目录
1.内联函数(inline)
编译器直接将函数体插入在函数调用的地方
没有普通函数调用时的额外开销(压栈,跳转,返回)
内联函数 由编译器处理;宏代码片段 由预处理器处理
本质:以牺牲代码段空间为代价,提高程序的运行时间的效率。(以空间换时间)
2.占位参数
void fun(int x, int)
{
cout<<"x="<<x<<endl;
}
fun(100,10); //10参数无效
3.函数重载
函数名相同;参数列表不同
4.拷贝构造函数
class Test
{
public:
Test()
{
m_x = 0;
m_y = 0;
}
//显示拷贝构造函数
Test(const Test &t)
{
m_x = t.m_x;
m_y = t.m_y;
}
private:
int m_x;
int m_y;
};
Test t1;
//调用拷贝构造函数
Test t2(t1); //法1
Test t3 = t1; //法2
//t3赋值操作(并不是在t3创建的时候初始化)
//Test t3;
//t3 = t1;
例1
class Test
{
public:
Test()
{
cout << "test()..." << endl;
m_x = 0;
m_y = 0;
}
Test(int x, int y)
{
cout << "Test(int x, int y)..." << endl;
m_x = x;
m_y = y;
}
Test(const Test & another)
{
cout << "Test(const Test &)..." << endl;
m_x = another.m_x;
m_y = another.m_y;
}
void operator=(const Test &another)
{
cout << "operatoer = (const Test &)" << endl;
m_x = another.m_x;
m_y = another.m_y;
}
void printT() {
cout << "x = " << m_x << ", m_y = " << m_y << endl;
}
~Test() {
cout << "~Test()..." << endl;
}
private:
int m_x;
int m_y;
};
void func(Test t)//Test t = t1; //Test t 的拷贝构造函数
{
cout << "func begin..." << endl;
t.printT();
cout << "func end..." << endl;
}
void test3()
{
cout << "test3 begin..." << endl;
Test t1(10, 20);
func(t1);
cout << "test3 end..." << endl;
}

例2
Test func2()
{
cout << "func2 begin..." << endl;
Test temp(10, 20);
temp.printT();
cout << "func2 end..." << endl;
return temp;
}//匿名的对象 = temp 匿名对象.拷贝构造(temp)
void test4()
{
cout << "test4 being.. " << endl;
func2();// 返回一个匿名对象。 当一个函数返回一个匿名对象的时候,函数外部没有任何
//变量去接收它, 这个匿名对象将不会再被使用,(找不到), 编译会直接将个这个匿名对象
//回收掉,而不是等待整改函数执行完毕再回收.
//匿名对象就被回收。
cout << "test4 end" << endl;
}

例3
Test func2()
{
cout << "func2 begin..." << endl;
Test temp(10, 20);
temp.printT();
cout << "func2 end..." << endl;
return temp;
}//匿名的对象 = temp 匿名对象.拷贝构造(temp)
void test5()
{
cout << "test 5begin.. " << endl;
Test t1 = func2(); //会不会触发t1拷贝构造来 t1.拷贝(匿名)?
//并不会触发t1拷贝,而是 将匿名对象转正 t1,
//把这个匿名对象 起了名字就叫t1
cout << "test 5 end.." << endl;
}

例4
void test6()
{
cout << "test6 begin..." << endl;
Test t1; //t1已经初始化了。
t1 = func2(); //t1已经被初始化了,所以func2返回的匿名对象不会再次转正,而依然是匿名对象。
//所以t1会调用等号操作符,t1.operator=(匿名对象), 然后编译器会立刻回收掉匿名对象
t1.printT();
cout << "test6 end.." << endl;
}

