一、数组的基础知识
1、数组有什么用?
如果需要同一个类型的多个对象,就可以使用数组。数组是一种数组结构,它可以包含同一个类型的多个元素.
2、数组的初始化方式
第一种:先声明后赋值
int[] array = new int[3]; array[0] = 0; array[1] = 1; array[2] = 2;
第二种:使用数组初始化器对数组进行赋值。注:数组初始化器只能在声明数组变量时使用,不能在声明数组变量之后使用.
//正确 int[] array = new int[3] { 1, 2, 3 }; //错误 int[] array1=new int[3]; array1 = { 1, 2, 3 };
关于第二种方法,C#提供了两个方式的"语法糖";
//语法糖一 int[] array = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }; //语法糖二 int[] array={1,2,3};
3、引用类型数组
C#除了能声明和处理预定义类型的数组之外,还能声明自定义类型的数组。
public class Person { public string FirstName{get;set;} public string LastName{get;set;} } Person[] person=new Person[2];
预定义类型数组能干的事,自定义类型数组也都能干.
4、多维数组
二维数组的声明方式:
int[,] twodim = new int[2, 3]; twodim[0, 0] = 1; twodim[0, 1] = 2; twodim[0, 2] = 3; twodim[1, 0] = 4; twodim[1, 1] = 5; twodim[1, 2] = 6; twodim[2, 0] = 7; twodim[2, 1] = 8; twodim[2, 2] = 9;
语法糖:
int[,] twodim ={ {1,2,3}, {4,5,6}, {7,8,9} };
三维数组:
因为日常开发中不常用到,所以就不解释了.百度百科
5、锯齿数组
锯齿数组是一个特殊的二维数组,常规的二维数组都是矩形,大部分都是各行的个数都相同,而锯齿数组则不一样,锯齿数组的第一行有3个,第二行可能有6个,第三行可能有7个......以此类推.锯齿数组的声明方式如下:
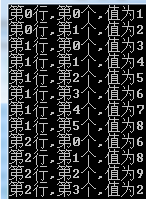
int[][] jagged = new int[3][]; jagged[0]=new int[2]{1,2}; jagged[1] = new int[6] { 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }; jagged[2] = new int[4] { 6, 8, 9, 2 }; for (int row = 0; row < jagged.Length; row++) { for (int element = 0; element < jagged[row].Length; element++) { Console.WriteLine("第{0}行,第{1}个,值为{2}", row, element, jagged[row][element]); } } Console.ReadKey();
二、Array类
使用方括号创建数组其实是用Array的表示法,当我们使用方括号创建了一个数组时,C#编译器会创建一个派生自抽象基类的Array的新类.这样使用方括号创建的数组对象就可以使用Array类为每个数组定义的方法和属性了.如:可以使用foreach迭代数组,其实就是使用了Array类中GetEnumerator()方法.
1、使用静态方法CreateInstance创建一维数组,并使用SetValue对数组进行赋值,使用GetValue获取数组中的值
Array array=Array.CreateInstance(typeof(int), 5); for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) { array.SetValue(i + 10, i); } for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine(array.GetValue(i)); }
2、使用静态方法CreateInstance创建二维数组,并使用SetValue对数组进行赋值,使用GetValue获取数组中的值
注:通过GetUpperBound获取维度的上限,通过GetLowerBound获取维度的下限
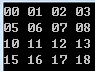
Array array=Array.CreateInstance(typeof(int),5,6); int value = 0; for(int row=0;row<array.GetUpperBound(0);row++) for (int element = 0; element < array.GetUpperBound(1); element++) { array.SetValue(value, row, element); value++; } for (int row = 0; row < array.GetUpperBound(0); row++) for (int element = 0; element < array.GetUpperBound(1); element++) { if (element == array.GetUpperBound(1) - 1) { Console.WriteLine(); } else { string nbsp = " "; string res = array.GetValue(row, element).ToString().PadLeft(2, '0'); res=element == array.GetUpperBound(1) - 1 ? res : res + nbsp; Console.Write(res);
} } } Console.ReadKey();
3、使用静态方法CreateInstance创建三维数组,并使用SetValue对数组进行赋值,使用GetValue获取数组中的值
注:通过GetUpperBound获取维度的上限,通过GetLowerBound获取维度的下限
Array array = Array.CreateInstance(typeof(int), 5, 6, 7); int value = 0; for (int x = 0; x < array.GetUpperBound(0); x++) for (int y = 0; y < array.GetUpperBound(1); y++) for (int z = 0; z < array.GetUpperBound(2); z++) { array.SetValue(value, x, y, z); value++; } for (int x = 0; x < array.GetUpperBound(0); x++) for (int y = 0; y < array.GetUpperBound(1); y++) for (int z = 0; z < array.GetUpperBound(2); z++) { Console.WriteLine("x坐标:{0},y坐标:{1},z坐标:{2},值为:{3}", x, y, z, array.GetValue(x, y, z)); } Console.ReadKey();
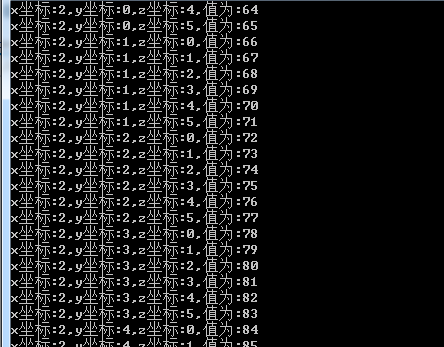
部分截图
4、复制数组
数组是引用类型,所以将一个数组变量赋值给另一个数组变量,就会得到两个引用同一个数组的变量,所以通过任何一个引用修改数组的值,两个引用都会受影响.
