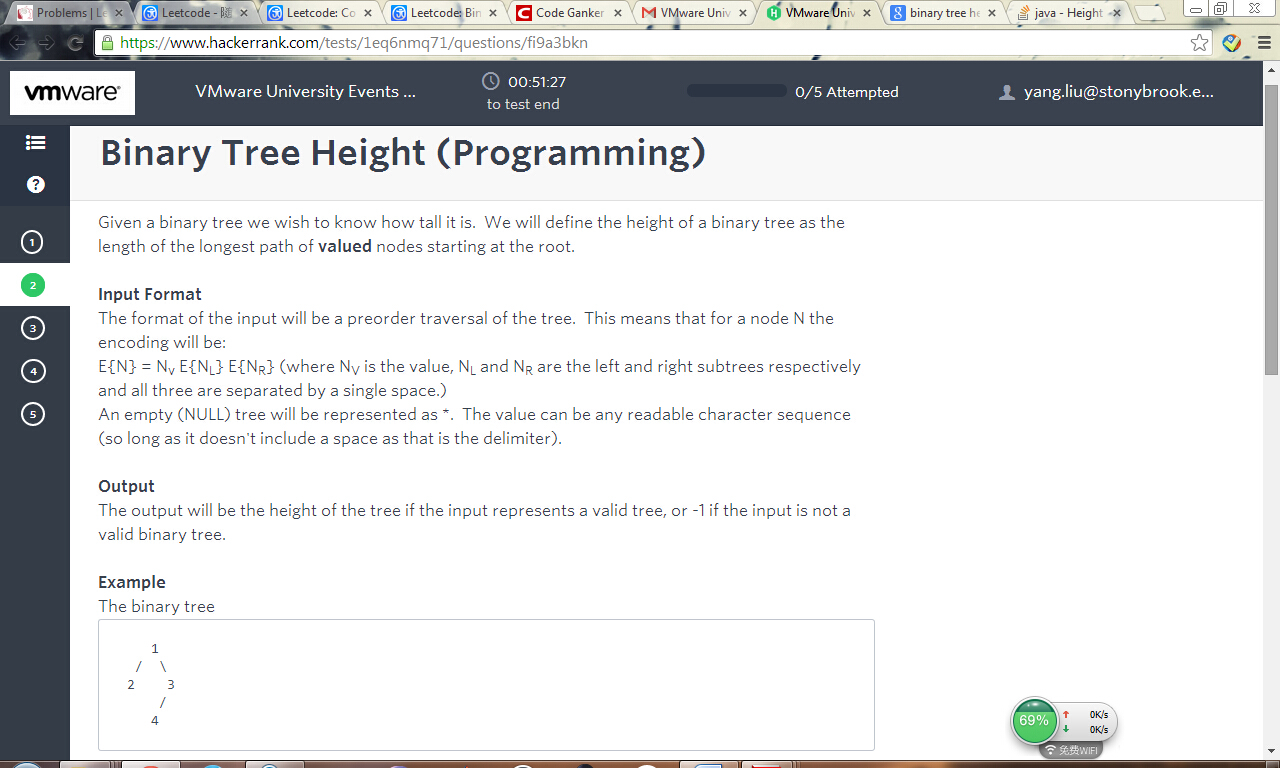
思路:这道题要观察,举个例子,1 2 * * 3 * 4 5 * * 6 7 * 8 * *, 用Stack,先序遍历,遇到数字就入栈,如果遇到 * *,说明栈顶节点是叶子节点,一条根到叶子的路径这时候就存在于栈之中,只要计算栈的size(),就知道当前这条路径的深度,树的height就是这些深度的最大值。
空格的引入增添了不少判断上的麻烦, 比如: ab * *, 这棵树的height是1 而不是2. 在遍历节点的时候需要注意取空格之前的所有元素一起看
第三遍办法:倒序读数组,用stack存。遇到“*”存入0,遇到数字,pop两次,取最大值+1,再push入栈
1 public class Solution5 { 2 public int treeHeight(String preorder) { 3 if (preorder==null || preorder.length()==0) return -1; 4 preorder.trim(); 5 if (preorder.length() == 0) return -1; 6 String[] strs = preorder.split(" "); 7 int len = strs.length; 8 Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<Integer>(); 9 for (int i=len-1; i>=0; i--) { 10 if (strs[i].length() == 0) return -1; // cases that input has two spaces, wrong input 11 if (strs[i].equals("*")) { 12 st.push(0); 13 } 14 else { 15 if (st.size() == 0) return -1; 16 int num1 = st.pop(); 17 if (st.size() == 0) return -1; 18 int num2 = st.pop(); 19 st.push(Math.max(num1, num2) + 1); 20 } 21 } 22 if (st.size() != 1) return -1; 23 return st.peek(); 24 } 25 26 public static void main (String[] args) { 27 Solution5 a = new Solution5(); 28 int ret = a.treeHeight("a b * * *"); 29 System.out.println(ret); 30 } 31 }
第二遍做法:仿效preorder traversal的iterative做法,用Stack, 因为有空格,先split(" "), 这样把它转化为array,且解决了上面ab * *的问题,
但是做OA的时候,大部分case过了,还是有小case过不了
1 public class Solution { 2 public int treeHeight(String preorder) { 3 if (preorder==null || preorder.length()==0) return -1; 4 preorder.trim(); 5 if (preorder.length() == 0) return -1; 6 String[] ar = preorder.split(" "); 7 Stack<String> st = new Stack<String>(); 8 int maxHeight = 0; 9 int curHeight = 0; 10 String root = ar[0]; 11 int i = 0; 12 while (!root.equals("*") || !st.isEmpty()) { 13 if (!root.equals("*")) { // not null 14 st.push(root); 15 curHeight++; // this node's height 16 maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, curHeight); //all time heighest 17 root = ar[++i]; // next node in preorder tranversal 18 } 19 else { 20 st.pop(); 21 if (ar[i-1].equals("*")) curHeight = st.size() + 1; //only a[i]=="*" && a[i-1]=="*", curheight will change 22 root = ar[++i]; 23 } 24 } 25 if (i != ar.length) return -1; // if not reaching the end of the preorder array, then the tree is not valid 26 return maxHeight; 27 } 28 }
第21行比较tricky, 解释如下,如果遇到两个星的情况如**,表示遇到叶子节点了,pop操作之后,下一个节点(假设叫x)一定是某个节点(假设叫y)的第一个右节点,而且节点y已经不在stack里了,刚被pop掉,所以当前curHeight更新为 stack.size()+1, 这个1就是加上节点y的一层