1. 基本路由
gin 框架中采用的路由库是基于httprouter做的
1、router:=gin.Default():这是默认的服务器。使用gin的Default方法创建一个路由Handler;
2、然后通过Http方法绑定路由规则和路由函数。不同于net/http库的路由函数,gin进行了封装,把request和response都封装到了gin.Context的上下文环境中。
3、最后启动路由的Run方法监听端口。还可以用http.ListenAndServe(":8080", router),或者自定义Http服务器配置。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
package mainimport ( "net/http" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin")func main() { r := gin.Default() //不带默然中间件的路由 //r := gin.New() //Handle r.Handle("GET", "/", func(context *gin.Context) { }) //直接使用httpMethod r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) { c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello word") }) r.POST("/xxxpost", func(context *gin.Context) { }) r.PUT("/xxxput", func(context *gin.Context) { }) //监听端口默认为8080 r.Run(":8000")} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
//default源码func Default() *Engine { debugPrintWARNINGDefault() engine := New() //不带中间件的路由 engine.Use(Logger(), Recovery()) return engine}//Run源码func (engine *Engine) Run(addr ...string) (err error) { defer func() { debugPrintError(err) }() address := resolveAddress(addr) debugPrint("Listening and serving HTTP on %s
", address) err = http.ListenAndServe(address, engine) //engine就是r := gin.Default() return} |
2. Restful风格的API
-
gin支持Restful风格的API
-
即Representational State Transfer的缩写。直接翻译的意思是"表现层状态转化",是一种互联网应用程序的API设计理念:URL定位资源,用HTTP描述操作
1.获取文章 /blog/getXxx Get blog/Xxx
2.添加 /blog/addXxx POST blog/Xxx
3.修改 /blog/updateXxx PUT blog/Xxx
4.删除 /blog/delXxxx DELETE blog/Xxx
3. API参数
-
可以通过Context的Param方法来获取API参数
-
localhost:8000/xxx/zhangsan
gin的路由来自httprouter库。因此httprouter具有的功能,gin也具有,不过gin不支持路由正则表达式。
冒号:加上一个参数名组成路由参数。可以使用c.Params的方法读取其值。当然这个值是字串string。
除了:gin还提供了*号处理参数,*号能匹配的规则就更多。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
package mainimport ( "net/http" "strings" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin")func main() { r := gin.Default() r.GET("/:name/*action", func(c *gin.Context) { name := c.Param("name") action := c.Param("action") //截取 action = strings.Trim(action, "/") c.String(http.StatusOK, name+" is "+action) }) //路由冲突,abc会被上面的name匹配 //编译不通过 r.GET("/abc/:name/*action", func(c *gin.Context) { name := c.Param("name") action := c.Param("action") //截取 action = strings.Trim(action, "/") c.String(http.StatusOK, name+" == "+action) }) r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) { c.String(200, "are you ok?") }) //默认为监听8080端口 r.Run(":9000")} |

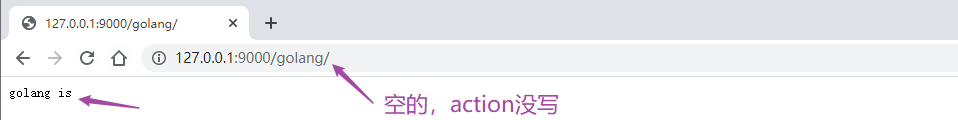
4. URL参数
- URL参数可以通过DefaultQuery()或Query()方法获取
- DefaultQuery()若参数不村则,返回默认值,Query()若不存在,返回空串
web提供的服务通常是client和server的交互。其中客户端向服务器发送请求,除了路由参数,其他的参数无非两种,查询字符串query string和报文体body参数。所谓query string,即路由用,用?以后连接的key1=value2&key2=value2的形式的参数。当然这个key-value是经过urlencode编码。
URL 参数通过 DefaultQuery 或 Query 方法获取。
对于参数的处理,经常会出现参数不存在的情况,对于是否提供默认值,gin也考虑了,并且给出了一个优雅的方案,使用c.DefaultQuery方法读取参数,其中当参数不存在的时候,提供一个默认值。使用Query方法读取正常参数,当参数不存在的时候,返回空字串。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
package mainimport ( "fmt" "net/http" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin")func main() { r := gin.Default() r.GET("/user", func(c *gin.Context) { //指定默认值 //http://localhost:8080/user 才会打印出来默认的值 name := c.DefaultQuery("name", "golang") c.String(http.StatusOK, fmt.Sprintf("hello %s", name)) }) r.Run()} |
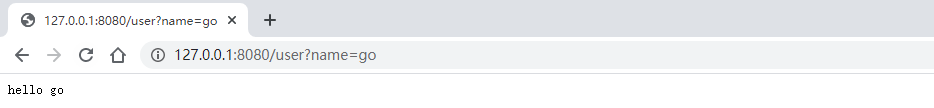
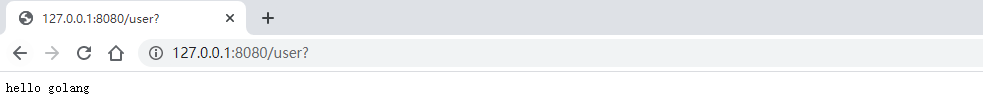
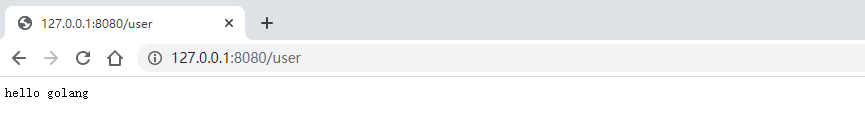
5. 表单参数
- 表单传输为post请求,http常见的传输格式为四种:
- application/json
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- application/xml
- multipart/form-data
- 表单参数可以通过PostForm()方法获取,该方法默认解析的是x-www-form-urlencoded或from-data格式的参数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
package mainimport ( "fmt" "net/http" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin")func main() { r := gin.Default() r.POST("/form", func(c *gin.Context) { //可以设置默然自 types := c.DefaultPostForm("type", "post") username := c.PostForm("username") password := c.PostForm("userpassword") // c.String(http.StatusOK, fmt.Sprintf("username:%s,password:%s,type:%s", username, password, types)) c.String(http.StatusOK, fmt.Sprintf("username:%s,password:%s,type:%s", username, password, types)) }) r.Run()} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title></head><body><form action="http://localhost:8080/form" method="post" action="application/x-www-form-urlencoded"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="请输入你的用户名"> <br> 密 码:<input type="password" name="userpassword" placeholder="请输入你的密码"> <br> <input type="submit" value="提交"></form></body></html> |

