基于 Kafka Version 2.4
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer#partition 这个方法是在执行时分配 Partition 的入口
/**
* computes partition for given record.
* if the record has partition returns the value otherwise
* calls configured partitioner class to compute the partition.
*/
private int partition(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, byte[] serializedKey, byte[] serializedValue, Cluster cluster) {
Integer partition = record.partition();
return partition != null ?
partition :
partitioner.partition(
record.topic(), record.key(), serializedKey, record.value(), serializedValue, cluster);
}
Partition 接口:
//Partitioner 接口
public interface Partitioner extends Configurable, Closeable {
//根据给定的数据,找到 partition
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster);
// 关闭 partition
public void close();
//在批量操作前,可以修改 partition , 默认没有实现
default public void onNewBatch(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
}
}
当前有三个实现类:
DefaultPartitioner 默认的实现类,实现如下:
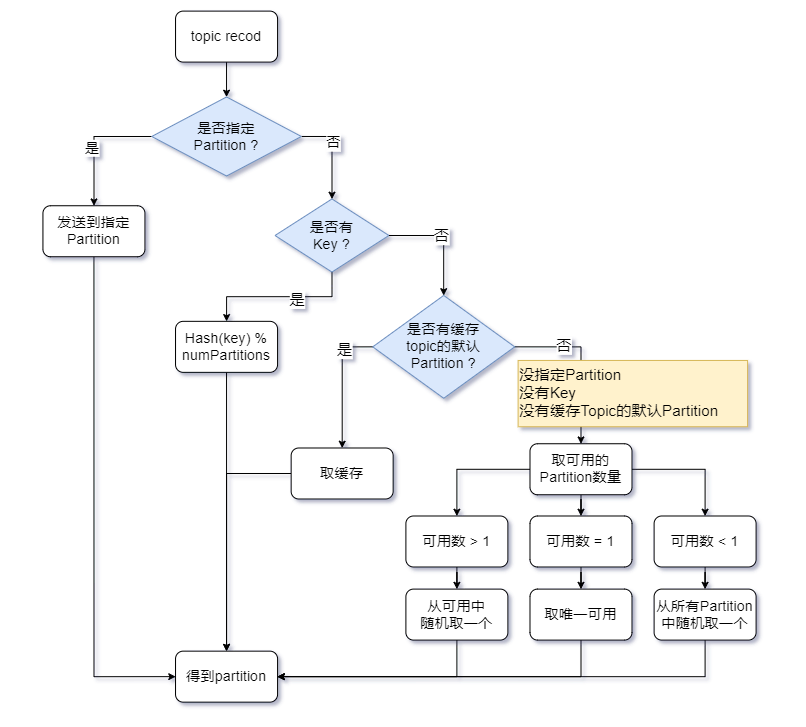
/**
默认的 partition 分配策略
1. record 有指定的,使用指定的
2. key 有值,Hash(key) & numPartitions , 得到 partition
3. 没有可用的,从所有中随机取一个
4. 有可用的,从可用中随机取一个
*/
public class DefaultPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final StickyPartitionCache stickyPartitionCache = new StickyPartitionCache();
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {}
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record
*/
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
if (keyBytes == null) {
return stickyPartitionCache.partition(topic, cluster);
}
List<PartitionInfo> partitions = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
int numPartitions = partitions.size();
// hash the keyBytes to choose a partition
return Utils.toPositive(Utils.murmur2(keyBytes)) % numPartitions;
}
public void close() {}
/**
* If a batch completed for the current sticky partition, change the sticky partition.
* Alternately, if no sticky partition has been determined, set one.
*/
public void onNewBatch(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
stickyPartitionCache.nextPartition(topic, cluster, prevPartition);
}
}
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.StickyPartitionCache Partition 的本地缓存策略。
/**
* An internal class that implements a cache used for sticky partitioning behavior. The cache tracks the current sticky
* partition for any given topic. This class should not be used externally.
*/
public class StickyPartitionCache {
//本地缓存
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Integer> indexCache;
public StickyPartitionCache() {
this.indexCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
public int partition(String topic, Cluster cluster) {
//一个没有 key 的 topic,缓存一次后,永远只往一个 partition 写数据
Integer part = indexCache.get(topic);
if (part == null) {
return nextPartition(topic, cluster, -1);
}
return part;
}
public int nextPartition(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
List<PartitionInfo> partitions = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
Integer oldPart = indexCache.get(topic);
Integer newPart = oldPart;
// Check that the current sticky partition for the topic is either not set or that the partition that
// triggered the new batch matches the sticky partition that needs to be changed.
if (oldPart == null || oldPart == prevPartition) {
//没有缓存,新分配一个
//取所有可用的 Partition
List<PartitionInfo> availablePartitions = cluster.availablePartitionsForTopic(topic);
if (availablePartitions.size() < 1) {
//没有可用的,从所有的里,随机取一个
Integer random = Utils.toPositive(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());
newPart = random % partitions.size();
} else if (availablePartitions.size() == 1) {
//只有一个,直接取了
newPart = availablePartitions.get(0).partition();
} else {
while (newPart == null || newPart.equals(oldPart)) {
//有多个可用的,从中随机取一个
Integer random = Utils.toPositive(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());
newPart = availablePartitions.get(random % availablePartitions.size()).partition();
}
}
// Only change the sticky partition if it is null or prevPartition matches the current sticky partition.
if (oldPart == null) {
//缓存没有的,新放入缓存
indexCache.putIfAbsent(topic, newPart);
} else {
//缓存已有,更新缓存
indexCache.replace(topic, prevPartition, newPart);
}
//最后再从缓存中取出来
return indexCache.get(topic);
}
return indexCache.get(topic);
}
默认实现类 流程图:
RoundRobinPartitioner
/**
* 轮询方式,即均匀分布
* 轮询所有的分区,使 topic 的数据,可以均匀到每个 partition
*/
public class RoundRobinPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, AtomicInteger> topicCounterMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {}
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*/
@Override
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
List<PartitionInfo> partitions = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
int numPartitions = partitions.size();
//从0开始计数
int nextValue = nextValue(topic);
//取所有可用的 partition
List<PartitionInfo> availablePartitions = cluster.availablePartitionsForTopic(topic);
if (!availablePartitions.isEmpty()) {
//有可用的,从中轮询
int part = Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % availablePartitions.size();
return availablePartitions.get(part).partition();
} else {
//没有可用的,从所有的 partition中 轮询
// no partitions are available, give a non-available partition
return Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % numPartitions;
}
}
private int nextValue(String topic) {
//topic 从0开始计数,不关心 key 值
AtomicInteger counter = topicCounterMap.computeIfAbsent(topic, k -> {
return new AtomicInteger(0);
});
return counter.getAndIncrement();
}
public void close() {}
}
UniformStickyPartitioner
/**
与默认实现 类似。
只是不关心 key 的值,没有 hash 操作
*/
public class UniformStickyPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final StickyPartitionCache stickyPartitionCache = new StickyPartitionCache();
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {}
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*/
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
//不关心 key 的值。没有 hash操作
return stickyPartitionCache.partition(topic, cluster);
}
public void close() {}
/**
* If a batch completed for the current sticky partition, change the sticky partition.
* Alternately, if no sticky partition has been determined, set one.
*/
public void onNewBatch(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
stickyPartitionCache.nextPartition(topic, cluster, prevPartition);
}
}
如果文章有帮助到您,请点个赞,您的反馈会让我感到文章是有价值的