理解HTTP之keep-alive
在前面一篇文章中讲了TCP的keepalive,这篇文章再讲讲HTTP层面keep-alive。两种keepalive在拼写上面就是不一样的,只是发音一样,于是乎大家就都迷茫了。HTTP层面的keep-alive是我们接触比较多的,也是大家平时口头上的"keepalive"。下面我们就来谈谈HTTP的keep-alive
短连接&长连接&并行连接
再说keep-alive之前,先说说HTTP的短连接&长连接。
-
短连接
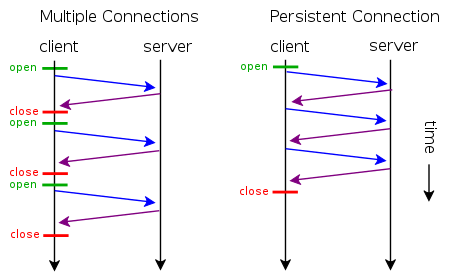
所谓短连接,就是每次请求一个资源就建立连接,请求完成后连接立马关闭。每次请求都经过“创建tcp连接->请求资源->响应资源->释放连接”这样的过程
-
长连接
所谓长连接(persistent connection),就是只建立一次连接,多次资源请求都复用该连接,完成后关闭。要请求一个页面上的十张图,只需要建立一次tcp连接,然后依次请求十张图,等待资源响应,释放连接。
-
并行连接
所谓并行连接(multiple connections),其实就是并发的短连接。
keep-alive
具体client和server要从短连接到长连接最简单演变需要做如下改进:
- client发出的HTTP请求头需要增加Connection:keep-alive字段
- Web-Server端要能识别Connection:keep-alive字段,并且在http的response里指定Connection:keep-alive字段,告诉client,我能提供keep-alive服务,并且"应允"client我暂时不会关闭socket连接
在HTTP/1.0里,为了实现client到web-server能支持长连接,必须在HTTP请求头里显示指定
Connection:keep-alive
在HTTP/1.1里,就默认是开启了keep-alive,要关闭keep-alive需要在HTTP请求头里显示指定
Connection:close
现在大多数浏览器都默认是使用HTTP/1.1,所以keep-alive都是默认打开的。一旦client和server达成协议,那么长连接就建立好了。
接下来client就给server发送http请求,继续上面的例子:请求十张图片。如果每次"请求->响应"都是独立的,那还好,10张图片的内容都是独立的。但是如果pipeline模式,上一个请求还没响应,下一个请求就发出,这样并发地发出10个请求,对于10个response client要怎么区分呢?而HTTP协议又是没有办法区分的,所以这种情况下必须要求server端地响应是顺序的,通过Conten-Length区分每次请求,这还只是针对静态资源,那对于动态资源无法预知页面大小的情况呢?我还没有深入研究,可以查看https://www.byvoid.com/blog/http-keep-alive-header
另外注意: 指定keep-alive是一种client和server端尽可能需要满足的约定,client和server可以在任意时刻都关闭keep-alive,彼此都不应该受影响。
Nginx keepa-alive配置
具体到Nginx的HTTP层的keepalive配置有
- keepalive_timeout
Syntax: keepalive_timeout timeout [header_timeout];
Default: keepalive_timeout 75s;
Context: http, server, location
The first parameter sets a timeout during which a keep-alive client connection will stay open on the server side. The zero value disables keep-alive client connections. The optional second parameter sets a value in the “Keep-Alive: timeout=time” response header field. Two parameters may differ.
- keepalive_requests
Syntax: keepalive_requests number;
Default: keepalive_requests 100;
Context: http, server, location
Sets the maximum number of requests that can be served through one keep-alive connection. After the maximum number of requests are made, the connection is closed.
可以看看Nginx的关于 keepalive_timeout 是实现
./src/http/ngx_http_request.c
static void
ngx_http_finalize_connection(ngx_http_request_t *r){
...
if (!ngx_terminate
&& !ngx_exiting
&& r->keepalive
&& clcf->keepalive_timeout > 0)
{
ngx_http_set_keepalive(r);
return;
}
...
}
static void
ngx_http_set_keepalive(ngx_http_request_t *r){
//如果发现是pipeline请求,判断条件是缓存区里有N和N+1个请求同时存在
if (b->pos < b->last) {
/* the pipelined request */
}
// 本次请求已经结束,开始释放request对象资源
r->keepalive = 0;
ngx_http_free_request(r, 0);
c->data = hc;
// 如果尝试读取keep-alive的socket返回值不对,可能是客户端close了。那么就关闭socket
if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) {
ngx_http_close_connection(c);
return;
}
//开始正式处理pipeline
...
rev->handler = ngx_http_keepalive_handler;
...
// 设置了一个定时器,触发时间是keepalive_timeout的设置
ngx_add_timer(rev, clcf->keepalive_timeout);
...
}
static void
ngx_http_keepalive_handler(ngx_event_t *rev){
// 发现超时则关闭socket
if (rev->timedout || c->close) {
ngx_http_close_connection(c);
return;
}
// 读取keep-alive设置从socket
n = c->recv(c, b->last, size);
if (n == NGX_AGAIN) {
if (ngx_handle_read_event(rev, 0) != NGX_OK) {
ngx_http_close_connection(c);
return;
}
...
}
//此处尚有疑惑?
ngx_reusable_connection(c, 0);
c->data = ngx_http_create_request(c);
// 删除定时器
ngx_del_timer(rev);
// 重新开始处理请求
rev->handler = ngx_http_process_request_line;
ngx_http_process_request_line(rev);
}
参考资料
from: http://www.firefoxbug.com/index.php/archives/2806/