一、前言
很久没有更新blog了,太忙了,都没时间来整理一下知识点,年底了有点时间了,可以好好整理以前写的项目代码了,顺便把常用的业务方法都封装成通用的方法,以便以后使用到能快速完成。切入主题,封装了一个常用的多线程使用场景的类库,提供两种模式,跟大家分享。
二、并发模式
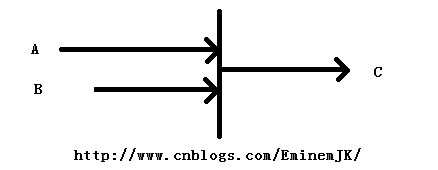
很多时候,我们会遇到这种情况,事件A和事件B毫无关系,是两个很耗时的相对独立事件,但是事件C需要用到事件A、B完成之后的结果。如下图,假设,我们的目的是建造一栋房子,事件A表示去拉砖头,事件B表示去找工人,事件C表示开始建房,
步骤代码片段:
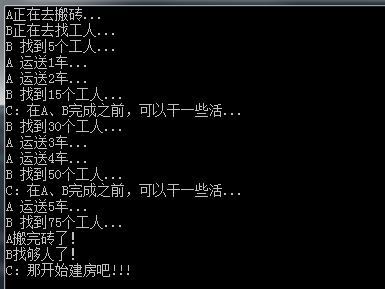
static void Main(string[] args) { ThreadWRR.Init(ThreadWRR.RunningType.Concurrent); ThreadWRR.AddTask(Test1, "A"); ThreadWRR.AddTask(Test2, "B"); //ThreadWRR.AddTask(Test3, null); ThreadWRR.Start(); while (ThreadWRR.IsRunning) { Console.WriteLine("C:在A、B完成之前,可以干一些活..."); } Console.WriteLine("C:那开始建房吧!!!"); Console.ReadKey(); } static void Test1(object s) { Console.WriteLine(s + "正在去搬砖..."); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { Console.WriteLine(s.ToString() +" 运送"+ i+"车..."); Thread.Sleep(500); } Console.WriteLine(s + "搬完砖了!"); } static void Test2(object s) { Console.WriteLine(s + "正在去找工人..."); int ipeople = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { ipeople += i * 5; Console.WriteLine(s.ToString() + " 找到" + ipeople + "个工人..."); Thread.Sleep(500); } Console.WriteLine(s + "找够人了!"); }
二、顺序模式
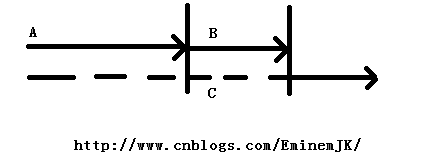
另一种情况,事件B必须等事件A的结果,才能进行下一步任务的进行,C则等待AB都完成之后开始下一步任务,如图,假设,事件A表示组装电脑,事件B表示等A组装好之后进行打包工作,事件C表示装车去配送,C在AB过程中可以做一些事件,比如去拿车,去加油等等,总之do something。
步骤代码片段:
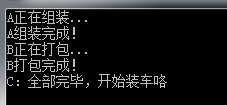
static void Main(string[] args) { ThreadWRR.Init(ThreadWRR.RunningType.Order); ThreadWRR.AddTask(Test1, "A"); ThreadWRR.AddTask(Test2, "B"); //ThreadWRR.AddTask(Test3, null); ThreadWRR.Start(); while (ThreadWRR.IsRunning) { //Console.WriteLine("C:去加油"); } Console.WriteLine("C:全部完毕,开始装车咯"); Console.ReadKey(); } static void Test1(object s) { Console.WriteLine(s + "正在组装..."); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Thread.Sleep(500); } Console.WriteLine(s + "组装完成!"); } static void Test2(object s) { Console.WriteLine(s + "正在打包..."); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Thread.Sleep(500); } Console.WriteLine(s + "打包完成!"); }
咋一看是A组装一台,B打包一台才是,这里不是只有一台电脑而已嘛?!我认为两个事件已经在不同的线程上,需要相关业务逻辑去控制的,应该是我们去控制,不应该影响线程内部,才是符合OOA的开闭原则,当然,开发中比这复杂的业务还很多,不一定能应景。欢迎探讨~~
ThreadWRR类库代码:

public sealed class ThreadWRR { private readonly static object objLock = new object(); private static bool isRunning = false; private static RunningType runningType = RunningType.Order; private static List<Thread> lsThread = null; private static List<MethodParameter> listTask = null; /// <summary> /// 线程是否正在运行 /// </summary> public static bool IsRunning { get { Thread.Sleep(1000); if (runningType == RunningType.Order) { return isRunning; } else { if (lsThread != null && lsThread.Count > 0) { int iFinish = 0; lsThread.ForEach((th) => { if (th.ThreadState == ThreadState.Stopped) { iFinish++; } }); return iFinish != lsThread.Count; } return false; } } } /// <summary> /// 等待所有线程 /// </summary> public static void WaitAllTask() { while (IsRunning) { } } /// <summary> /// 初始化线程 /// </summary> /// <param name="runType">运行方式</param> public static void Init(RunningType runType) { listTask = new List<MethodParameter>(); lsThread = new