前言
索引的主要作用是起到约束和加速查找,ORM框架(sqlalchemy)是用类和对象对数据库进行操作
索引的种类
按种类去分
1.普通索引:能够加速查找
2.主键索引:能够加速查找、不能为空、不能重复
3.唯一索引:加速查找、可以为空、不能重复
4.联合索引(多列):
①联合主键索引
②联合唯一索引
③联合普通索引
按数据结构去分
1.hash索引:哈希索引。创建一个索引表,把这些数据(下面用到的'name')转化成哈希值,再把这些哈希值放入表中,并加上这个数据的存储地址。在索引表中的顺序和数据表中的数据不一定会一致,因为它里面的顺序是无序的,如果在数据表中按一个范围去找值那效能不一定会高,但是如果只找单值的时候它就会很快的查找出结果。
2.btree索引(常用):也就是binary tree索引、二元树索引。在innodb引擎中它创建btree索引。在范围内找值效率高。
索引的加速查找
首先创建一个表
create table dataset( id int not null auto_increment primary key, name varchar(32), data int, )engine = innodb default charset = utf8;
再创建一个存储过程,当我们执行的存储过程时往表里插入10w笔数据
delimiter // create procedure inserdatapro() begin declare i int default 1; -- 定义一个计数器i declare t_name varchar(16); -- 临时名字变量 declare t_data int; -- 临时数据变量 while i <= 100000 do -- 如果i小于10W就执行下面的操作 set t_name = CONCAT('aaa',i); -- 让'aaa'和i相连接变成字符串'aaa1','aaa2'...的形式 set t_data = CEIL(RAND()*100); -- 产生一个0-100的乱数 insert into dataset(name,data) values(t_name,t_data); -- 将t_name,t_data插入dataset内 set i = i + 1; -- 将i加一 end while; -- 结束循环 end // delimiter ;
执行存储过程,往表中插入数据完成要花一定的时间,具体还需要看电脑的性能
call inserdatapro();
比较两种语句的执行速度:
select * from dataset where name = 'aaa94021';
select * from dataset where id = 94021;
结果:
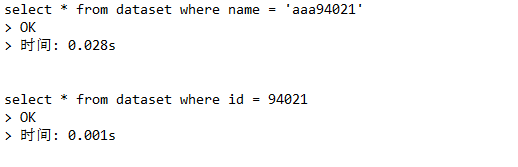
通过比较可以看出用索引(id)去查数据会比较快,像第一种查询方式因为没有索引,所以它必须要逐个去翻找出我们要的结果,因此我们可以再创建一个索引去查找数据。
create index nindex on dataset(name); -- 创建名字的索引
再去执行第一个查询语句:

