题目连接
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1541
Stars
Description
Astronomers often examine star maps where stars are represented by points on a plane and each star has Cartesian coordinates. Let the level of a star be an amount of the stars that are not higher and not to the right of the given star. Astronomers want to know the distribution of the levels of the stars. 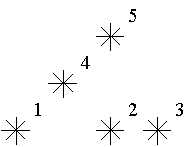
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
Input
The first line of the input file contains a number of stars N (1<=N<=15000). The following N lines describe coordinates of stars (two integers X and Y per line separated by a space, 0<=X,Y<=32000). There can be only one star at one point of the plane. Stars are listed in ascending order of Y coordinate. Stars with equal Y coordinates are listed in ascending order of X coordinate.
Output
The output should contain N lines, one number per line. The first line contains amount of stars of the level 0, the second does amount of stars of the level 1 and so on, the last line contains amount of stars of the level N-1.
Sample Input
5
1 1
5 1
7 1
3 3
5 5
Sample Output
1
2
1
1
0

1 #include<algorithm> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstdlib> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<cstdio> 6 #include<vector> 7 #include<map> 8 using std::cin; 9 using std::cout; 10 using std::endl; 11 using std::find; 12 using std::sort; 13 using std::pair; 14 using std::vector; 15 #define pb(e) push_back(e) 16 #define sz(c) (int)(c).size() 17 #define mp(a, b) make_pair(a, b) 18 #define all(c) (c).begin(), (c).end() 19 #define iter(c) decltype((c).begin()) 20 #define cls(arr,val) memset(arr,val,sizeof(arr)) 21 #define cpresent(c, e) (find(all(c), (e)) != (c).end()) 22 #define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (int)(n); i++) 23 #define tr(c, i) for (iter(c) i = (c).begin(); i != (c).end(); ++i) 24 const int Max_N = 15100; 25 typedef unsigned long long ull; 26 struct Node { 27 int v, s, less; 28 Node *ch[2]; 29 inline void setc(int _v, int _s, Node *p) { 30 v = _v, s = less = _s; 31 ch[0] = ch[1] = p; 32 } 33 inline void push_up() { 34 s = ch[0]->s + ch[1]->s + 1; 35 } 36 }; 37 struct SBT { 38 int lev, ans[Max_N]; 39 Node *root, *null, *tail, stack[Max_N]; 40 inline void init() { 41 tail = &stack[0]; 42 null = tail++; 43 null->setc(0, 0, NULL); 44 root = null; 45 } 46 inline Node *newNode(int v) { 47 Node *p = tail++; 48 p->setc(v, 1, null); 49 return p; 50 } 51 inline void rotate(Node *&x, bool d) { 52 Node *k = x->ch[!d]; x->ch[!d] = k->ch[d]; k->ch[d] = x; 53 k->s = x->s; 54 x->push_up(); 55 if (!d) k->less += x->less; 56 else x->less -= k->less; 57 x = k; 58 } 59 inline void Maintain(Node *&x, bool d) { 60 if (!x->s) return; 61 if (x->ch[d]->ch[d]->s > x->ch[!d]->s) rotate(x, !d); 62 else if (x->ch[d]->ch[!d]->s > x->ch[!d]->s) rotate(x->ch[d], d), rotate(x, !d); 63 else return; 64 Maintain(x, 0), Maintain(x, 1); 65 } 66 inline void insert(Node *&o, int v) { 67 if (!o->s) { o = newNode(v); return; } 68 if (v >= o->v) lev += o->less; 69 if (v <= o->v) o->less++; 70 if (v == o->v) return; 71 o->s++; 72 insert(o->ch[v > o->v], v); 73 o->push_up(); 74 Maintain(o, v > o->v); 75 } 76 inline void work(int n) { 77 init(); 78 int x, y; 79 cls(ans, 0); 80 rep(i, n) { 81 lev = 0; 82 scanf("%d %d", &x, &y); 83 insert(root, x); 84 ans[lev]++; 85 } 86 rep(i, n) printf("%d ", ans[i]); 87 } 88 }sbt; 89 int main() { 90 #ifdef LOCAL 91 freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); 92 freopen("out.txt", "w+", stdout); 93 #endif 94 int n; 95 while (~scanf("%d", &n)) { 96 sbt.work(n); 97 } 98 return 0; 99 }
