原题链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4587
TWO NODES
Time Limit: 24000/12000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1448 Accepted Submission(s): 441
Problem Description
Suppose that G is an undirected graph, and the value of stab is defined as follows:
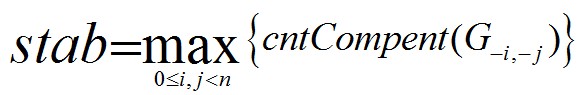
Among the expression,G-i, -j is the remainder after removing node i, node j and all edges that are directly relevant to the previous two nodes. cntCompent is the number of connected components of X independently.
Thus, given a certain undirected graph G, you are supposed to calculating the value of stab.
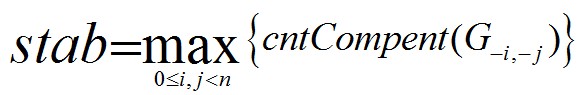
Among the expression,G-i, -j is the remainder after removing node i, node j and all edges that are directly relevant to the previous two nodes. cntCompent is the number of connected components of X independently.
Thus, given a certain undirected graph G, you are supposed to calculating the value of stab.
Input
The input will contain the description of several graphs. For each graph, the description consist of an integer N for the number of nodes, an integer M for the number of edges, and M pairs of integers for edges (3<=N,M<=5000).
Please note that the endpoints of edge is marked in the range of [0,N-1], and input cases ends with EOF.
Please note that the endpoints of edge is marked in the range of [0,N-1], and input cases ends with EOF.
Output
For each graph in the input, you should output the value of stab.
Sample Input
4 5
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 0
0 2
Sample Output
2
Source
Recommend
zhuyuanchen520
题意
给你个图,问你去掉两个点之后能有最多多少连通块。
题解
先枚举其中一个点,然后在剩下的点中求割点,Tarjan的时候统计一下每个割点分割几个连通块,取个最大的割点,然后再dfs一次求连通块个数。
代码
#include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #define MAX_N 5555 using namespace std; vector<int> G[MAX_N]; bool vis[MAX_N]; int dfn[MAX_N],low[MAX_N],ind=0; int cut[MAX_N]; int node; void Tarjan(int u,int p){ int child=0; dfn[u]=low[u]=++ind; vis[u]=1; for(int i=0;i<G[u].size();i++){ int v=G[u][i]; if(v==p||v==node)continue; if(!vis[v]){ Tarjan(v,u); low[u]=min(low[v],low[u]); child++; if((p==-1&&child>1)||(p!=-1&&low[v]>=dfn[u])) cut[u]++; } else low[u]=min(dfn[v],low[u]); } } int n,m; void init(){ for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)G[i].clear(); ind=0; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); memset(cut,0,sizeof(cut)); } bool used[MAX_N]; int cu; void dfs(int u,int p){ if(u==p||used[u]||u==node||u==cu)return; used[u]=1; for(int i=0;i<G[u].size();i++)dfs(G[u][i],u); } int main(){ while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)==2){ int stab=1; init(); int u,v; for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); G[u].push_back(v); G[v].push_back(u); } for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ node=i; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); ind=0; memset(cut,0,sizeof(cut)); for(int j=0;j<n;j++) if((!vis[j])&&j!=node) Tarjan(j,-1); int maxC=0; for(int j=0;j<n;j++) if(j!=node&&cut[j]>=maxC){ cu=j; maxC=cut[j]; } int ans=0; memset(used,0,sizeof(used)); for(int j=0;j<n;j++) if((!used[j])&&j!=node&&j!=cu){ dfs(j,-1); ans++; } stab=max(stab,ans); } printf("%d ",stab); } return 0; }