未涉及虚拟机
引子
记得上次中秋一哥们写个需求,没写完。他中秋过后还请一天假,有点错,打电话叫我帮他继续搞。
由于测试支撑,叫到我加班了。第二天过来看,打开页面直接报错,再次点击报错就不一样了。前次报错是有代码行的,第二次直接页面说类发现什么的错。
看了下代码,类似如下:
1 package san; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.util.logging.Level; 5 import java.util.logging.Logger; 6 7 import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext; 8 import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement; 9 import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement; 10 11 //每个类有一个Log4j的静态日志成员 12 //这里是单例 13 public class ClassWithStatic { 14 private static ClassWithStatic instance = new ClassWithStatic(); 15 private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(ClassWithStatic.class.getName()); 16 17 private ClassWithStatic() { 18 JAXBContext jc; 19 try { 20 //do something that maybe throw IOExption; 21 throw new FileNotFoundException(); 22 } catch (Exception e) { 23 logger.log(Level.ALL, "xxx", e); 24 } 25 } 26 27 /** 28 * @return the instance 29 */ 30 public static ClassWithStatic getInstance() { 31 return instance; 32 } 33 34 public void doSomeThing() { 35 System.out.println("doSomeThing"); 36 } 37 38 public static void main(String[] args) { 39 ClassWithStatic.getInstance().doSomeThing(); 40 } 41 } 42 43 @XmlRootElement(name = "Scenes") 44 class Scenes{ 45 @XmlElement(name = "id", required = true) 46 protected String id; 47 48 /** 49 * @return the id 50 */ 51 public String getId() { 52 return id; 53 } 54 55 /** 56 * @param id the id to set 57 */ 58 public void setId(String id) { 59 this.id = id; 60 } 61 62 }
报错
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
Caused by: java.lang.NullPointerException
at san.ClassWithStatic.<init>(ClassWithStatic.java:21)
at san.ClassWithStatic.<clinit>(ClassWithStatic.java:12)
这是和静态成员初始化顺序有关。
基础知识如下:
Java代码中一个类初始化顺序:static变量 -- 其他成员变量 -- 构造函数 三者的调用先后顺序:
初始化父类Static --> 子类的Static (如果是类实例化,接下来还会: 初始化父类的其他成员变量->父类构造方法->子类其他成员变量->子类的构造方法)。
系统默认值的给予比通过等号的赋予先执行。
一个类中的static变量或成员变量的初始化顺序,是按照声明的顺序初始化的。
测试类
1 public class ClassWithStatic extends Super{ 2 private static int iTest0 = 0; 3 private static ClassWithStatic instance = new ClassWithStatic(); 4 private static int iTest1; 5 private static int iTest2 = 0; 6 static { 7 System.out.println(ClassWithStatic.class.getName() + " : static{}"); 8 iTest0++; 9 iTest1++; 10 iTest2++; 11 } 12 13 public ClassWithStatic() { 14 System.out.println(this.getClass().getName() + " : Constuctor."); 15 iTest0++; 16 iTest1++; 17 iTest2++; 18 } 19 20 /** 21 * @return the instance 22 */ 23 public static ClassWithStatic getInstance() { 24 return instance; 25 } 26 27 public void doSomeThing() { 28 System.out.println("iTest0 = " + iTest0); 29 System.out.println("iTest1 = " + iTest1); 30 System.out.println("iTest2 = " + iTest2); 31 } 32 33 public static void main(String[] args) { 34 //private static void main(String[] args) 35 //Error: Main method not found in class san.ClassWithStatic, please define the main method as: 36 // public static void main(String[] args) 37 // or a JavaFX application class must extend javafx.application.Application 38 System.out.println("public static void main(String[] args)"); 39 ClassWithStatic.getInstance().doSomeThing(); 40 41 } 42 } 43 44 class Super { 45 private static Super instance = new Super(); 46 private static int iTest1; 47 private int iTest2 = 0; 48 static { 49 System.out.println(Super.class.getName() + " : static{}"); 50 iTest1++; 51 } 52 53 public Super() { 54 System.out.println(this.getClass().getName() + " : Constuctor."); 55 iTest2++; 56 } 57 }
结果:
san.Super : Constuctor.
san.Super : static{}
san.ClassWithStatic : Constuctor.
san.ClassWithStatic : Constuctor.