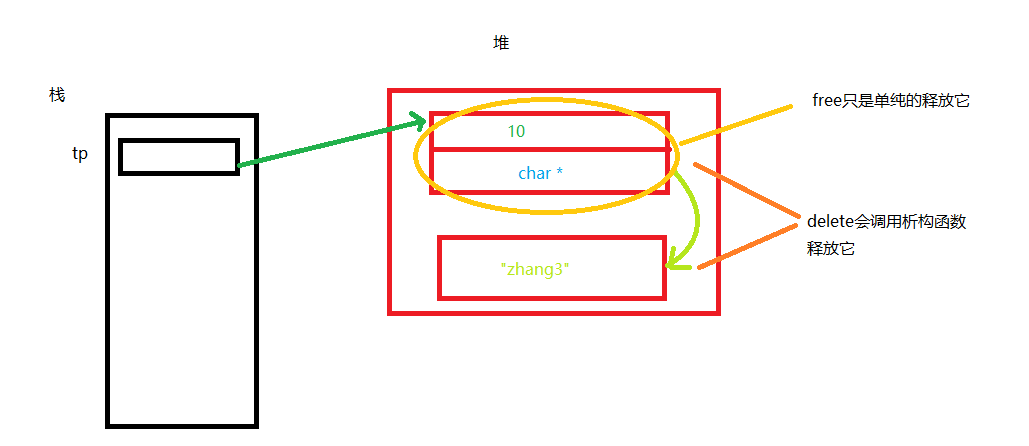
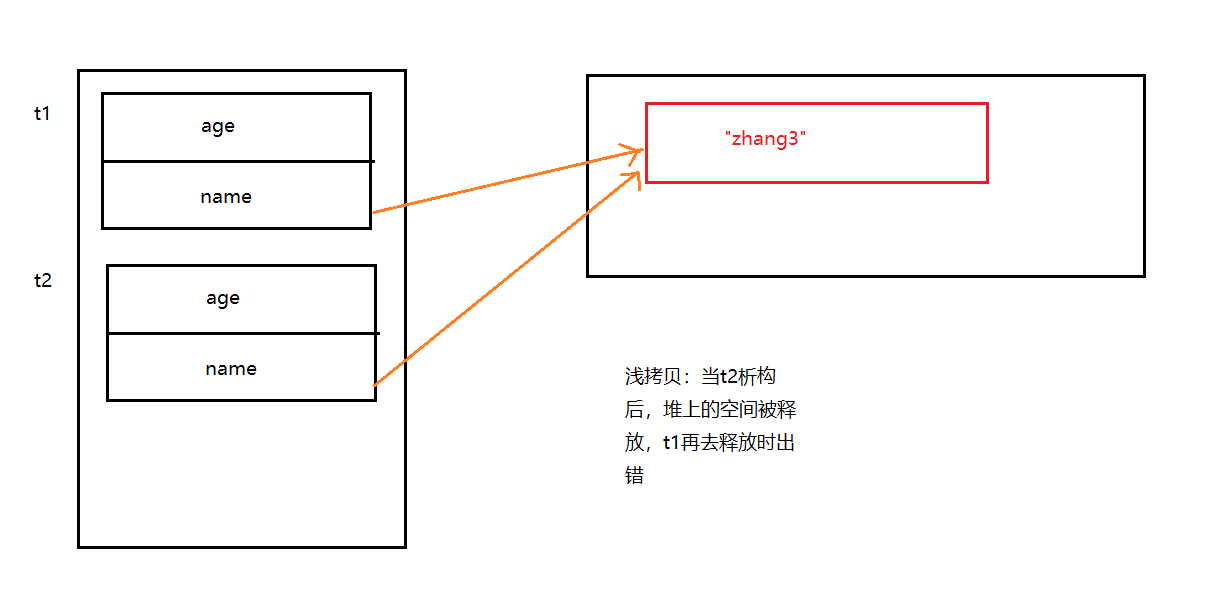
5.类的深拷贝、浅拷贝(同c中结构体)
6.构造函数的初始化列表
1.产生原因:
class A {
public:
A(int a) {
m_a = a;
}
private:
int m_a;
};
class B {
public:
B(int b) {
m_b = b;
}
private:
int m_b;
A obja; //当A的对象 是B类的一个成员 并且 A没有默认构造函数
//在初始化B对象的时候,无法给B 分配空间,因为无法初始化A类对象
//(或者:B中包含const 变量,要用构造函数初始化列表)
};
int main(void)
{
A obja(10);
B objb(20);//error,
return 0;
}
2.
class A
{
public:
A(int a)
{
cout << "A()..."<<a << endl;
m_a = a;
}
~A() {
cout << "~A()" << endl;
}
void printA() {
cout << "a = " << m_a << endl;
}
private:
int m_a;
};
class B
{
public:
//构造函数的初始化列表
B(A a1, A a2, int b) : m_a1(a1), m_a2(a2)
{
cout << "B(A&, A&, int)..." << endl;
m_b = b;
}
//构造对象成员的顺序跟初始化列表的顺序无关
//而是跟成员对象的定义顺序有关(private中)
B(int a1, int a2, int b) : m_a1(a1), m_a2(a2)
{
cout << "B(int, int, int)..." << endl;
m_b = b;
}
void printB() {
cout << "b = " << m_b << endl;
m_a1.printA();
m_a2.printA();
}
~B()
{
cout << "~B().." << endl;
}
private:
int m_b;
A m_a2;
A m_a1;
};
void test1()
{
A a1(10), a2(100);
B b(a1, a2, 1000);
b.printB();
}
3.构造中调⽤用构造是危险的⾏行为
class MyTest
{
public:
MyTest(int a, int b, int c)
{
_a = a;
_b = b;
_c = c;
}
MyTest(int a, int b)
{
_a = a;
_b = b;
MyTest(a, b, 100); //产⽣生新的匿名对象
}
~MyTest()
{
printf("MyTest~:%d, %d, %d
", _a, _b, _c);
}
int getC()
{
return _c;
}
void setC(int val)
{
_c = val;
}
private:
int _a;
int _b;
int _c;
};
int main()
{
MyTest t1(1, 2);
printf("c:%d
", t1.getC()); //请问c的值是?
return 0;
}