Recently, Pari and Arya did some research about NP-Hard problems and they found the minimum vertex cover problem very interesting.
Suppose the graph G is given. Subset A of its vertices is called a vertex cover of this graph, if for each edge uv there is at least one endpoint of it in this set, i.e. 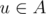 or
or  (or both).
(or both).
Pari and Arya have won a great undirected graph as an award in a team contest. Now they have to split it in two parts, but both of them want their parts of the graph to be a vertex cover.
They have agreed to give you their graph and you need to find two disjoint subsets of its vertices A and B, such that both A and B are vertex cover or claim it's impossible. Each vertex should be given to no more than one of the friends (or you can even keep it for yourself).
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 100 000) — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the prize graph, respectively.
Each of the next m lines contains a pair of integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n), denoting an undirected edge between ui and vi. It's guaranteed the graph won't contain any self-loops or multiple edges.
If it's impossible to split the graph between Pari and Arya as they expect, print "-1" (without quotes).
If there are two disjoint sets of vertices, such that both sets are vertex cover, print their descriptions. Each description must contain two lines. The first line contains a single integer k denoting the number of vertices in that vertex cover, and the second line contains k integers — the indices of vertices. Note that because of m ≥ 1, vertex cover cannot be empty.
4 2
1 2
2 3
1
2
2
1 3
3 3
1 2
2 3
1 3
-1
In the first sample, you can give the vertex number 2 to Arya and vertices numbered 1 and 3 to Pari and keep vertex number 4 for yourself (or give it someone, if you wish).
In the second sample, there is no way to satisfy both Pari and Arya.
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/688/problem/C
题意:一个由n个点m条边组成的图,把他分成二部图。
思路:DBF或者BFS暴力搜索,当前这个点在一组,与他相邻的点必须在另一组。不符合就输出-1,符合输出2组点。
代码:

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 struct node 4 { 5 int from; 6 int to; 7 int d; 8 int next; 9 } edge[200100]; 10 int head[200100]; 11 void add(int i,int u,int v,int d) 12 { 13 edge[i].from=u; 14 edge[i].to=v; 15 edge[i].d=d; 16 edge[i].next=head[u]; 17 head[u]=i; 18 } 19 int sign[200100]; 20 int ans,sum1,sum2; 21 queue<int>Q; 22 void BFS(int u) 23 { 24 while(!Q.empty()) Q.pop(); 25 Q.push(u); 26 while(!Q.empty()) 27 { 28 u=Q.front(); 29 Q.pop(); 30 int i=head[u]; 31 while(i!=0) 32 { 33 if(sign[edge[i].from]==1&&sign[edge[i].to]==0) 34 { 35 sum2++; 36 sign[edge[i].to]=2; 37 Q.push(edge[i].to); 38 } 39 else if(sign[edge[i].from]==2&&sign[edge[i].to]==0) 40 { 41 sum1++; 42 sign[edge[i].to]=1; 43 Q.push(edge[i].to); 44 } 45 else if(sign[edge[i].from]==1&&sign[edge[i].to]==1) ans=0; 46 else if(sign[edge[i].from]==2&&sign[edge[i].to]==2) ans=0; 47 if(ans==0) break; 48 i=edge[i].next; 49 } 50 if(ans==0) break; 51 } 52 } 53 int main() 54 { 55 int i,j,n,m; 56 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 57 memset(head,0,sizeof(head)); 58 for(i=1,j=1; i<=m; i++) 59 { 60 int u,v; 61 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); 62 add(j++,u,v,1); 63 add(j++,v,u,1); 64 } 65 ans=1; 66 sum1=sum2=0; 67 memset(sign,0,sizeof(sign)); 68 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) 69 { 70 if(sign[i]!=0) continue; 71 sign[i]=1; 72 sum1++; 73 BFS(i); 74 } 75 if(ans==1) 76 { 77 cout<<sum1<<endl; 78 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) 79 if(sign[i]==1) cout<<i<<" "; 80 cout<<endl<<sum2<<endl; 81 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) 82 if(sign[i]==2) cout<<i<<" "; 83 cout<<endl; 84 } 85 else cout<<"-1"<<endl; 86 return 0; 87 }

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 vector<int>v[100005]; 4 queue<int>Q; 5 int sign[100005]; 6 int ans,sum1,sum2; 7 void BFS(int u) 8 { 9 while(!Q.empty()) Q.pop(); 10 Q.push(u); 11 while(!Q.empty()) 12 { 13 u=Q.front(); 14 Q.pop(); 15 for(int i=0; i<v[u].size(); i++) 16 { 17 if(sign[v[u][i]]==sign[u]) 18 { 19 ans=0; 20 return; 21 } 22 else if(sign[v[u][i]]==0) 23 { 24 if(sign[u]==1) 25 { 26 sum2++; 27 sign[v[u][i]]=2; 28 } 29 else 30 { 31 sum1++; 32 sign[v[u][i]]=1; 33 } 34 Q.push(v[u][i]); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 int main() 40 { 41 int i,n,m,a,b; 42 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 43 memset(sign,0,sizeof*(sign)); 44 for(i=0; i<m; i++) 45 { 46 scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); 47 v[a].push_back(b); 48 v[b].push_back(a); 49 } 50 ans=1; 51 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) 52 { 53 if(sign[i]!=0) continue; 54 sign[i]=1; 55 sum1++; 56 BFS(i); 57 if(ans==0) break; 58 } 59 if(ans==1) 60 { 61 cout<<sum1<<endl; 62 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) 63 if(sign[i]==1) cout<<i<<" "; 64 cout<<endl<<sum2<<endl; 65 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) 66 if(sign[i]==2) cout<<i<<" "; 67 cout<<endl; 68 } 69 else cout<<"-1"<<endl; 70 }