san.ClassWithStatic : static{}
public static void main(String[] args)
iTest0 = 2
iTest1 = 2
iTest2 = 1
这里两遍子类构造,为了区分,改一下构造函数里的打印语句代码。
1 public class ClassWithStatic extends Super{ 2 private static int iTest0 = 0; 3 private static ClassWithStatic instance = new ClassWithStatic(); 4 private static int iTest1; 5 private static int iTest2 = 0; 6 static { 7 System.out.println(ClassWithStatic.class.getName() + " : static{}"); 8 iTest0++; 9 iTest1++; 10 iTest2++; 11 } 12 13 public ClassWithStatic() { 14 System.out.println(ClassWithStatic.class.getName() + " : Constuctor with this = " + this); 15 iTest0++; 16 iTest1++; 17 iTest2++; 18 } 19 20 /** 21 * @return the instance 22 */ 23 public static ClassWithStatic getInstance() { 24 return instance; 25 } 26 27 public void doSomeThing() { 28 System.out.println("iTest0 = " + iTest0); 29 System.out.println("iTest1 = " + iTest1); 30 System.out.println("iTest2 = " + iTest2); 31 } 32 33 public static void main(String[] args) { 34 //private static void main(String[] args) 35 //Error: Main method not found in class san.ClassWithStatic, please define the main method as: 36 // public static void main(String[] args) 37 // or a JavaFX application class must extend javafx.application.Application 38 System.out.println("public static void main(String[] args)"); 39 ClassWithStatic.getInstance().doSomeThing(); 40 41 } 42 } 43 44 class Super { 45 private static Super instance = new Super(); 46 private static int iTest1; 47 private int iTest2 = 0; 48 static { 49 System.out.println(Super.class.getName() + " : static{}"); 50 iTest1++; 51 } 52 53 public Super() { 54 System.out.println(Super.class.getName() + " : Constuctor with this = " + this); 55 iTest2++; 56 } 57 }
结果:
san.Super : Constuctor with this = san.Super@15db9742
san.Super : static{}
san.Super : Constuctor with this = san.ClassWithStatic@6d06d69c
san.ClassWithStatic : Constuctor with this = san.ClassWithStatic@6d06d69c
san.ClassWithStatic : static{}
public static void main(String[] args)
iTest0 = 2
iTest1 = 2
iTest2 = 1
public class ClassWithStatic extends Super { protected static int iTest0 = Super.iTest0 + 1; private static ClassWithStatic instance = new ClassWithStatic(); protected static int iTest1; private static int iTest2 = 0; static { System.out.println(ClassWithStatic.class.getName() + " : static{}"); iTest1++; iTest2++; } public ClassWithStatic() { System.out.println(ClassWithStatic.class.getName() + " : Constuctor with this = " + this); iTest1++; iTest2++; } /** * @return the instance */ public static ClassWithStatic getInstance() { return instance; } public void doSomeThing() { System.out.println("ClassWithStatic.iTest0 = " + iTest0); System.out.println("ClassWithStatic.iTest1 = " + iTest1); System.out.println("ClassWithStatic.iTest2 = " + iTest2); } public static void main(String[] args) { //private static void main(String[] args) //Error: Main method not found in class san.ClassWithStatic, please define the main method as: // public static void main(String[] args) // or a JavaFX application class must extend javafx.application.Application System.out.println("public static void main(String[] args)"); ClassWithStatic.getInstance().doSomeThing(); System.out.println("Super.iTest0 = " + Super.iTest0); System.out.println(Const.constanceString);//对类的静态变量进行读取、赋值操作的。