package car; public class Vehicle { //定义成员变量 private int wheels; private double weight; public int getWheels() { return wheels; } public void setWheels(int wheels) { this.wheels = wheels; } public double getWeight() { return weight; } public void setWeight(double weight) { this.weight = weight; } //构造方法 public Vehicle(int wheels, double weight) { super(); this.wheels = wheels; this.weight = weight; } }
package car; public class Car extends Vehicle { // 定义新的成员变量 private int loader; public int getLoader() { return loader; } public void setLoader(int loader) { this.loader = loader; } // 调用父类构造方法 public Car(int wheels, double weight,int loader) { super(wheels, weight); this.loader=loader; } }
package car; public class Truck extends Car { //添加新的成员变量 private double payload; public double getPayload() { return payload; } public void setPayload(double payload) { this.payload = payload; } //调用父类构造方法 public Truck(int wheels, double weight, int loader, double payload ) { super(wheels, weight, loader); this.payload=payload; } }
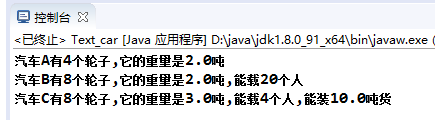
package car; public class Text_car { public static void main(String[] args) { //实例化Vehicle对象 Vehicle v= new Vehicle(4,2); System.out.println("汽车A有"+v.getWheels()+"个轮子,它的重量是"+v.getWeight()+"吨"); //实例化car对象 Car c = new Car(8,2,20); System.out.println("汽车B有"+c.getWheels()+"个轮子,它的重量是"+c.getWeight()+"吨,能载"+c.getLoader()+"个人"); //实例化Truck对象 Truck t= new Truck(8,3,4,10); System.out.println("汽车C有"+t.getWheels()+"个轮子,它的重量是"+t.getWeight()+"吨,能载"+t.getLoader()+"个人,能装"+t.getPayload()+"吨货"); } }