装饰模式
修饰模式(装饰模式),是面向对象编程领域中,一种动态地往一个类中添加新的行为的设计模式。就功能而言,修饰模式相比生成子类更为灵活,这样可以给某个对象而不是整个类添加一些功能。
装饰模式的UML如下所示:
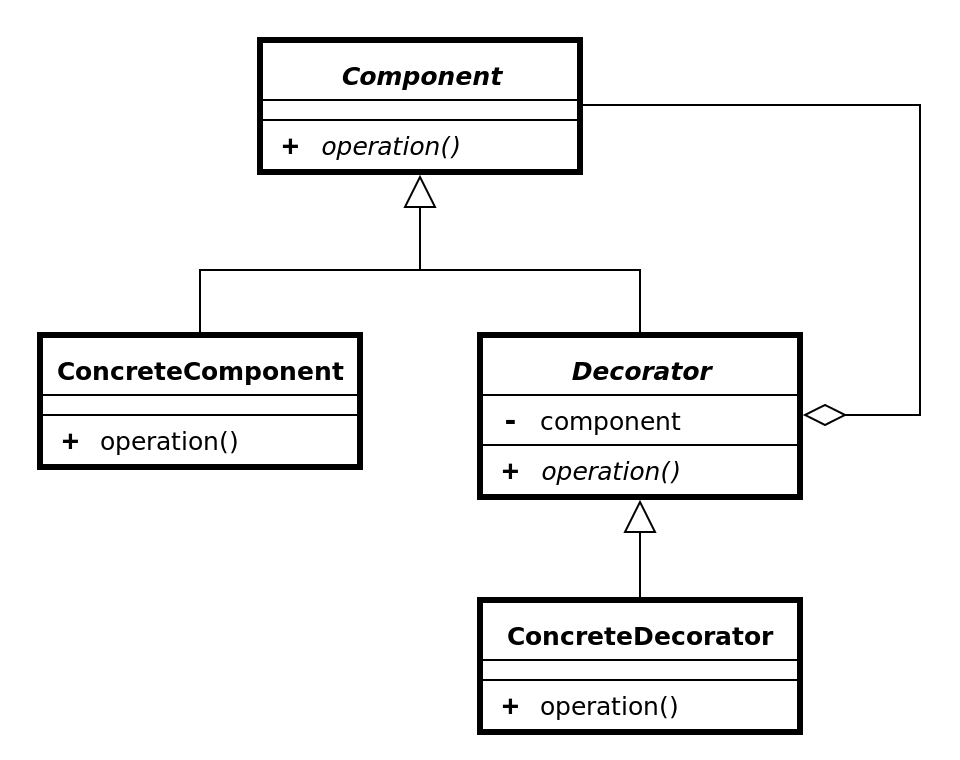
装饰模式中有四个角色:
- Component 抽象构件,最基本、最核心、最原始的接口或抽象类
- ConcreteComponent 具体构件的引用
- Decorator 装饰角色, 持有对构件的引用
- ConcreteDecorator 具体装饰角色
Java IO中的装饰模式
Java IO流就是装饰模式的典型应用。
与装饰模式中角色对应的类如下:
- Component:
InputStream,OutputStream - ConcreteComponent:
FileInputStream,PipeInputStream,ByteArrayInputStream... - Decorator:
FilterInputStream,FilterOutputStream - ConcreteDecorator:
DataInputStream,BufferedInputStream,LineNumberInputStream...
FilterInputStream和FilterOutputStream做的事情很简单,只是持有了一个Stream的引用并做了代理:
package java.io;
public
class FilterInputStream extends InputStream {
protected volatile InputStream in;
protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read();
}
//...省略掉一些方法
}
BufferedInputStream
来看下BufferedInputStream的代码(当然只是一部分):
package java.io;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater;
public
class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;
protected volatile byte buf[];
protected int count;
protected int pos;
protected int markpos = -1;
protected int marklimit;
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {
super(in);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
private void fill() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = getBufIfOpen();
if (markpos < 0)
pos = 0; /* no mark: throw away the buffer */
else if (pos >= buffer.length) /* no room left in buffer */
if (markpos > 0) { /* can throw away early part of the buffer */
int sz = pos - markpos;
System.arraycopy(buffer, markpos, buffer, 0, sz);
pos = sz;
markpos = 0;
} else if (buffer.length >= marklimit) {
markpos = -1; /* buffer got too big, invalidate mark */
pos = 0; /* drop buffer contents */
} else if (buffer.length >= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE) {
throw new OutOfMemoryError("Required array size too large");
} else { /* grow buffer */
int nsz = (pos <= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - pos) ?
pos * 2 : MAX_BUFFER_SIZE;
if (nsz > marklimit)
nsz = marklimit;
byte nbuf[] = new byte[nsz];
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, nbuf, 0, pos);
if (!bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, nbuf)) {
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
buffer = nbuf;
}
count = pos;
int n = getInIfOpen().read(buffer, pos, buffer.length - pos);
if (n > 0)
count = n + pos;
}
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
if (pos >= count) {
fill();
if (pos >= count)
return -1;
}
return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;
}
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len)
throws IOException
{
getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed stream
if ((off | len | (off + len) | (b.length - (off + len))) < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = 0;
for (;;) {
int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n);
if (nread <= 0)
return (n == 0) ? nread : n;
n += nread;
if (n >= len)
return n;
// if not closed but no bytes available, return
InputStream input = in;
if (input != null && input.available() <= 0)
return n;
}
}
}
BufferedInputStream中有一个byte数组作为缓存,存放从制定的InputStream中读出的字节;- 它的read放回会先查看buf数组中是否还有可读的字节,如果没有就先调用一次
fill()方法从指定的stream中读取字节到buf数组中(或者直接去stream中读取足够的字节,再调用fill()方法); BufferedInputStream支持mark,fill()方法会在buf中保留markpos到pos的这个区间内(包括markpos,不包括pos)的字节,当然前提是markpos有效;- 当markpos为0,buf数组中没有空间,buf数组的长度小于等于pos并小于 marklimit和MAX_BUFFER_SIZE,buf将被一个长度为 marklimit、MAX_BUFFER_SIZE和 2 * p中较小值的数组代替(原数组中的字节会被拷贝)。
关于mark的问题
BufferedInputStream的mark()方法是这样的:
/**
* See the general contract of the <code>mark</code>
* method of <code>InputStream</code>.
*
* @param readlimit the maximum limit of bytes that can be read before
* the mark position becomes invalid.
* @see java.io.BufferedInputStream#reset()
*/
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {
marklimit = readlimit;
markpos = pos;
}
按照doc的意思,markpos应该在读取的字节数超过了readlimit的时候就应该失效。
但是实际上,只有fill方法中的这一段代码让markpos失效了:
if (buffer.length >= marklimit) {
markpos = -1; /* buffer got too big, invalidate mark */
pos = 0; /* drop buffer contents */
}
也就是说,如果marklimit小于buf数组长度,markpos是不会失效的:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[]{0, 1, 2, 3};
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
BufferedInputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in);
//如果制定了size为1,这段代码将会报错
//BufferedInputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in, 1);
bin.mark(1);
bin.read();
bin.read();
bin.reset();
}
当然,之前也有提到,如果markpos为0, buf是有可能扩容的。
参考资料
JDK8源码
《设计模式之禅》第二版
修饰模式