static,final且值确定是常量,是编译时确定的,调用的时候直接用,不会加载对应的类 System.out.println("------------------------"); Const.doStaticSomeThing(); } } class Super { protected static int iTest0; private static Super instance = new Super(); protected static int iTest1 = 0; static { System.out.println(Super.class.getName() + " : static{}"); iTest0 = ClassWithStatic.iTest0 + 1;//1 } public Super() { System.out.println(Super.class.getName() + " : Constuctor with this = " + this + ", iTest0 = " + iTest0); iTest1++; } } class Const { public static final String constanceString = "Const.constanceString"; static { System.out.println(Const.class.getName() + " : static{}"); } public static void doStaticSomeThing() { System.out.println(Const.class.getName() + " : doStaticSomeThing();"); } }
san.Super : Constuctor with this = san.Super@15db9742, iTest0 = 0
san.Super : static{}
san.Super : Constuctor with this = san.ClassWithStatic@6d06d69c, iTest0 = 1
san.ClassWithStatic : Constuctor with this = san.ClassWithStatic@6d06d69c
san.ClassWithStatic : static{}
public static void main(String[] args)
ClassWithStatic.iTest0 = 2
ClassWithStatic.iTest1 = 2
ClassWithStatic.iTest2 = 1
Super.iTest0 = 1
Const.constanceString
------------------------
san.Const : static{}
san.Const : doStaticSomeThing();
0、<init>与<clinit>的区别
其实:
在编译生成class文件时,会自动产生两个方法,一个是类的初始化方法<clinit>, 另一个是实例的初始化方法<init>
<clinit>:在jvm第一次加载class文件时调用,包括静态变量初始化语句和静态块的执行
<init>:在实例创建出来的时候调用,包括调用new操作符;调用Class或java.lang.reflect.Constructor对象的newInstance()方法;调用任何现有对象的clone()方法;通过java.io.ObjectInputStream类的getObject()方法反序列化。
简要说明下final、static、static final修饰的字段赋值的区别:
- static修饰的字段在类加载过程中的准备阶段被初始化为0或null等默认值,而后在初始化阶段(触发类构造器<clinit>)才会被赋予代码中设定的值,如果没有设定值,那么它的值就为默认值。
- final修饰的字段在运行时被初始化(可以直接赋值,也可以在实例构造器中赋值),一旦赋值便不可更改;
- static final修饰的字段在Javac时生成ConstantValue属性,在类加载的准备阶段根据ConstantValue的值为该字段赋值,它没有默认值,必须显式地赋值,否则Javac时会报错。可以理解为在编译期即把结果放入了常量池中。
1、类的加载过程
类加载的时机就很简单了:在用到的时候就加载(和系统内存管理差不多,一个进程都是写时复制CopyOnWrite)。下来看一下类加载的过程:
加载->验证->准备->解析->初始化->使用->卸载
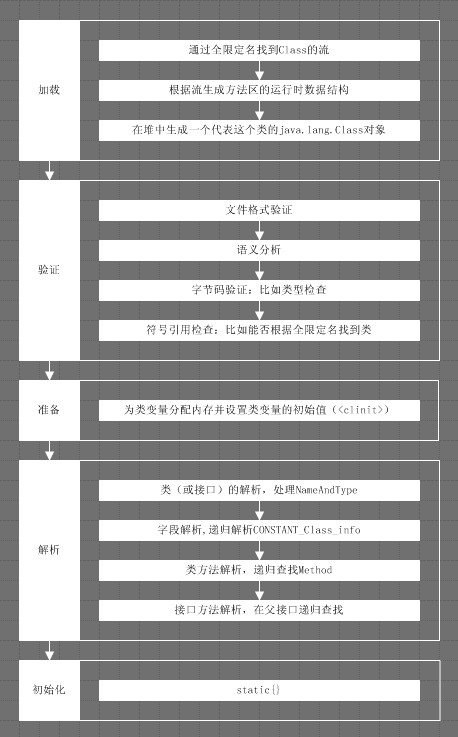
所有的Java虚拟机实现必须在每个类或接口被Java程序 “首次主动使用”时才初始化他们。
有必要提一点的是:准备和初始化
准备
准备阶段是正式为类变量分配内存并设置类变量初始值的阶段,这些内存都将在方法区中分配。对于该阶段有以下几点需要注意:
1、这时候进行内存分配的仅包括类变量(static),而不包括实例变量,实例变量会在对象实例化时随着对象一块分配在Java堆中。
2、这里所设置的初始值通常情况下是数据类型默认的零值(如0、0L、null、false等),而不是被在Java代码中被显式地赋予的值。
假设一个类变量的定义为:
public static int value = 3;
那么变量value在准备阶段过后的初始值为0,而不是3,因为这时候尚未开始执行任何Java方法,而把value赋值为3的putstatic指令是在程序编译后,存放于类构造器<clinit>()方法之中的,所以把value赋值为3的动作将在初始化阶段才会执行。
详细查看:【深入Java虚拟机】之四:类加载机制 http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/17881581
2、类的使用方式
Java 程序对类的使用方式可分为两种 :