可以看出效能得到了很显著的提升
查找方式:
1.无索引
从前到后依次查找
2.有索引
会创建一个数据结构或创建额外的文件,它按照某种格式去进行存储。所以它的查找方式会从这个索引文件中查询这个数据在这张表的什么位置。
查询快,但插入更行删除慢
当我们在使用索引查找资料时要命中索引,比如说:
select * from dataset where name like 'aaa94021';
索引相关操作:
1.普通索引
①创建表
create table t( nid int not null auto_increment primary key, name varchar(32), data int, index index_name(name) )
②创建索引
create index index_name on t(name);
③删除索引
drop index index_name on t;
④查看索引
show index from t;
2.唯一索引
①创建表
create table t2( id int not null auto_increment primary key, name varchar(32) not null, data int, unique index_name(name) )
②创建唯一索引
create unique index index_name on t2(name);
③删除唯一索引
drop unique index index_name on t2;
3.主键索引
①创建表
-- 写法一 create table t3( id int not null auto_increment primary key, name varchar(32) not null, int data, index index_name(name) ) -- 写法二 craete table t4( id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(32) not null, int data, primary key(id), index index_name(name) )
②创建主键
alter table t3 add primary key(id);
③删除主键
alter table t3 modify id int,drop primary key; alter table t3 drop primary key;
4.联合索引
①创建表
create table mtable( id int not null auto_increment, name varchar(32) not null, data int, gender varchar(16), primary key(id,name) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
②创建联合索引
create index index_id_name on mtable(id,name,gender);
最左前缀匹配:只支持最左边与其他索引之间的匹配方式,如:(id,name)、(id,gender)、(id,name,gender),如果用(name,gender)等就不能达到我们想要的查找效果
-- 符合最左前缀匹配 select * from mtable id = 15 and name = 'aaa15'; select * from mtable id = 15 and gender = 'male'; -- 不符合最左前缀匹配 select * from mtable name = 'aaa20' and id = 20;
组合索引的效率大于索引合并
覆盖索引和索引合并
不是真实存在,只是一个名词
覆盖索引:在索引文件中直接获取数据
比方说从表dataset去找'name = aaa12456'的存储数据
select * from dataset where name = 'aaa12456';
那我们如果想要取它的ID或data就可以通过这种方式拿到:
select id,data from dataset where name = 'aaa12456';
索引合并:把多个单列索引合并使用
例:
select * from dataset where name = 'aaa12456' and id = 12456;
命中索引
当我们需要在一个列中频繁的查找我们才需要创建索引,之后我们就要去命中索引,下面是命中索引的情况
1.like '%xx'(模糊查询)
select * from t where name like '%cn';
2.使用函数(速度慢,可以在程序级别中使用函数避免效能降低)
select * from t where reverse(name) = '3215aaa';
3.or
当这里id是索引,name不是索引的时候
select * from dataset where id = 15 or name = 'aaa20169';
特殊情况:
当这里id、name是索引,data不是索引,语句在执行时会把不是索引的部分给去掉把是索引的两端给连起来
select * from dataset where id = 15 or data = 98 and name = 'aaa20169';
4.类型不一致
当查询的类型为字符串和非字符串的类型时,两边所执行的时间会不大相同
select * from dataset where data = '98'; select * from dataset where data = 98;
效能比较:

5.!=
非主键情况:
select * from dataset where data != 98; select * from dataset where data = 98;
效能比较:

主键情况,还是会走索引:
select * from dataset where id != 12345; select * from dataset where id = 12345;
效能比较:

6.>
非数字类型(效能不是很高):
select * from dataset where name > 'aaa1345'; -- name不是主键
数字类型(如果是主键的话,还会走索引)
select * from dataset where id > 1345;
7.order by
索引排序的时候,选择的映射如果不是索引,则不走索引
select data from dataset order by data desc; select name from dataset order by data desc;
效能比较:

特殊情况,当对主键进行排序那还是走索引:
select * from dataset order by id desc;
8.联合索引最左前缀
执行计划
让Mysql去预估执行操作(一般情况下预估结果是正确的),语法:explain + MySQL查询语句
例一:
explain select * from dataset;
执行结果:

type等于All表示全表扫描,执行速度慢
例二:
explain select * from dataset where id = 9; -- id为主键
执行结果:

type等于const表示常数
例三:
explain select * from dataset where name = 'aaa17849'; -- name为索引
执行结果:

type等于ref表示按索引查询,执行速度快
select_type为查询类型:
SIMPLE 简单查询 PRIMARY 最外层查询 SUBQUERY 映射为子查询 DERIVED 子查询 UNION 联合 UNION RESULT 使用联合的结果
table为表名
possible_keys为可能使用的索引
key为真正使用的索引
key_len为MySQL中使用的索引字节长度
rows为预估读取长度
extra为包含MySQL解决查询的详细信息
type表示查询时的访问类型,下面性能的快慢顺序:
ALL < INDEX < RANGE < INDEX_MERGE < REF_OR_NULL < REF < EQ_REF < SYSTEM/CONST
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/explain-output.html#jointype_system
索引注意事项
1.避免使用select *去查询
2.count(1)或count(列)代替count(*)
3.创建表时尽量用char代替varchar
4.表的字段顺序固定长度的字段优先
5.组合索引代替多个单列索引(经常使用多个条件查询时)
6.尽量使用短索引
7.使用连接(JOIN)来替代子查询(SUB-QUERIES)
8.连表时注意条件和类型需一致
9.索引散列值(重复少)不适合建索引,比如:性别
慢日志
用于记录执行时间长的SQL、未命中索引把它们放到一个日志文件路径
内存中配置慢日志
查看当前配置信息
show variables like '%query%';
执行结果:
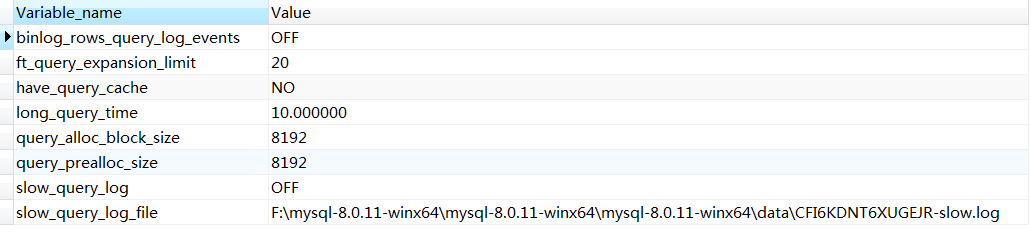
这里的long_query_time = 10 表示时间超过十秒的都会被记录下来、slow_query_log = OFF 表示是否开启慢日志、slow_query_log_file 表示日志文件路径
除此之外
show variables like '%queries%';
也可以查询到配合信息,执行结果:

这里的log_queries_not_using_indexed = OFF 表示使用的索引的搜索是否记录
若想要修改当前配置:
set global 变量名 = 值;
启动慢日志:
set global slow_query_log = ON;
配置文件
通过启动服务端
mysqld --default-file=配置文件路径
这样我们就可以在一个'my.conf'文件中去看这些日志记录
那这些记录内容就是相关的SQL执行操作。
除了新建一个'my.conf'去记录日志,也可以通过使用Mysql的'my-default.ini'去记录日志
注意:在修改了配置文件之后要记得备份和重启服务
分页
当一个数据的量很大时,作为用户不可能一下就去阅览上千条的量,所以我们要设计一个量,方便用户去阅读
首先我们先获得前十条数据:
select * from dataset limit 0,10;
执行结果:

那以此类推我们可以再去获得后十条,再后十条的数据从而达到分页的效果,但是其实我们使用limit它会去将数据进行扫描,当从0-10分10条数据时,它会扫10条数据,而当10-20分十条数据时,它会扫20条的数据...那如果在一个很大的数据量中扫描再去获取十条数据,那么它的效能就会非常的慢
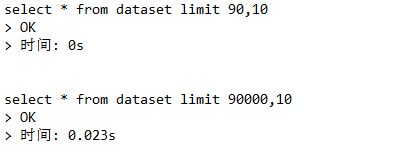
因此这种分页的方式实不可取的,那如何去解决?
方式一:隐藏分页
方式二:索引表扫描(用到覆盖索引)
但其实用这种方法和全扫相比也不会快到哪里去
select * from dataset where id in(select id from dataset limit 90000,10);
方式三:制定方案(记录当前页最大ID和最小ID)
如果要找后十条数据:
select * from dataset where id > 90000 limit 10;
查询速度:

如果要找前十条数据:
select * from dataset where id < 90001 order by id desc limit 10 ;
查询速度:
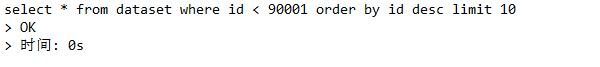
那如果要实现一个很大的跨度的话,比如说直接跳10000页,在数据库上是没法实现的,不过可以通过其他的方法像缓存等。between..and..不能实现问题在于数据库中ID是不是连续的,因为这些ID会因为一些增删改的操作出现变动。
在记录当前页的最大ID和最小ID还有两种实现方法:
①页面只有上一页或下一页
假设max_id为当前页最大ID、min_id为当前页最小ID
实现下一页功能:
select * from dataset where id > max_id limit 10;
实现上一页功能:
select * from dataset where id < min_id order by id desc limit 10;
②在上一页和下一页中间有很多页码

当前页(196):cur_page
目标页(199):tar_page
当前页最大ID:max_id
select * from dataset where id in (select id from (select id from dataset where id > max_id limit (tar_page-cur_page)*10) as T order by T.id desc limit 10);
当前页(196):cur_page
目标页(193):tar_page
当前页最小ID:min_id
select * from dataset where id in (select id from (select id from dataset where id < min_id limit (cur_page - tar_page)*10) as T order by T.id desc limit 10);