先来一张容器的API框架图,我们在java中所学的所有知识,都是根据下面这张图来学习的....
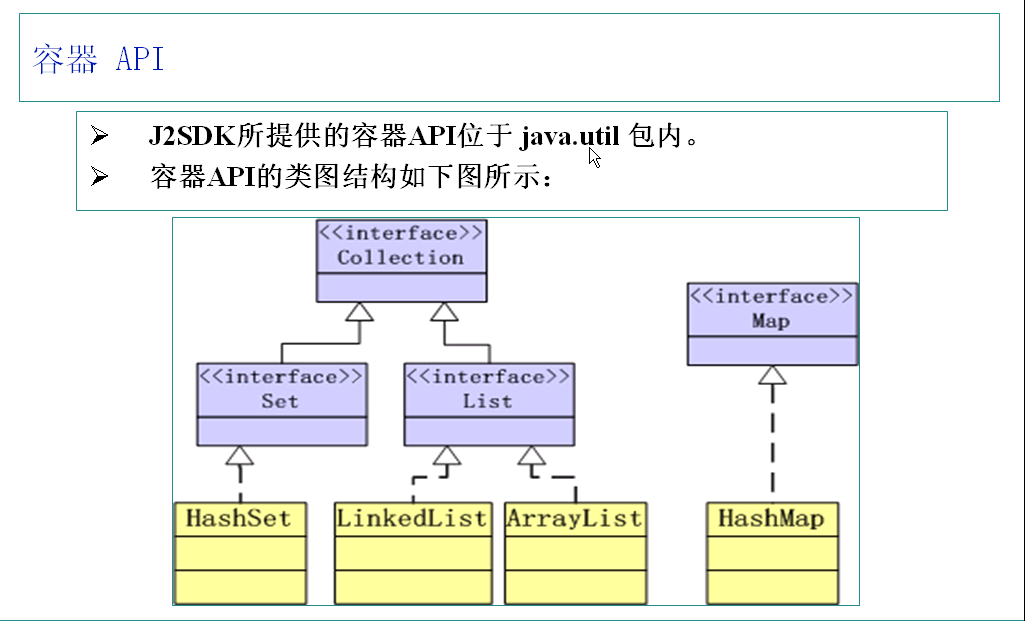
容器API:
1、Collection接口------定义了存储一组对象的方法,其子接口Set和List分别定义了存储的方式。
①、Set中的数据对象没有顺序且不可以重复。
②、List中的数据对象有顺序且可以重复。
2、Map接口定义了存储“键(key)---值(value)映射对”的方法。
Collection接口:
Collection接口中定义的方法(意思就是只要你实现了Collection接口,你将拥有下面所有方法):