6. 上传单个文件
-
multipart/form-data格式用于文件上传
-
gin文件上传与原生的net/http方法类似,不同在于gin把原生的request封装到c.Request中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package mainimport ( "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "net/http")func main() { r := gin.Default() //限制上传最大尺寸 r.MaxMultipartMemory = 8 << 20 //8M r.POST("/upload", func(c *gin.Context) { file, err := c.FormFile("file") if err != nil { c.String(500, "上传图片出错") } /* 也可以直接使用io操作,拷贝文件数据。 out, err := os.Create(filename) defer out.Close() _, err = io.Copy(out, file) */ // c.JSON(200, gin.H{"message": file.Header.Context}) c.SaveUploadedFile(file, file.Filename) c.String(http.StatusOK, file.Filename) }) r.Run()} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title></head><body><form action="http://localhost:8080/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> 上传文件:<input type="file" name="file" > <input type="submit" value="提交"></form></body></html> |

7. 上传多个文件
所谓多个文件,无非就是多一次遍历文件,然后一次copy数据存储即可。
与单个文件上传类似,只不过使用了c.Request.MultipartForm得到文件句柄,再获取文件数据,然后遍历读写。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
package mainimport ( "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "net/http" "fmt")func main() { // 创建路由 // 默认使用了2个中间件Logger(), Recovery() r := gin.Default() // 限制表单上传大小 8MB,默认为32MB r.MaxMultipartMemory = 8 << 20 r.POST("/upload", func(c *gin.Context) { form, err := c.MultipartForm() if err != nil { c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, fmt.Sprintf("get err %s", err.Error())) } // 获取所有图片 files := form.File["files"] // 遍历所有图片 for _, file := range files { // 逐个存 if err := c.SaveUploadedFile(file, file.Filename); err != nil { c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, fmt.Sprintf("upload err %s", err.Error())) return } } c.String(200, fmt.Sprintf("upload ok %d files", len(files))) }) //默认端口号是8080 r.Run(":8000")} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title></head><body><form action="http://localhost:8000/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> 上传文件:<input type="file" name="files" multiple> <input type="submit" value="提交"></form></body></html> |

8. 路由组
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
package mainimport ( "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "fmt")// gin的helloWorldfunc main() { // 创建路由 // 默认使用了2个中间件Logger(), Recovery() r := gin.Default() // 路由组1 ,处理GET请求 v1 := r.Group("/v1") // {} 是书写规范 { v1.GET("/login", login) v1.GET("submit", submit) } v2 := r.Group("/v2") { v2.POST("/login", login) v2.POST("/submit", submit) } r.Run(":8000")}func login(c *gin.Context) { name := c.DefaultQuery("name", "jack") c.String(200, fmt.Sprintf("hello %s
", name))}func submit(c *gin.Context) { name := c.DefaultQuery("name", "lily") c.String(200, fmt.Sprintf("hello %s
", name))} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
func main() { r := gin.Default() userGroup := r.Group("/user") { userGroup.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) userGroup.GET("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) userGroup.POST("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) } shopGroup := r.Group("/shop") { shopGroup.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) shopGroup.GET("/cart", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) shopGroup.POST("/checkout", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) } r.Run()} |
路由组也是支持嵌套的,例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
shopGroup := r.Group("/shop") { shopGroup.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) shopGroup.GET("/cart", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) shopGroup.POST("/checkout", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) // 嵌套路由组 xx := shopGroup.Group("xx") xx.GET("/oo", func(c *gin.Context) {...}) } |
9. 重定向
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package mainimport "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"func main() { //请求重定向 r := gin.Default() r.GET("/index", func(context *gin.Context) { /*301: 永久重定向 常用的例如域名跳转:http:**** => https:**** 302: 临时重定向 需要向服务端请求是否过期,过期返回新数据,没过期返回状态吗302,然后客户端重定向, 期间差别主要在于数据包的大小(没有过期的情况下,不需要再在数据包中附加数据返回,从而加速网络传输,提升速度)*/ context.Redirect(301, "https://www.bilibili.com/") }) //路由重定向 r.GET("/a", func(context *gin.Context) { context.Request.URL.Path = "/b" r.HandleContext(context) }) r.GET("/b", func(context *gin.Context) { context.String(200, "are you ok?") }) r.Run()} |