最近工作需要,研究学习 NLP ,但是 苦于官方文档太过纷繁,容易找不到重点,于是打算自己写一份学习线路
NLP 路线图
好博客韩小阳
斯坦福NLP公开课
统计学习方法
好博客
链接地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1myVT-yMzqzJIcl50mGs2JA
提取密码:tw6r
参考文档:
依照 印度小哥的 视频 跑了一个小 demo
step 1 用 IDEA 构建一个 maven 项目,引入 相关依赖包,当前依赖包最新版本为 3.9.2
<dependency>
<groupId>edu.stanford.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>stanford-corenlp</artifactId>
<version>3.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>edu.stanford.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>stanford-corenlp</artifactId>
<version>3.9.2</version>
<classifier>models</classifier>
</dependency>
<!--添加中文支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>edu.stanford.nlp</groupId>
<artifactId>stanford-corenlp</artifactId>
<version>3.9.2</version>
<classifier>models-chinese</classifier>
</dependency>
step 2 使用 nlp 包
package com.ghc.corhort.query.utils;
import edu.stanford.nlp.coref.CorefCoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.coref.data.CorefChain;
import edu.stanford.nlp.ling.CoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.ling.CoreLabel;
import edu.stanford.nlp.pipeline.*;
import edu.stanford.nlp.semgraph.SemanticGraph;
import edu.stanford.nlp.semgraph.SemanticGraphCoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.trees.Tree;
import edu.stanford.nlp.trees.TreeCoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.util.CoreMap;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author :Frank Li
* @date :Created in 2019/8/7 13:39
* @description:${description}
* @modified By:
* @version: $version$
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// creates a StanfordCoreNLP object, with POS tagging, lemmatization, NER, parsing, and coreference resolution
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("annotators", "tokenize, ssplit, pos, lemma, ner, parse, dcoref");
StanfordCoreNLP pipeline = new StanfordCoreNLP(props);
// read some text in the text variable
String text = "I like eat apple!";
// create an empty Annotation just with the given text
Annotation document = new Annotation(text);
// run all Annotators on this text
pipeline.annotate(document);
// these are all the sentences in this document
// a CoreMap is essentially a Map that uses class objects as keys and has values with custom types
List<CoreMap> sentences = document.get(CoreAnnotations.SentencesAnnotation.class);
for(CoreMap sentence: sentences) {
// traversing the words in the current sentence
// a CoreLabel is a CoreMap with additional token-specific methods
for (CoreLabel token: sentence.get(CoreAnnotations.TokensAnnotation.class)) {
// this is the text of the token
String word = token.get(CoreAnnotations.TextAnnotation.class);
// this is the POS tag of the token
String pos = token.get(CoreAnnotations.PartOfSpeechAnnotation.class);
// this is the NER label of the token
String ne = token.get(CoreAnnotations.NamedEntityTagAnnotation.class);
System.out.println("word:"+word+"-->pos:"+pos+"-->ne:"+ne);
}
// this is the parse tree of the current sentence
Tree tree = sentence.get(TreeCoreAnnotations.TreeAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(String.format("tree:
%s",tree.toString()));
// this is the Stanford dependency graph of the current sentence
SemanticGraph dependencies = sentence.get(SemanticGraphCoreAnnotations.CollapsedCCProcessedDependenciesAnnotation.class);
}
// This is the coreference link graph
// Each chain stores a set of mentions that link to each other,
// along with a method for getting the most representative mention
// Both sentence and token offsets start at 1!
Map<Integer, CorefChain> graph =
document.get(CorefCoreAnnotations.CorefChainAnnotation.class);
}
}
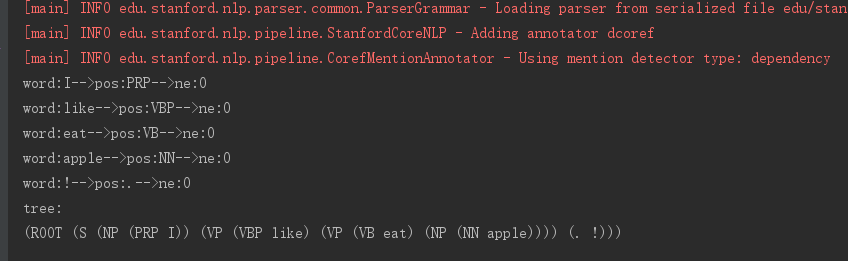
输出结果
浅度原理
stanford corenlp的TokensRegex
最近做一些音乐类、读物类的自然语言理解,就调研使用了下Stanford corenlp,记录下来。
功能
Stanford Corenlp是一套自然语言分析工具集包括:
POS(part of speech tagger)-标注词性
NER(named entity recognizer)-实体名识别
Parser树-分析句子的语法结构,如识别出短语词组、主谓宾等
Coreference Resolution-指代消解,找出句子中代表同一个实体的词。下文的I/my,Nader/he表示的是同一个人
Sentiment Analysis-情感分析
Bootstrapped pattern learning-自展的模式学习(也不知道翻译对不对,大概就是可以无监督的提取一些模式,如提取实体名)
Open IE(Information Extraction)-从纯文本中提取有结构关系组,如"Barack Obama was born in Hawaii" =》 (Barack Obama; was born in; Hawaii)
需求
语音交互类的应用(如语音助手、智能音箱echo)收到的通常是口语化的自然语言,如:我想听一个段子,给我来个牛郎织女的故事,要想精确的返回结果,就需要提出有用的主题词,段子/牛郎织女/故事。看了一圈就想使用下corenlp的TokensRegex,基于tokens序列的正则表达式。因为它提供的可用的工具有:正则表达式、分词、词性、实体类别,另外还可以自己指定实体类别,如指定牛郎织女是READ类别的实体。

接下来要做 nlp2sql 的事情了