Collection方法举例:
这里要说明的就是集合里面只能装引用类型的数据。
import java.util.*; public class TestCollection{ public static void main (String args[]){ Collection collection = new ArrayList(); //可以放入不同类型的对象 collection.add("hello"); collection.add(new Person("f1",18)); collection.add(new Integer(100)); System.out.println(collection.size()); System.out.println(collection); } } class Person{ private String name; private int age; public Person(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } }
接下来,我们继续使用上面的例子,说说Collection里面remove()方法的使用:
import java.util.*; public class TestCollection{ public static void main (String args[]){ Collection collection = new HashSet(); //可以放入不同类型的对象 collection.add("hello"); collection.add(new Person("f1",18)); collection.add(new Integer(100)); collection.remove("hello"); collection.remove(new Integer(100)); System.out.println(collection.remove(new Person("f1",18))); System.out.println(collection); } } class Person{ private String name; private int age; public Person(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName(){ return name; } public int getAge(){ return age; } /*public boolean equals(Object obj){ if(obj instanceof Person){ Person person = (Person)obj; return (name.equals(person.name) && age == person.age); } return super.equals(obj); } public int hashCode(){ return name.hashCode(); }*/ }
执行上面的例子,你会发现我们插入的数据”hello“和new Integer(100)都可以用remove()方法直接删除,但是对于new person("f1",18)这对象可以用remove()方法直接删除吗?答案是不可以的....
容器类对象在调用remove、contains等方法时需要比较对象是否相等,这会涉及到对象类型的equals方法和hashCode方法;对于自定义的类型,需要重写equals方法和hashCode方法以实现自定义对象相等规则。
注意,相等的对象应该具有相等的hash Codes
Ieterator接口(简单说:Iterator就是一个统一的遍历我们集合中所有元素的方法)
1、所有实现了Collection接口的容器类都有一个iterator方法用以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象。
2、Iterator对象称作迭代器,用以方便的实现对容器元素的遍历实现。
3、Iterator实现了下列方法:
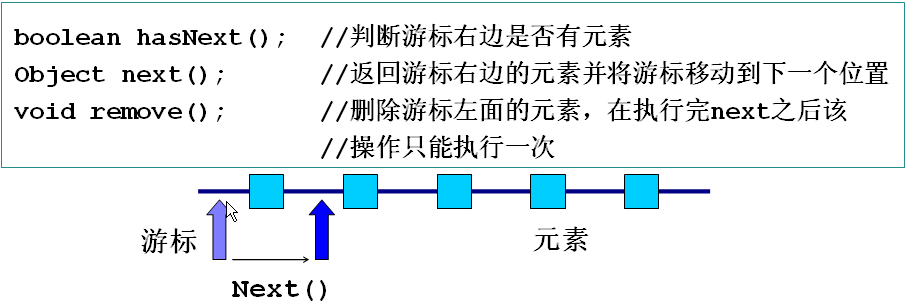
下面我们写一个用Iterator遍历集合元素的方法。(注:程序运行信息输出顺序可能跟我们输入的顺序不一致,这就是Set集合无序的效果)
import java.util.*; public class TestCollection{ public static void main (String args[]){ Collection collection = new HashSet(); collection.add(new Person("zhang",1)); collection.add(new Person("gao",2)); collection.add(new Person("wang",3)); collection.add(new Person("du",4)); collection.add(new Person("liang",5)); collection.add(new Person("li",6)); Iterator iterator = collection.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ //next()的返回值类型是Object类型,需要转换为相应类型 Person person = (Person)iterator.next(); System.out.println(person.name); } } } class Person{ public String name; private int age; public Person(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName(){ return name; } public int getAge(){ return age; } }
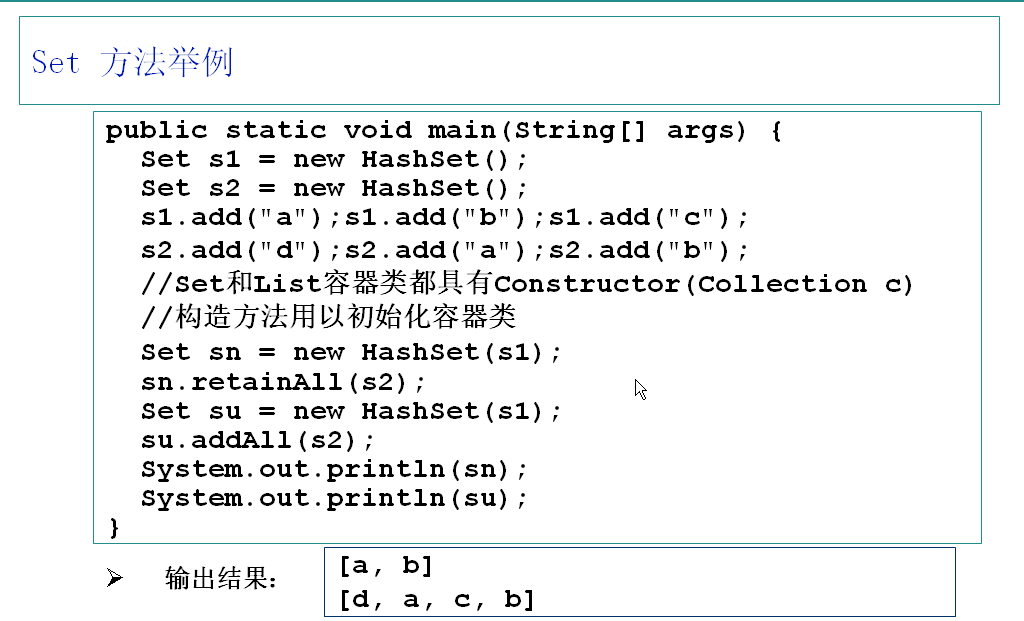
Set接口
1、Set接口是Collection的子接口,Set接口没有提供的额外方法,但实现Set接口的容器类中的元素是没有顺序的,而且不可以重复
2、Set接口可以与数学中”集合“的概念相对应。
3、J2SDK API中所提供的容器类有HashSet、TreeSet等...
Set方法举例:

Set方法举例:
List接口:
1、List接口是Collection的子接口,实现List接口的容器类中元素是有顺序的,而且可以重复。
2、List容器中元素都对应一个整数型的序号记载其在内容中的位置,可以根据序号存取容器中的元素。
3、L2SDK所提供的List容器类有ArrayList,LinkedList等...
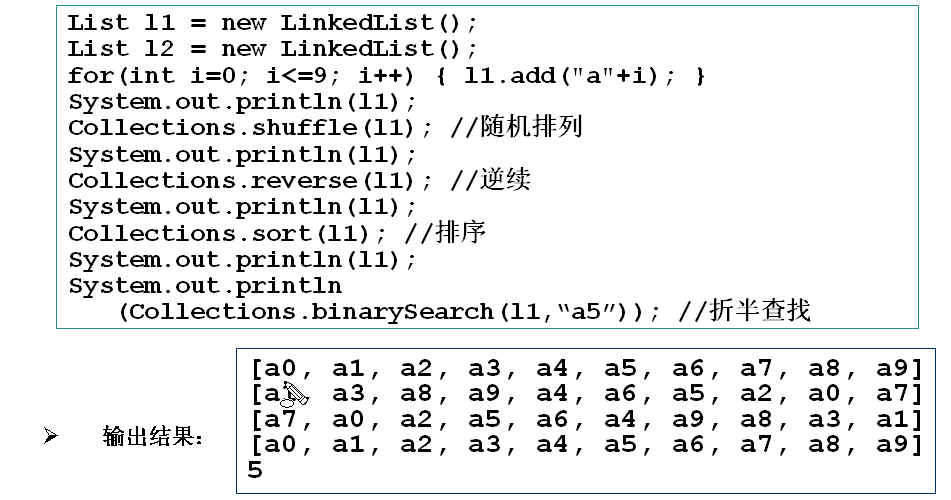
List 方法举例:

List常用算法:

List常用算法举例: