一、哈希表概述
1、散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
2、散列函数:用于将键映射到特定的桶,理想的散列函数,将键均匀分布在哈希桶中,最大程度地减少散列冲突(哈希碰撞)。散列函数,常用取余法,即将key对base取余,对应的余数为哈希桶的索引;base通常取质数,可以尽量保证key均匀分布在哈希桶中;哈希桶的数量为base。
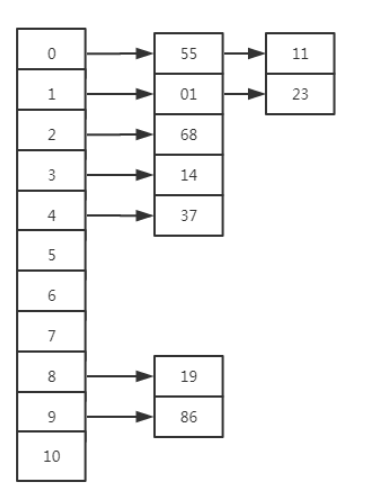
3、散列冲突:不同的键通过哈希函数映射到同一个哈希桶中。解决散列冲突,常用拉链法和开放定址法(线性探测法)。拉链法,是指产生hash冲突后在存储数据后面加一个指针,指向后面冲突的数据,如下图:
二、手动设计哈希集合与哈希映射
leetcode_705. 设计哈希集合哈希集合:
struct List {
int val;
struct List *next;
};
void listPush(struct List *head, int key)
{
// 头插法
struct List *temp = (struct List *)malloc(sizeof(struct List));
temp->val = key;
temp->next = head->next;
head->next = temp;
}
void listDelete(struct List *head, int key)
{
struct List *temp = head;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
if (temp->next->val == key) {
struct List *node = temp->next;
temp->next = node->next;
free(node);
return;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
}
bool listContain(struct List *head, int key)
{
struct List *temp = head->next;
while (temp != NULL) {
if (temp->val == key) {
return true;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
return false;
}
void listFree(struct List *head)
{
struct List *temp = NULL;
while (head->next != NULL) {
temp = head->next;
head->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
}
const int base = 769;
int hash(int key) {
return key % base;
}
typedef struct {
struct List *data;
} MyHashSet;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyHashSet* myHashSetCreate() {
// 拉链法
MyHashSet *obj = (MyHashSet*)malloc(sizeof(MyHashSet));
obj->data = (struct List*)malloc(sizeof(struct List) * base);
for (int i = 0; i < base; i++) {
// 头节点不参加判断,赋任意值,不影响
obj->data[i].val = 0;
obj->data[i].next = NULL;
}
return obj;
}
void myHashSetAdd(MyHashSet* obj, int key) {
int h = hash(key);
if (listContain(&(obj->data[h]), key) != true) {
listPush(&(obj->data[h]), key);
}
}
void myHashSetRemove(MyHashSet* obj, int key) {
int h = hash(key);
listDelete(&(obj->data[h]), key);
}
/** Returns true if this set contains the specified element */
bool myHashSetContains(MyHashSet* obj, int key) {
int h = hash(key);
return listContain(&(obj->data[h]), key);
}
void myHashSetFree(MyHashSet* obj) {
for (int i = 0; i < base; i++) {
listFree(&(obj->data[i]));
}
free(obj->data);
}
/**
* Your MyHashSet struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyHashSet* obj = myHashSetCreate();
* myHashSetAdd(obj, key);
* myHashSetRemove(obj, key);
* bool param_3 = myHashSetContains(obj, key);
* myHashSetFree(obj);
*/
leetcode_706. 设计哈希映射
struct List {
int key;
int val;
struct List *next;
};
void hashMapPut(struct List *head, int key, int val)
{
// 头插法
struct List *temp = head->next;
while (temp != NULL) {
if (temp->key == key) {
return temp->val = val;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
struct List *node = (struct List *)malloc(sizeof(struct List));
node->key = key;
node->val = val;
node->next = head->next;
head->next = node;
}
int hashMapGet(struct List *head, int key)
{
struct List *temp = head->next;
while (temp != NULL) {
if (temp->key == key) {
return temp->val;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
return -1;
}
void hashMapRemove(struct List *head, int key)
{
struct List *temp = NULL;
while (head->next != NULL) {
if (head->next->key == key) {
temp = head->next;
head->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
return;
}
head = head->next;
}
}
void hashMapFree(struct List *head)
{
struct List *temp = NULL;
while (head->next != NULL) {
temp = head->next;
head->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
}
const int base = 769;
int hash(int key)
{
return key % 769;
}
typedef struct {
struct List *data;
} MyHashMap;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyHashMap* myHashMapCreate() {
MyHashMap *obj = (MyHashMap*)malloc(sizeof(MyHashMap));
obj->data = (struct List*)malloc(base * sizeof(struct List));
for (int i = 0; i < base; i++) {
obj->data[i].key = 0;
obj->data[i].val = 0;
obj->data[i].next = NULL;
}
return obj;
}
/** value will always be non-negative. */
void myHashMapPut(MyHashMap* obj, int key, int value) {
int h = hash(key);
hashMapPut(&(obj->data[h]), key, value);
}
/** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or -1 if this map contains no mapping for the key */
int myHashMapGet(MyHashMap* obj, int key) {
int h = hash(key);
return hashMapGet(&(obj->data[h]), key);
}
/** Removes the mapping of the specified value key if this map contains a mapping for the key */
void myHashMapRemove(MyHashMap* obj, int key) {
int h = hash(key);
hashMapRemove(&(obj->data[h]), key);
}
void myHashMapFree(MyHashMap* obj) {
for (int i = 0; i < base; i++) {
hashMapFree(&(obj->data[i]));
}
free(obj->data);
}
/**
* Your MyHashMap struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyHashMap* obj = myHashMapCreate();
* myHashMapPut(obj, key, value);
* int param_2 = myHashMapGet(obj, key);
* myHashMapRemove(obj, key);
* myHashMapFree(obj);
*/
三、ustash使用
1、概述
(1)ustash是C语言中哈希函数集合,本质上是一组宏定义;使用时需要包含头文件uthash.h;
(2)常用结构体:
typedef struct {
int id;
int val;
UT_hash_handle hh; // 必须定义
} HASH_TABLE;
(3)常用宏定义:
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/fan_h_l/article/details/107241520
增加元素:HASH_ADD_INT
查找元素:HASH_FIND_INT
删除元素:HASH_DEL
遍历元素:HASH_ITER
统计元素:HASH_COUNT
2、leetcode_349. 两个数组的交集
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
typedef struct {
int id;
UT_hash_handle hh;
} HASH_TABLE;
int* intersection(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int* returnSize)
{
int i;
int count = 0;
// 指针必须初始化
HASH_TABLE *table1 = NULL;
HASH_TABLE *table2 = NULL;
HASH_TABLE *temp= NULL;
*returnSize = 0;
for(i = 0; i < nums1Size; i++) {
HASH_FIND_INT(table1, &(nums1[i]), temp);
if (temp != NULL) {
continue;
}
temp = (HASH_TABLE*)malloc(sizeof(HASH_TABLE));
temp->id = nums1[i];
HASH_ADD_INT(table1, id, temp);
}
for(i = 0; i < nums2Size; i++) {
HASH_FIND_INT(table2, &(nums2[i]), temp);
if (temp != NULL) {
continue;
}
HASH_FIND_INT(table1, &(nums2[i]), temp);
if (temp == NULL) {
continue;
}
temp = (HASH_TABLE*)malloc(sizeof(HASH_TABLE));
temp->id = nums2[i];
HASH_ADD_INT(table2, id, temp);
count++;
}
int *ret = (int*)malloc(count * sizeof(int));
for (temp = table2, i = 0; temp != NULL; temp = (HASH_TABLE*)temp->hh.next) {
ret[i++] = temp->id;
}
*returnSize = count;
return ret;
}