1.虚拟地址空间
对每一个运行的进程,操作系统都会为其分配一个0~4G的地址空间
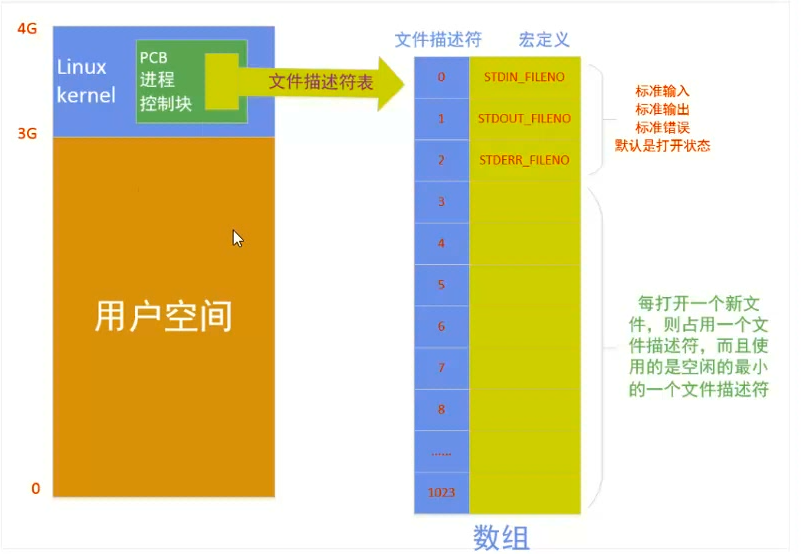
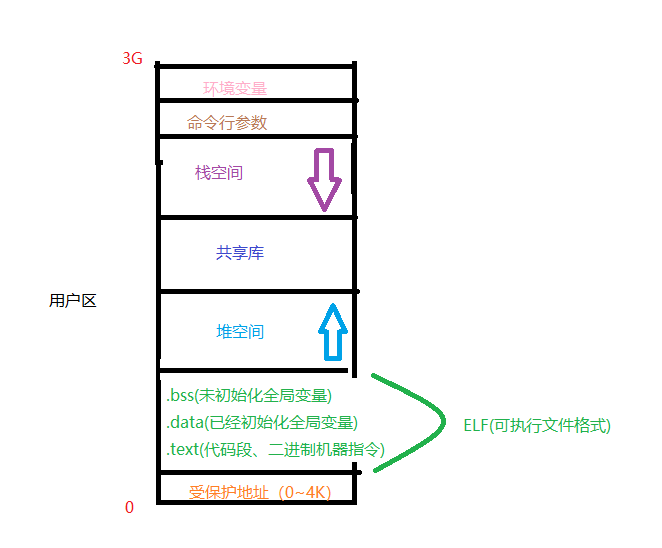
父子进程打印的全局,静态,局部变量值不一样的,但是它们的地址是一样的。所以我们可以确定父进程在fork子进程时,子进程几乎把整个父进程复制了过去(包括0-4G虚拟地址空间)。
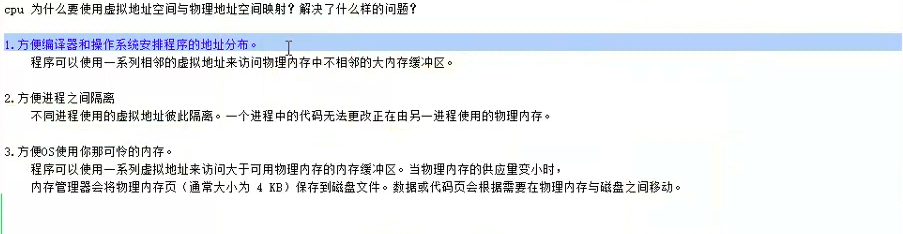
在修改数据时,虽然父子进程的数据的虚拟地址相同,但是虚拟地址实际映射到的物理地址却是不同的。
换句话说,虚拟地址在映射到物理内存的地址时,系统会在物理内存中找一块还没有用,空闲的物理内存,把这个虚拟地址映射到这块空闲的内存的物理地址。
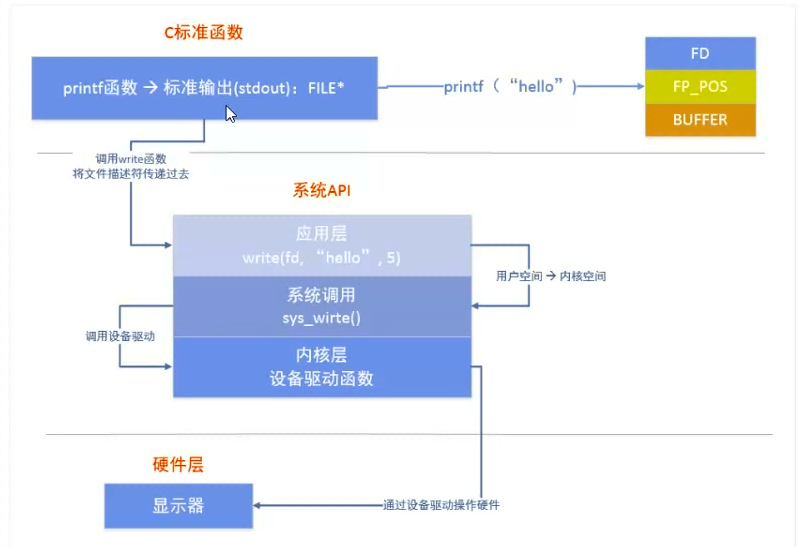
2.C库函数与系统函数关系
```
read write 每次读一个byte
getc putc 每次读一个byte 效率高(C库函数,有缓冲区,不频繁在用户区和内核区之间转换)
```
3.系统函数
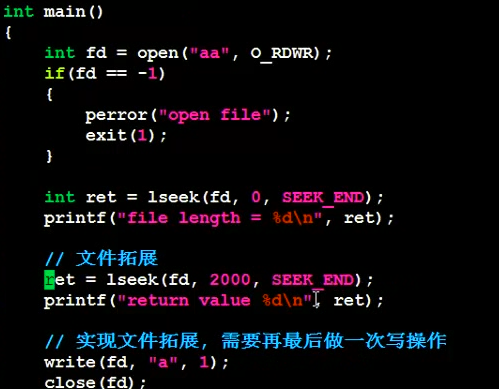
3.1lseek
获取文件大小、文件拓展(空洞文件:迅雷下载文件,刚开始下载就在本地上有相应大小的文件,支持多线程)、重置文件指针
3.2stat
命令
函数
利用 stat 模拟ls -l file
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("./a.out filename
");
exit(1);
}
struct stat st;
int ret = stat(argv[1], &st);
if(ret == -1)
{
perror("stat");
exit(1);
}
// 存储文件类型和访问权限
char perms[11] = {0};
// 判断文件类型
switch(st.st_mode & S_IFMT)
{
case S_IFLNK:
perms[0] = 'l';
break;
case S_IFDIR:
perms[0] = 'd';
break;
case S_IFREG:
perms[0] = '-';
break;
case S_IFBLK:
perms[0] = 'b';
break;
case S_IFCHR:
perms[0] = 'c';
break;
case S_IFSOCK:
perms[0] = 's';
break;
case S_IFIFO:
perms[0] = 'p';
break;
default:
perms[0] = '?';
break;
}
// 判断文件的访问权限
// 文件所有者
perms[1] = (st.st_mode & S_IRUSR) ? 'r' : '-';
perms[2] = (st.st_mode & S_IWUSR) ? 'w' : '-';
perms[3] = (st.st_mode & S_IXUSR) ? 'x' : '-';
// 文件所属组
perms[4] = (st.st_mode & S_IRGRP) ? 'r' : '-';
perms[5] = (st.st_mode & S_IWGRP) ? 'w' : '-';
perms[6] = (st.st_mode & S_IXGRP) ? 'x' : '-';
// 其他人
perms[7] = (st.st_mode & S_IROTH) ? 'r' : '-';
perms[8] = (st.st_mode & S_IWOTH) ? 'w' : '-';
perms[9] = (st.st_mode & S_IXOTH) ? 'x' : '-';
// 硬链接计数
int linkNum = st.st_nlink;
