宽搜
思路很简单,开一个四维数组used[i][j][k][l]表示指定点在(i, j),空格在(j, k)是否走过,每次让空格上下左右走,遇到指定旗子就改变旗子位置,时间复杂度(O(qn^4))
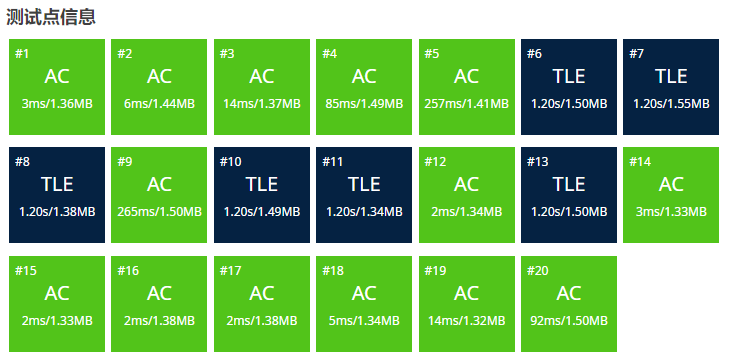
于是,我们得到了一份70分的代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int mp[31][31];
struct hehe{
int x, y, dx, dy, step;
};
bool used[31][31][31][31];
int mx[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1};
int my[] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
int main()
{
int n, m, T;
cin >> n >> m >> T;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> mp[i][j];
}
while(T--)
{
bool fl = 0;
queue<hehe>q;
memset(used, 0, sizeof(used));
int qx, qy, zx, zy, kx, ky;
cin >> qx >> qy >> zx >> zy >> kx >> ky;
hehe now;
now.dx = qx;
now.dy = qy;
now.x = zx;
now.y = zy;
now.step = 0;
used[qx][qy][zx][zy] = 1;
q.push(now);
while(q.size())
{
now = q.front();
q.pop();
int x = now.x, y = now.y, xx = now.dx, yy = now.dy;
if(x == kx && y == ky)
{
fl = 1;
cout << now.step << endl;
break;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
{
int xxx = xx + mx[i], yyy = yy + my[i];
if(xxx > n || yyy > m || xxx < 1 || yyy < 1) continue;
int qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
}
}
if(!fl)
{
cout << -1 << endl;
}
}
}
接下来才是这篇题解的重点:
如何卡常
O2优化+关闭流同步
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
上面的语句是开启O2优化
虽然在你谷不让在程序中自己写
但是可以手动开啊)
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
这句话是关闭cin、cout的流同步
原理大概是让cin、cout执行过程中不另开缓存
会让cin、cout跑得比scanf、printf都快
加上这两句话,成功拿到了另外10分:
循环展开
定睛一看:嘶,#7#8被优化到了可观测的TLE之内(1.20s以内)
想想之前看过一个神仙卡常毒瘤题P4604 [WC2017]挑战
其中一个基本操作就是“循环展开”
具体一点:
以下代码
for(int i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
{
int xxx = xx + mx[i], yyy = yy + my[i];
if(xxx > n || yyy > m || xxx < 1 || yyy < 1) continue;
int qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
}
将其循环展开后变成这样:
int i = 1;
int xxx = xx + mx[i], yyy = yy + my[i];
if(xxx > n || yyy > m || xxx < 1 || yyy < 1) goto s1;
qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
s1: i++;
xxx = xx + mx[i], yyy = yy + my[i];
if(xxx > n || yyy > m || xxx < 1 || yyy < 1) goto s2;
qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
s2: i++;
xxx = xx + mx[i], yyy = yy + my[i];
if(xxx > n || yyy > m || xxx < 1 || yyy < 1) goto s3;
qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
s3: i++;
xxx = xx + mx[i], yyy = yy + my[i];
if(xxx > n || yyy > m || xxx < 1 || yyy < 1) continue;
qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
这样可以优化常数——因为这个循环每次bfs新节点的时候都要做一次,这样理论上相当于优化了(10^8)级别的常数——虽然达不到
但是效果依然很明显:
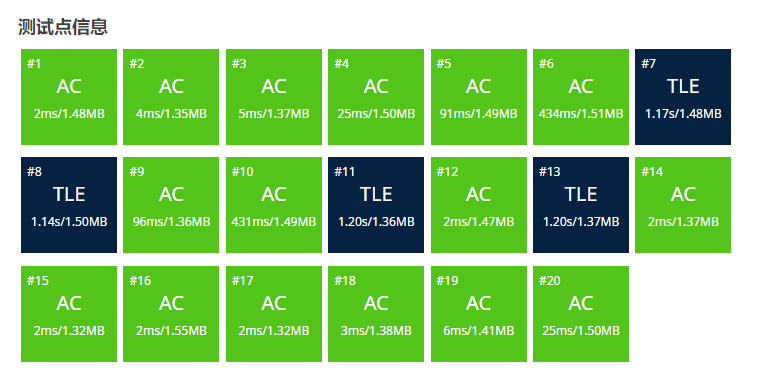
好,#7#8已经在0.01级别了!#11#13也优化到可视范围内了!