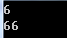
int[] array = { 1, 2, 3 }; int[] otherArray = array; array[2] = 6; Console.WriteLine(otherArray[2]); otherArray[2] = 66; Console.WriteLine(array[2]);
所以单纯的通过复制引用的方法,并不能实现数组的复制,必须通过其它的方法来复制数组,C#提供了两种复制数组的方式:
第一种:C#中的数组都实现了ICloneable接口,所以通该接口中定义的Clone()方法就能实现数组的浅拷贝(什么是浅拷贝,后续会介绍).
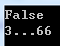
int[] array = { 1, 2, 3 }; int[] arrayClone = (int[])array.Clone(); array[2]=66; Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(array,arrayClone));//False 说明使用Clone()方法拷贝后的数组是重新创建的 Console.WriteLine(arrayClone[2] +"..." + array[2]);
第二种:Array.Copy()
复制一维数组:
int[] array = { 1, 2, 3 }; int[] arrayCopy=new int[array.Length]; Array.Copy(array, arrayCopy,array.Length);//最后一个参数为要复制的个数 for (int i = 0; i < arrayCopy.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine(arrayCopy[i]); }

复制二维数组:
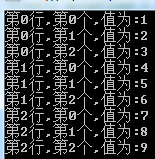
int[,] array = { {1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9} }; int[,] arrayCopy = new int[array.GetUpperBound(0)+1, array.GetUpperBound(1)+1]; Array.Copy(array,arrayCopy,array.Length);//最后一个参数为要复制的个数 for (int i = 0; i <= arrayCopy.GetUpperBound(0); i++) for (int x = 0; x <= arrayCopy.GetUpperBound(1); x++) Console.WriteLine("第{0}行,第{1}个,值为:{2}",i,x,arrayCopy.GetValue(i,x)); Console.ReadKey();
第三种:CopyTo
int[] array = { 1, 2, 3 }; int[] arrayCopyTo=new int[array.Length]; array.CopyTo(arrayCopyTo,0); Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(array,arrayCopyTo)); for (int i = 0; i < arrayCopyTo.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine(arrayCopyTo[i]); }

Clone()和Array.Copy()的区别主要是:Clone()方法直接复制整个目标数组,然后进行拆箱就可以使用,但是Array.Copy()方法则必须要提供相同维数的数组和需要复制的元素个数,才能复制成功。
Clone()和CopyTo()方法的区别主要是:CopyTo()需要提供一个开始复制的起始索引.
什么是浅拷贝和深拷贝?
当数组中存在引用类型的元素时,这个时候使用Clone()或者Array.Copy()或者CopyTo()方法进行的数组复制都是浅拷贝,只会复制引用类型的索引,这意味这当修改原数组中的引用类型的值时,拷贝后的数组中的引用类型的值也会做相应的改变,所以使用上述方法进行的数组拷贝都将是浅拷贝.所以如果你想要创建包含引用类型的数组的深层副本,就必须迭代数组并创建新对象.这个过程也叫深拷贝.
Person p = new Person("张三", 23); object[] array = { 1, 2, 3, p,6 }; object[] arrayClone = (object[])array.Clone(); p.Name = "李四"; Console.WriteLine((arrayClone[3] as Person).Name); class Person { public Person() { } public Person(string name,int age) { this.Name = name; this.Age = age; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } }
 说明Clone()方法确实是浅拷贝,至于Array.Copy()和CopyTo()也是浅拷贝-这两个请自行验证.
说明Clone()方法确实是浅拷贝,至于Array.Copy()和CopyTo()也是浅拷贝-这两个请自行验证.
