思路1 :用一个变量记录属于哪个线程执行,然后另外一个线程阻塞掉即可。
public class main { static volatile int a = 1; public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for(int i = 0 ; i < 26 ; i++){ while(a % 2 == 1){ try { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(a/2); a = a+1; } } }).start(); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for(int i = 0 ; i < 26 ; i++){ while(a % 2 == 0){ try { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println((char)((a/2)+'A')); a = a+1; } } }).start(); } }
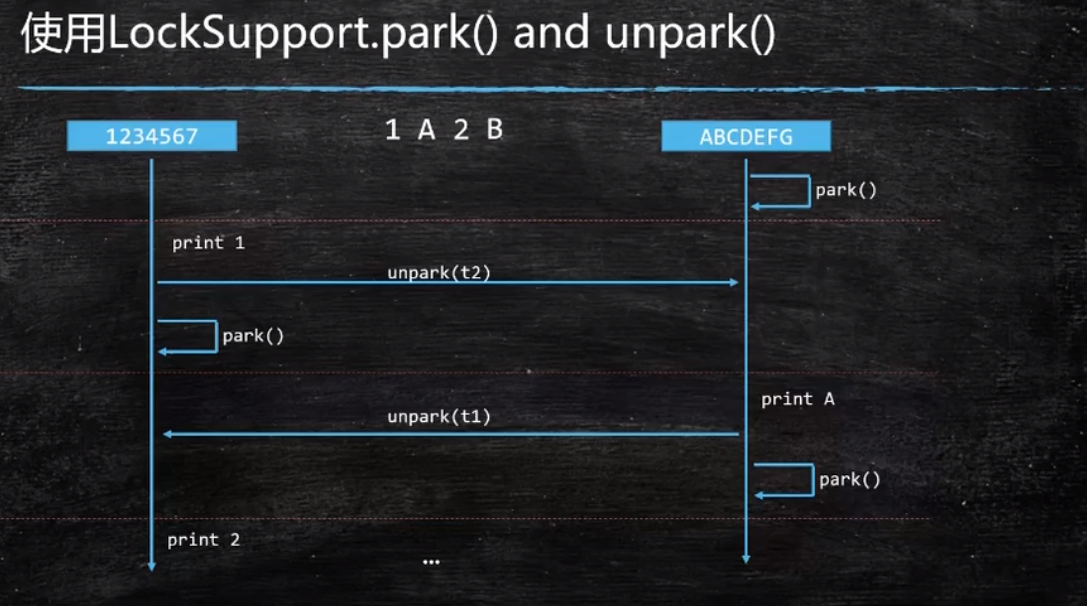
思路2 :使用LockSupport中的unpark和park方法唤醒对方线程并阻塞当前线程。
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport; public class Test_LockSupport { static Thread t1 = null,t2 = null; public static void main(String[] args) { char []aI = "123456789".toCharArray(); char []aC = "ABCDEFJHI".toCharArray(); t1 = new Thread(()->{ for (char c : aI) { System.out.println(c); LockSupport.unpark(t2);//唤醒t2 LockSupport.park();//阻塞t1 } },"t1"); t2 = new Thread(()->{ for (char c : aC) { LockSupport.park();//阻塞t2,等着t1叫醒它 System.out.println(c); LockSupport.unpark(t1);//唤醒t1 } },"t2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
思路3:CAS自旋锁的思路,一个线程while死循环等待。
public class test_cas { enum ReadToRun{T1,T2} static volatile ReadToRun r = ReadToRun.T1; public static void main(String[] args) { char []aI = "123456789".toCharArray(); char []aC = "ABCDEFJHI".toCharArray(); new Thread(()->{ for (char c : aI) { while(r != ReadToRun.T2){ } System.out.println(c); r = ReadToRun.T1; } },"t1").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (char c : aC) { while(r != ReadToRun.T1) { } System.out.println(c); r = ReadToRun.T2; } },"t2").start(); }
思路4:sync锁 wait notify(注意wait notify顺序不能换)
public class test_sync_wait_notify { public static void main(String[] args) { char []aI = "123456789".toCharArray(); char []aC = "ABCDEFJHI".toCharArray(); final Object o = new Object(); new Thread(()->{ synchronized (o){ for (char c : aI) { System.out.println(c); try { o.notify();//叫醒另外一个线程 o.wait();//让出锁 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } o.notify();//必须 否则无法停止程序 } },"t1").start(); new Thread(()->{ synchronized (o){ for (char c : aC) { System.out.println(c); try { o.notify(); o.wait();//让出锁 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } o.notify();//必须 否则无法停止程序 } },"t2").start(); } }
可以用CountDownLatch控制先后。
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; public class test_sync_wait_notify { private static CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);//控制两个线程先后 public static void main(String[] args) { char []aI = "123456789".toCharArray(); char []aC = "ABCDEFJHI".toCharArray(); final Object o = new Object(); new Thread(()->{ try { countDownLatch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (o){ for (char c : aC) { System.out.println(c); try { o.notify();//叫醒另外一个线程 o.wait();//让出锁 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } o.notify();//必须 否则无法停止程序 } },"t1").start(); new Thread(()->{ synchronized (o){ for (char c : aI) { System.out.println(c); countDownLatch.countDown(); try { o.notify(); o.wait();//让出锁 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } o.notify();//必须 否则无法停止程序 } },"t2").start(); } }
思路5:reentrantlock和condition实现。
public class test_Lock_Condition { public static void main(String[] args) { char []aI = "123456789".toCharArray(); char []aC = "ABCDEFJHI".toCharArray(); Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //condition是一个队列,有一个condition就有一个队列,好处是指定哪个队列唤醒 Condition conditionT1 = lock.newCondition(); Condition conditionT2 = lock.newCondition(); new Thread(()->{ try{ lock.lock();//锁住,相当于sync for (char c : aI) { System.out.println(c); conditionT2.signal();//叫醒conditionT2队列的线程 conditionT1.await(); } conditionT2.signal(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } },"t1").start(); new Thread(()->{ try{ lock.lock(); for (char c : aC) { System.out.println(c); conditionT1.signal(); conditionT2.await(); } conditionT1.signal(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } },"t2").start(); } }