优化掉i++和move数组
这两个微不足道的东西足以卡掉零点几秒的时间,甚至更多。
变成:
int xxx = xx + 1, yyy = yy + 0;
s1:
xxx = xx + 0, yyy = yy + 1;
...
s2:
xxx = xx - 1, yyy = yy + 0;
...
s3:
xxx = xx + 0, yyy = yy - 1;
...
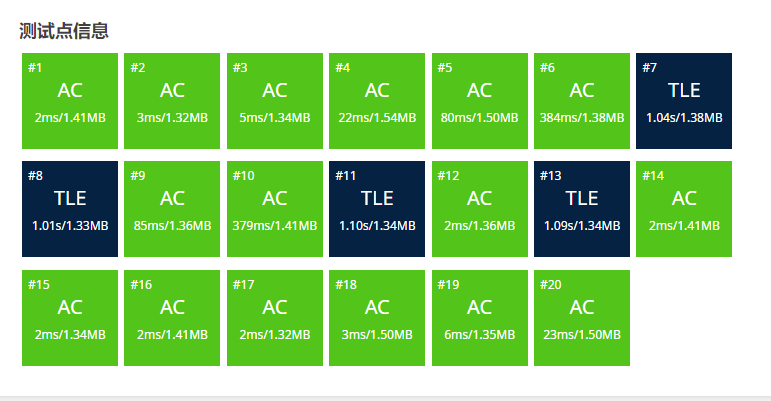
好耶!多过了两个点!顺便把#11#13优化成了个位数的毫秒级!
最后,去掉goto
苦思冥想了好久,想起在goto身上还有一个常数
于是把判断去掉——因为在第0行、第0列、第n+1行、第m+1列都是零
将goto优化掉了
if(xxx > n || yyy > m || xxx < 1 || yyy < 1) goto s1;
...
去掉。
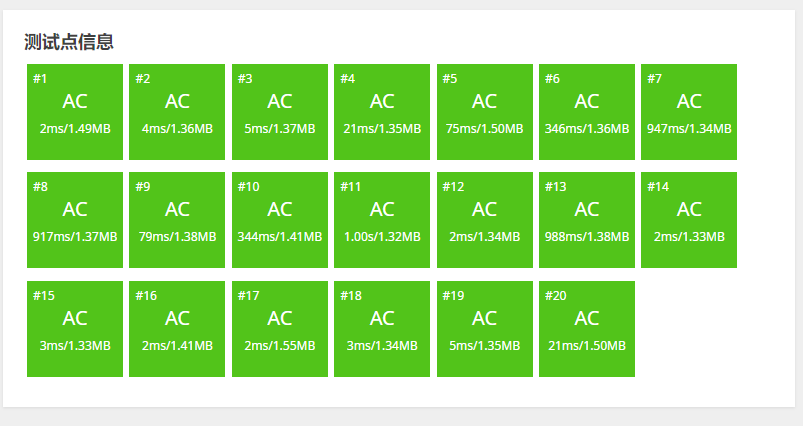
惊险AC。
最终代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int mp[31][31];
struct hehe{
int x, y, dx, dy, step;
};
bool used[31][31][31][31];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n, m, T;
cin >> n >> m >> T;
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(register int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> mp[i][j];
}
while(T--)
{
bool fl = 0;
queue<hehe>q;
memset(used, 0, sizeof(used));
int qx, qy, zx, zy, kx, ky;
cin >> qx >> qy >> zx >> zy >> kx >> ky;
hehe now;
now.dx = qx;
now.dy = qy;
now.x = zx;
now.y = zy;
now.step = 0;
used[qx][qy][zx][zy] = 1;
q.push(now);
while(q.size())
{
now = q.front();
q.pop();
int x = now.x, y = now.y, xx = now.dx, yy = now.dy;
if(x == kx && y == ky)
{
fl = 1;
cout << now.step << endl;
break;
}
int qwq, qaq;
int xxx = xx + 1, yyy = yy + 0;
if(xxx < n || yyy < m || xxx > 1 || yyy > 1)
{
qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
}
xxx = xx + 0, yyy = yy + 1;
if(xxx < n || yyy < m || xxx > 1 || yyy > 1)
{
qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
}
xxx = xx - 1, yyy = yy + 0;
if(xxx < n || yyy < m || xxx > 1 || yyy > 1)
{
qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
}
xxx = xx + 0, yyy = yy - 1;
if(xxx < n || yyy < m || xxx > 1 || yyy > 1)
{
qwq = x, qaq = y;
if(x == xxx && y == yyy) qwq = xx, qaq = yy;
if(mp[xxx][yyy] && !used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq])
{
used[xxx][yyy][qwq][qaq] = 1;
hehe nxt;
nxt.x = qwq;
nxt.y = qaq;
nxt.dx = xxx;
nxt.dy = yyy;
nxt.step = now.step + 1;
q.push(nxt);
}
}
}
if(!fl)
{
cout << -1 << endl;
}
}
}