// 文件所有者
char* fileUser = getpwuid(st.st_uid)->pw_name;
// 文件所属组
char* fileGrp = getgrgid(st.st_gid)->gr_name;
// 文件大小
int fileSize = (int)st.st_size;
// 修改时间
char* time = ctime(&st.st_mtime);
char mtime[512] = {0};
strncpy(mtime, time, strlen(time)-1);
char buf[1024];
sprintf(buf, "%s %d %s %s %d %s %s", perms, linkNum, fileUser, fileGrp, fileSize, mtime, argv[1]);
printf("%s
", buf);
return 0;
}
stat函数与lstat函数区别
stat:穿透(最终)函数,利用stat查看软链接大小,实为文件大小
lstat:非穿透函数,利用lstat查看软链接大小则为软链接大小
4.unlink
删除文件(如果是软链接,直接删除;如果是硬链接,硬链接计数减1,当计数为0时,但有进程已经打开该文件,则要等到关闭该文件才会真正删除该文件)
应用场景:
临时创建一个文件,进行独写,当关闭文件后自动删除。
int main()
{
int fd = open("temp",O_CREAT|O_RDWR,777);
int ret = unlink("temp");
write(fd, "hello", 5);
//重置文件指针
lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
char buf[256] = {0};
read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
write(1, buf, sizeof(buf));
return 0;
}
5.opendir、readdir、closedir
统计目录底下的所有文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int get_file_num(char* root)
{
int total = 0;
DIR* dir = NULL;
// 打开目录
dir = opendir(root);
// 循环从目录中读文件
char path[1024];
// 定义记录xiang指针
struct dirent* ptr = NULL;
while( (ptr = readdir(dir)) != NULL)
{
// 跳过. he ..
if(strcmp(ptr->d_name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(ptr->d_name, "..") == 0)
{
continue;
}
// 判断是不是目录
if(ptr->d_type == DT_DIR)
{
sprintf(path, "%s/%s", root, ptr->d_name);
// 递归读目录
total += get_file_num(path);
}
// 如果是普通文件
if(ptr->d_type == DT_REG)
{
total ++;
}
}
closedir(dir);
return total;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("./a.out path");
exit(1);
}
int total = get_file_num(argv[1]);
printf("%s has regfile number: %d
", argv[1], total);
return 0;
}