主动 |
创建类的实例 |
遇到 |
Test a = new Test(); |
访问某个类或接口的非编译期静态变量, |
读写某个类的静态变量 |
||
调用类的静态方法 |
调用某个类的静态方法 Test.doSomething(); |
||
反射 |
Class.forName("xxxx")
|
||
初始化一个类的子类(不是对父类的主动使用就初始化子类, |
Child.class、Parent.class,初始化Child时, |
||
Java虚拟机启动时被标明为启动类的类 |
就是main方法那个所在类 |
||
被动 |
除了以上六种情况,其他使用Java类的方式都被看作是对 |
||
•主动使用(六种)
– 创建类的实例 -------Test a = new Test();
– 访问某个类或接口的非编译期静态变量,或者对该非编译期静态变量赋值 -------读写某个类的静态变量 int b = a.staticVariable;或a.staticVariable=b;
– 调用类的静态方法 -------调用某个类的静态方法 Test.doSomething();
– 反射(如 Class.forName (“ com.shengsiyuan.Test ”) ) -------比如Class.forName("xxxx");
– 初始化一个类的子类(不是对父类的主动使用就初始化子类,这样的话生成一个Object类,那岂不是每个类都要初始化) -------Child.class、Parent.class,初始化Child时,就是对Parent的主动使用,先初始化父类
– Java虚拟机启动时被标明为启动类的类( Java Test ) -------就是main方法那个所在类
•被动使用
除了以上六种情况,其他使用Java类的方式都被看作是对类的被动使用,都不会导致类的初始化
前3个可以归一类:遇到new、getstatic、putstatic、invokestatic这四条字节码指令时,如果类还没有进行过初始化,则需要先触发其初始化。
主要说下开始:当jvm启动时,用户需要指定一个要执行的主类(包含static void main(String[] args)的那个类),则jvm会先去初始化这个类。
友链:【深入Java虚拟机】之三:类初始化 http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/17845821
3、类的加载来源
• 类的加载指的是将类的 .class 文件中的二进制数据读入到内存中,将其放在运行时数据区的方法区内,然后在堆区创建一个 java.lang.Class 对象,用来封装类在方法区内的数据结构 • 加载 .class 文件的方式 – 从本地系统中直接加载 – 通过网络下载 .class 文件(URLClassLoader) – 从 zip、jar 等归档文件中加载 .class 文件 – 从专有数据库中提取 .class 文件 – 将 Java源文件动态编译为 .class 文件 4、重载之泛型参数不同可以吗
泛型编译后是一样的类型。
java5后新特性方便了书写,字面误导,需要深刻了解一下class。
//返回值参数重载吗 public class Overload { public int method(List<String> ls){ return 0; } /** * Method method(List<Integer>) has the same erasure method(List<E>) as another method in type Demo.Overload */ public boolean method(List<Integer> li){ return false; } /** * 会有问题吗,编译后是什么样的呢。。。 */ public int method(Integer s){ return s; } public int method(String i){ return 0; } }
重载条件:
在Java语言中,要重载一个方法,除了要与原方法具有相同的简单名称外,还要求必须拥有一个与原方法不同的(不包含返回值的)特征签名,特征签名就是一个方法中各个参数在常量池中的字段符号引用的集合,也就是因为返回值不会包含在特征签名之中,因此Java语言里无法仅仅依靠返回值的不同来对一个已有方法进行重载。
如果进行过Android的native编程,便会非常熟悉这种签名,因为Android源码中可以看到。
用方法描述符描述方法时,按照先参数后返回值的顺序描述,参数要按照严格的顺序放在一组小括号内,如方法 int getIndex(String name,char[] tgc,int start,int end,char target)的描述符为“(Ljava/lang/String[CIIC)I”。
重载调用选择:
另外,根据参数选择重载方法时,是静态时需要确定的,即编译后就确定。
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/17965867
public class Demo { /** * I am human * I am human */ public static void main(String[] args){ Demo sp = new Demo(); Human man = sp.new Man(); Human woman = sp.new Woman(); sp.say(man); sp.say(woman); } class Human{ } class Man extends Human{ } class Woman extends Human{ } public void say(Human hum){ System.out.println("I am human"); } public void say(Man hum){ System.out.println("I am man"); } public void say(Woman hum){ System.out.println("I am woman"); } }
5、参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/tianchi/archive/2012/11/11/2761631.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/o-andy-o/archive/2013/06/06/3120298.html
http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/17675609