5、数组排序
(1)、简单类型数组排序(简单类型如:System.String、System.Int、System.Double、System.Float等)
Array类使用QuickSort算法对数组中的元素进行排序。主要通过Array.Sort()方法来进行排序,Sort()方法需要数组中元素都实现IComparable接口,因为简单类型(如System.String和System.Int32)实现了IComparable接口,所以可以对包含这些类型的元素进行排序.如下代码,就是简单的对string类型数组和int数组进行排序,代码如下:
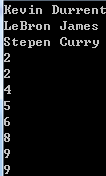
string[] player ={ "LeBron James", "Stepen Curry", "Kevin Durrent", }; Array.Sort<string>(player); foreach (var item in player) { Console.WriteLine(item); } int[] nums = { 9, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 2 }; Array.Sort<int>(nums); foreach (var item in nums) { Console.WriteLine(item); }
(2)、自定义类型利用Sort()方法排序
a、通过自定义类型实现IComparable接口,来实现自定义类型数组的排序。注:该方法适用于要进行的自定义实体类(本例中为Person类)可修改的情况下!
如果数组的类型为自定义类型,且需要使用Sort()对该书组进行排序,那么当前自定义类就必须实现IComparable接口,该接口只定义了一个方法CompareTo(),如果要比较的对象相等,该方法就返回0,如果该实例应排在参数的前面,该方法返回-1,如果该实例应排在参数的后面,该方法返回1.CompareTo方法的返回值规则和string.Compare()方法相同,如下图:


如上图示,当前实例应该排在参数的前面,所以result的值应为-1

ok,说明上面的结论正确(这里对象相等和当前实例排在参数后面的情况自行证明).那么CompareTo()方法的返回也应该这么写,代码如下:
static void Main(string[] args) { Person[] people = { new Person{FirstName="Damon",LastName="Hill"}, new Person{FirstName="Niki",LastName="Lauda"}, new Person{FirstName="Ayrton",LastName="Senna"} }; Array.Sort<Person>(people); foreach (var item in people) { if (item == null) Console.WriteLine("null"); else Console.WriteLine(item.ToString()); } Console.ReadKey(); } class Person:IComparable<Person> { public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public int CompareTo(Person other) { if (other == null) return 1; int result = string.Compare(this.FirstName, other.FirstName); if (result == 0)//如果FirstName相等,则判断LastName result = string.Compare(this.LastName, this.LastName); return result; } public override string ToString() { return this.FirstName + " " + this.LastName; } }
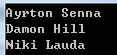
b、当要进行排序的自定义类型不能进行修改的时候,就采用b方法
static void Main(string[] args) { Person[] people = { new Person{FirstName="Damon",LastName="Hill"}, new Person{FirstName="Damon",LastName="Green"}, new Person{FirstName="Niki",LastName="Lauda"}, new Person{FirstName="Ayrton",LastName="Senna"} }; Array.Sort<Person>(people,new PersonCompare(PersonCompareType.LaseName)); foreach (var item in people) { if (item == null) Console.WriteLine("null"); else Console.WriteLine(item.ToString()); } Console.ReadKey(); } public enum PersonCompareType { FirstName=0, LaseName=1 } public class PersonCompare : IComparer<Person> { private PersonCompareType _compareType; public PersonCompare(PersonCompareType compareType) { this._compareType = compareType; } public int Compare(Person x, Person y) { if (x == null && y == null) return 0; if (x == null) return 1; if (y == null) return -1; switch (this._compareType) { case PersonCompareType.FirstName: return string.Compare(x.FirstName, y.FirstName); case PersonCompareType.LaseName: return string.Compare(x.LastName, y.LastName); default: throw new ArgumentException("unexcepted compare type"); } } } public class Person { public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public override string ToString() { return this.FirstName + " " + this.LastName; } }
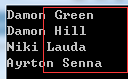
c、传递一个比较两个对象大小的委托delegate int Comparison<in T>(T x, T y),该方法最为简洁,即不污染要进行排序的对象,又能使用lambda表达式
static void Main(string[] args) { Person[] people = { new Person{FirstName="Damon",LastName="Hill"}, new Person{FirstName="Damon",LastName="Green"}, new Person{FirstName="Niki",LastName="Lauda"}, new Person{FirstName="Ayrton",LastName="Senna"} }; Comparison<Person> compare = (Person x, Person y) => { if (x == null && y == null) return 0; if (x == null) return 1; if (y == null) return -1; int result = string.Compare(x.FirstName, y.FirstName); if (result == 0) result = string.Compare(x.LastName, x.LastName); return result; }; Array.Sort<Person>(people, compare); foreach (var item in people) { if (item == null) Console.WriteLine("null"); else Console.WriteLine(item.ToString()); } Console.ReadKey(); } public class Person { public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public override string ToString() { return this.FirstName + " " + this.LastName; } }
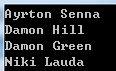
综合上面的三种方法,个人推荐第三种方法,进行自定义类型数组的排序工作,当然如果排序的逻辑很复杂,第三种未必就是最好的.