Google perftools
1、功能简介
它的主要功能就是通过采样的方式,给程序中cpu的使用情况进行“画像”,通过它所输出的结果,我们可以对程序中各个函数(得到函数之间的调用关系)耗时情况一目了然。在对程序做性能优化的时候,这个是很重要的,先把最耗时的若干个操作优化好,程序的整体性能提升应该十分明显,这也是做性能优化的一个最为基本的原则—先优化最耗时的。
2、安装
1、下载gperftools
Wget https://code.google.com/p/gperftools/downloads/detail?name=gperftools-2.0.tar.gz
2、tar –xzf gperftools-2.0.tar.gz
3、cd gperftools-2.0
4、./configure --prefix=/usr/local –enable-frame-pointers
5、make && make install
ps:编译时打开了 –enable-frame-pointers ,这要求被测试的程序在编译时要加上gcc编译选项,否则某些多线程程序可能会 core:
CCFLAGS=-fno-omit-frame-pointer
ps:perftools对2.4内核的多线程支持不是很好,只能分析主线程,但是2.6内核解决了这个问题。
安装图形化分析工具kcachegrind:
kcachegrind用来分析产生的profiling文件,linux环境下使用。
kcachegrind install:sudo apt-get install kcachegrind
3、使用
方法有三种:
1、直接调用提供的api:这种方式比较适用于对于程序的某个局部来做分析的情况,直接在要做分析的局部调用相关的api即可。
方式:调用函数:ProfilerStart() and ProfilerStop()
2、链接静态库:这种方式是最为常用的方式,后面会有详细的介绍。
方式:在代码link过程中添加参数 –lprofiler
For example:gcc […] -o helloworld –lprofiler
运行程序:env CPUPROFILE=./helloworld.prof ./helloworld
指定要profile的程序为helloworld,并且指定产生的分析结果文件的路径为./helloworld.prof
3、链接动态库:这种方式和静态库的方式差不多,但通常不推荐使用,除非使用者不想额外链一个静态库(因为链接静态库会增大binary的大小)的情况,可以考虑使用这种方式。
方式:运行时使用LD_PRELOAD,e.g. % env LD_PRELOAD="/usr/lib/libprofiler.so"
<binary>(不推荐这种方式)。
Ps:env是linux下插入环境变量的shell命令
4、 查看收集数据结果
查看profile结果:pprof工具,它是一个perl的脚本,通过这个工具,可以将google-perftool的输出结果分析得更为直观,输出为图片、pdf等格式。
Ps:在使用pprof之前需要先安装运行per15,如果要进行图标输出则需要安装dot,如果需要--gv模式的输出则需要安装gv。
调用pprof分析数据文件:
% pprof /bin/ls ls.prof
Enters "interactive" mode
% pprof --text /bin/ls ls.prof
Outputs one line per procedure
% pprof --gv /bin/ls ls.prof
Displays annotated call-graph via 'gv'
% pprof --gv --focus=Mutex /bin/ls ls.prof
Restricts to code paths including a .*Mutex.* entry
% pprof --gv --focus=Mutex --ignore=string /bin/ls ls.prof
Code paths including Mutex but not string
% pprof --list=getdir /bin/ls ls.prof
(Per-line) annotated source listing for getdir()
% pprof --disasm=getdir /bin/ls ls.prof
(Per-PC) annotated disassembly for getdir()
% pprof --text localhost:1234
Outputs one line per procedure for localhost:1234
% pprof --callgrind /bin/ls ls.prof
Outputs the call information in callgrind format
分析callgrind的输出:
使用kcachegrind工具来对.callgrind输出进行分析
e.g. % pprof --callgrind /bin/ls ls.prof > ls.callgrind
% kcachegrind ls.callgrind
4、举例
事例一:cpu_profiler_example.cpp,在代码中插入标签,可以针对某个函数进行特定的profile
代码如下:

关注两个函数:ProfilerStart() and ProfilerStop()
Makefile:
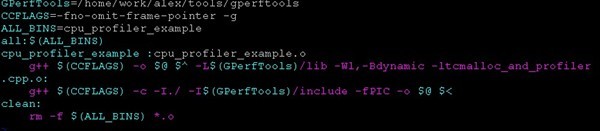
-L 动态链接库地址,但是有可能程序执行的时候,找不到动态链接库,所以得
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=LD_LIBRARY_PATH:"/home/work/alex/tools/gperftools/lib"
1)执行./cpu_profile_example

生成一个性能数据文件: cpu_profiler_example_29502.prof
Ps:当然指定性能数据文件生成的路径和文件名:
CPUPROFILE=/tmp/profile ./myprogram
将在/tmp目录下产生profile性能数据文件
2)分析性能数据
pprof -text cpu_profiler_example cpu_profiler_example_3875.prof

