // Extract records in descending order by first name. System.out.println("Fetching records in descending order..."); sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Registration" + " ORDER BY first DESC"; rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { // Retrieve by column name int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); } rs.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { // Handle errors for JDBC se.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // Handle errors for Class.forName e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // finally block used to close resources try { if (stmt != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { } // do nothing try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } // end finally try } // end try System.out.println("Goodbye!"); }// end main }// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
测试工程:https://github.com/easonjim/5_java_example/tree/master/jdbcbasics/test10/
