Leonid wants to become a glass carver (the person who creates beautiful artworks by cutting the glass). He already has a rectangular w mm × h mm sheet of glass, a diamond glass cutter and lots of enthusiasm. What he lacks is understanding of what to carve and how.
In order not to waste time, he decided to practice the technique of carving. To do this, he makes vertical and horizontal cuts through the entire sheet. This process results in making smaller rectangular fragments of glass. Leonid does not move the newly made glass fragments. In particular, a cut divides each fragment of glass that it goes through into smaller fragments.
After each cut Leonid tries to determine what area the largest of the currently available glass fragments has. Since there appear more and more fragments, this question takes him more and more time and distracts him from the fascinating process.
Leonid offers to divide the labor — he will cut glass, and you will calculate the area of the maximum fragment after each cut. Do you agree?
The first line contains three integers w, h, n (2 ≤ w, h ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000).
Next n lines contain the descriptions of the cuts. Each description has the form H y or V x. In the first case Leonid makes the horizontal cut at the distance y millimeters (1 ≤ y ≤ h - 1) from the lower edge of the original sheet of glass. In the second case Leonid makes a vertical cut at distance x (1 ≤ x ≤ w - 1) millimeters from the left edge of the original sheet of glass. It is guaranteed that Leonid won't make two identical cuts.
After each cut print on a single line the area of the maximum available glass fragment in mm2.
4 3 4
H 2
V 2
V 3
V 1
8
4
4
2
7 6 5
H 4
V 3
V 5
H 2
V 1
28
16
12
6
4
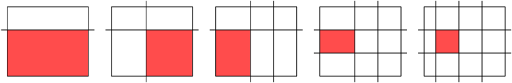
Picture for the first sample test:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <set> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 typedef long long LL; 7 multiset<int> x,y; // 点,可以不定义multiset 8 multiset<int> mx,my; // 边长 9 multiset<int>::iterator iter; 10 11 int main() 12 { 13 int w,h,n; 14 char c; int a; 15 scanf("%d%d%d",&w,&h,&n); 16 x.insert(0); x.insert(w); // 初始化插入起始点与终点 17 y.insert(0); y.insert(h); 18 mx.insert(w); my.insert(h); // 初始化为整条边长的长度 19 while(n--) 20 { 21 cin >> c >> a; 22 if(c=='H') 23 { 24 y.insert(a); // 向存储y坐标的set内插入切割的点 25 iter = y.find(a); // 找到该点 26 iter++; int r = *iter; // 找到该点左右的点,返回其值,其左右点是必然存在的 27 iter--;iter--; int l = *iter; 28 iter = my.find(r-l); // 找到被该点切割的原线段,从set中移除它 29 my.erase(iter); 30 my.insert(a-l); my.insert(r-a); // 将被分割后的两条线段长度插入存储边长的set 31 } 32 else 33 { 34 x.insert(a); 35 iter = x.find(a); 36 iter++; int r = *iter; 37 iter--;iter--; int l = *iter; 38 iter = mx.find(r-l); 39 mx.erase(iter); 40 mx.insert(a-l); mx.insert(r-a); 41 } 42 iter = mx.end(); // 利用set自动排序的性质,找到end前的迭代指针即为最大值 43 int mw = *(--iter); 44 iter = my.end(); 45 int mh = *(--iter); 46 LL ans = (LL)mw*mh; // 数据上限为2e5,相乘int会爆 47 printf("%I64d ",ans); 48 } 49 return 0; 50 }