Text输出结果分析:
14 2.1% 17.2% 58 8.7% std::_Rb_tree::find
含义如下:
14:find函数花费了14个profiling samples
2.1%:find函数花费的profiling samples占总的profiling samples的比例
17.2%:到find函数为止,已经运行的函数占总的profiling samples的比例
58:find函数加上find函数里的被调用者总共花费的profiling samples
8.7%:find函数加上find函数里的被调用者总共花费的profiling samples占总的profiling samples的比例
std::_Rb_tree::find:表示profile的函数
ps: 100 samples a second,所以得出的结果除以100,得秒单位
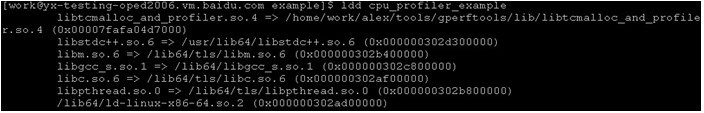
Ldd可以查看一个程序要链接那些动态库:
事例二:cpu_profiler_example.cpp,不需要在代码里添加任何标签,将profile所有的函数。
代码如下:

Makefile:

1)执行程序,生成性能数据文件
CPUPROFILE=/tmp/profile ./cpu_profiler_example
2)分析数据文件
1)pprof -text cpu_profiler_example profile
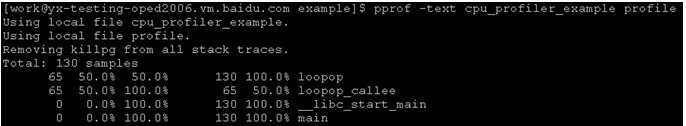
2)命令行交互模式

事例三:由于我们的程序有可能是服务程序,而服务程序不会自动执行完退出,如果以ctrl+c退出也不是正常的exit(0)的方式退出,而这会导致我们在profile的时候,收集到的数据不全甚至是空的,采用如下解决办法:
将ProfilerStart和ProfilerStop这2个函数封装到两个信号处理函数中,给服务程序发信号SIGUSR1,就开始profile,给服务程序发信号SIGUSR2,就停止profile。这样我们可以随时对程序进行profiling,并获得数据。
代码如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <sys/types.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <signal.h> 5 #include <google/profiler.h> 6 7 //SIGUSR1: start profiling 8 //SIGUSR2: stop profiling 9 10 static void gprof_callback(int signum) 11 { 12 if (signum == SIGUSR1) 13 { 14 printf("Catch the signal ProfilerStart\n"); 15 ProfilerStart("bs.prof"); 16 } 17 else if (signum == SIGUSR2) 18 { 19 printf("Catch the signal ProfilerStop\n"); 20 ProfilerStop(); 21 } 22 } 23 24 static void setup_signal() 25 { 26 struct sigaction profstat; 27 profstat.sa_handler = gprof_callback; 28 profstat.sa_flags = 0; 29 sigemptyset(&profstat.sa_mask); 30 sigaddset(&profstat.sa_mask, SIGUSR1); 31 sigaddset(&profstat.sa_mask, SIGUSR2); 32 33 if ( sigaction(SIGUSR1, &profstat,NULL) < 0 ) 34 { 35 fprintf(stderr, "Fail to connect signal SIGUSR1 with start profiling"); 36 } 37 if ( sigaction(SIGUSR2, &profstat,NULL) < 0 ) 38 { 39 fprintf(stderr, "Fail to connect signal SIGUSR2 with stop profiling"); 40 } 41 } 42 43 int loopop_callee() 44 { 45 int n=0; 46 for(int i=0; i<10000; i++) 47 { 48 for(int j=0; j<10000; j++) 49 { 50 n |= i%100 + j/100; 51 } 52 } 53 return n; 54 } 55 56 int loopop() 57 { 58 int n=0; 59 while(1) 60 { 61 for(int i=0; i<10000; i++) 62 { 63 for(int j=0; j<10000; j++) 64 { 65 n |= i%100 + j/100; 66 } 67 } 68 printf("result: %d\n", (loopop_callee)() ); 69 } 70 return n; 71 } 72 73 int main(int argc,char** argv) 74 { 75 char program[1024]={0}; 76 //snprintf(program,1023,"%s_%d.prof",argv[0],getpid()); 77 setup_signal(); 78 printf("result: %d\n", (loopop)() ); 79 return 0; 80 }
关注两个函数gprof_callback和setup_signal。
启动程序,可以采用kill -s SIGUSR1 5722和kill -s SIGUSR2 5722来开始采集和停止采集,5722是进程pid。
5、心得
最后,补充一点,要用google-perftool来分析程序,必须保证程序能正常退出。
采用kcachegrind查看函数之间依赖,并分析程序性能