List<Thread>(); isRunning = false; runningType = runType; } /// <summary> /// 添加运行方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="title"></param> /// <param name="method">方法名</param> /// <param name="parameter">方法参数</param> public static void AddTask(string title, FuncDelegateWithPara method, object parameter) { listTask.Add(new MethodParameter(title, method, parameter)); } /// <summary> /// 添加运行方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="title"></param> /// <param name="method">方法名</param> public static void AddTask(string title, FuncDelegate method) { listTask.Add(new MethodParameter(title, method)); } /// <summary> /// 开始运行 /// </summary> public static void Start() { if (!isRunning) { lock (objLock) { if (!isRunning) { isRunning = true; new Thread(() => { switch (runningType) { case RunningType.Order: OrderTask(); break; case RunningType.Concurrent: ConcurrentTask(); break; } }) { IsBackground = true }.Start(); } } } } private static void OrderTask() { foreach (MethodParameter funcObj in listTask) { IAsyncResult ia = null; if (funcObj.FuncWithPara == null) { ia = BeginInvoke(funcObj.Func); } else { ia = BeginInvoke(funcObj.FuncWithPara,funcObj.Parameter); } while (!ia.IsCompleted) { Thread.Sleep(500); } } isRunning = false; } private static void ConcurrentTask() { foreach (MethodParameter funcObj in listTask) { Thread thread = null; if (funcObj.FuncWithPara == null) { thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(funcObj.Func)) { IsBackground = true }; thread.Start(); } else { thread = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(funcObj.FuncWithPara)) { IsBackground = true }; thread.Start(funcObj.Parameter); } lsThread.Add(thread); } } #region BeginInvoke / Invoke public static void Invoke(FuncDelegate func) { func.Invoke(); } public static void Invoke(FuncDelegateWithPara func, object para) { func.Invoke(para); } public static IAsyncResult BeginInvoke(FuncDelegate func) { return func.BeginInvoke(null, null); } public static IAsyncResult BeginInvoke(FuncDelegateWithPara func, object para) { return func.BeginInvoke(para, null, null); } public static void Invoke(System.Windows.Forms.Control owner, FuncDelegate func) { if (owner.InvokeRequired) { owner.Invoke(func); } else { func(); } } public static void Invoke(System.Windows.Forms.Control owner, FuncDelegateWithPara func, object para) { if (owner.InvokeRequired) { owner.Invoke(func, para); } else { func(para); } } #endregion private class MethodParameter { public FuncDelegate Func = null; public FuncDelegateWithPara FuncWithPara = null; public object Parameter = null; public string title = ""; public MethodParameter(string title, FuncDelegate func) { this.title = title; this.Func = func; } public MethodParameter(string title, FuncDelegateWithPara func, object para) { this.title = title; this.FuncWithPara = func; this.Parameter = para; } } } public delegate void FuncDelegateWithPara(object parameter); public delegate void FuncDelegate(); /// <summary> /// 运行方式 /// </summary> public enum RunningType { /// <summary> /// 顺序运行 /// </summary> Order = 0x01, /// <summary> /// 并发运行 /// </summary> Concurrent = 0x02 }
