更新记录
- 2020年3月28日,初稿
源码地址
- CocoaPods/CocoaPods
- Pod是由Ruby实现的,所以想要读懂源码,还需要先了解一下Ruby的源码
源码运行过程(含注释),即输入Pod install(或update)的执行过程
前置环节-生成对应的Command子类对象(例如Install类和Update类)
- Pod::Command的run类方法
def self.run(argv)
help! 'You cannot run CocoaPods as root.' if Process.uid == 0 && !Gem.win_platform?
verify_minimum_git_version!
verify_xcode_license_approved!
super(argv)
ensure
UI.print_warnings
end
- CLAide::Command类的run方法
def self.run(argv = [])
plugin_prefixes.each do |plugin_prefix|
PluginManager.load_plugins(plugin_prefix)
end
argv = ARGV.coerce(argv)
#通过参数生成一个Command类的子类对象
command = parse(argv)
ANSI.disabled = !command.ansi_output?
unless command.handle_root_options(argv)
command.validate!
# 调用comman类子类对象的run方法
command.run
end
rescue Object => exception
handle_exception(command, exception)
end
- CLAide::Command类的parse方法
# @param [Array, ARGV] argv
# A list of (remaining) parameters.
#
# @return [Command] An instance of the command class that was matched by
# going through the arguments in the parameters and drilling down
# command classes.
#
def self.parse(argv)self.run
argv = ARGV.coerce(argv)
# 得到第一个参数
cmd = argv.arguments.first
if cmd && subcommand = find_subcommand(cmd)
argv.shift_argument
subcommand.parse(argv)
elsif abstract_command? && default_subcommand
load_default_subcommand(argv)
else
new(argv)
end
end
3.1 CLAide::Command类的argument方法
# @return [Array<Argument>]
# A list of arguments the command handles. This is shown
# in the usage section of the command’s help banner.
# Each Argument in the array represents an argument by its name
# (or list of alternatives) and whether it's required or optional
#
def arguments
# 如果@arguments不为空,则返回@arguments,否则返回空数组
@arguments ||= []
end
3.2 CLAide::Command类的find_subcommand方法
# Searches the list of subcommands that should not be ignored for command
# lookup for a subcommand with the given `name`.
#
# @param [String] name
# The name of the subcommand to be found.
#
# @return [CLAide::Command, nil] The subcommand, if found.
#
def self.find_subcommand(name)
subcommands_for_command_lookup.find { |sc| sc.command == name }
end
3.3 通过 find_subcommand 找到对应的子类对象,然后调用子类对象的parse方法(subcommand.parse(argv))
def self.parse(argv)
entries = []
#对argv数组的每个值进行to_s的表达式操作,生成一个新的数组,存储到copy变量中
copy = argv.map(&:to_s)
double_dash = false
#shift返回数组的第一个元素,并且移除该元素。类比stack的pop函数
while argument = copy.shift
# if为真,直接进入下次循环
next if !double_dash && double_dash = (argument == '--')
type = double_dash ? :arg : argument_type(argument)
parsed_argument = parse_argument(type, argument)
entries << [type, parsed_argument]
end
entries
end
实际pod主流程的核心环节(调用Installer类的install函数)
- 看到 CocoaPods/lib/cocoapods/command/install.rb中Install类的run方法
def run
verify_podfile_exists!
installer = installer_for_config
installer.repo_update = repo_update?(:default => false)
installer.update = false
installer.deployment = @deployment
installer.clean_install = @clean_install
installer.install!
end
- 我们对比一下 CocoaPods/lib/cocoapods/command/update.rb中Update类的run方法
def run
verify_podfile_exists!
installer = installer_for_config
installer.repo_update = repo_update?(:default => true)
installer.clean_install = @clean_install
if @pods.any? || @excluded_pods.any? || @source_pods.any?
verify_lockfile_exists!
verify_pods_are_installed!
verify_excluded_pods_are_installed!
@pods += @source_pods.select { |pod| config.lockfile.pod_names.include?(pod) }
@pods = config.lockfile.pod_names.dup if @pods.empty?
@pods -= @excluded_pods
installer.update = { :pods => @pods }
else
UI.puts 'Update all pods'.yellow
installer.update = true
end
installer.install!
end
- 对比Install类和Update类的run方法,我们发现
- 相同点
- 最后都会调用Installer类的
install!函数
- 最后都会调用Installer类的
- 明显的不同点
- Install命令类的
repo_update属性为false,Update命令类的repo_update函数为true - Install命令类的
update属性为false,Update命令类的update函数为true
- Install命令类的
- 相同点
- 参考Podfile.lock背后的那点事,我们可以提前知道
update变量的值,区分了Installer调用install函数下,使用pod install和pod update的场景。
本篇结论
- 本篇分析执行Pod install或者update的前几个步骤,主要是通过命令行参数(install或者update)的解析,实例化不同的
Command子类对象。 - install和update参数的命令执行,最后都会进入Installer类的install函数,执行核心的依赖库安装过程。
- Installer类的install函数,是通过update的值,来判断两种不同的场景(即update和install)来进行不同的操作
- 另附上简单版(真的是简单版,别见怪)类图,流程图
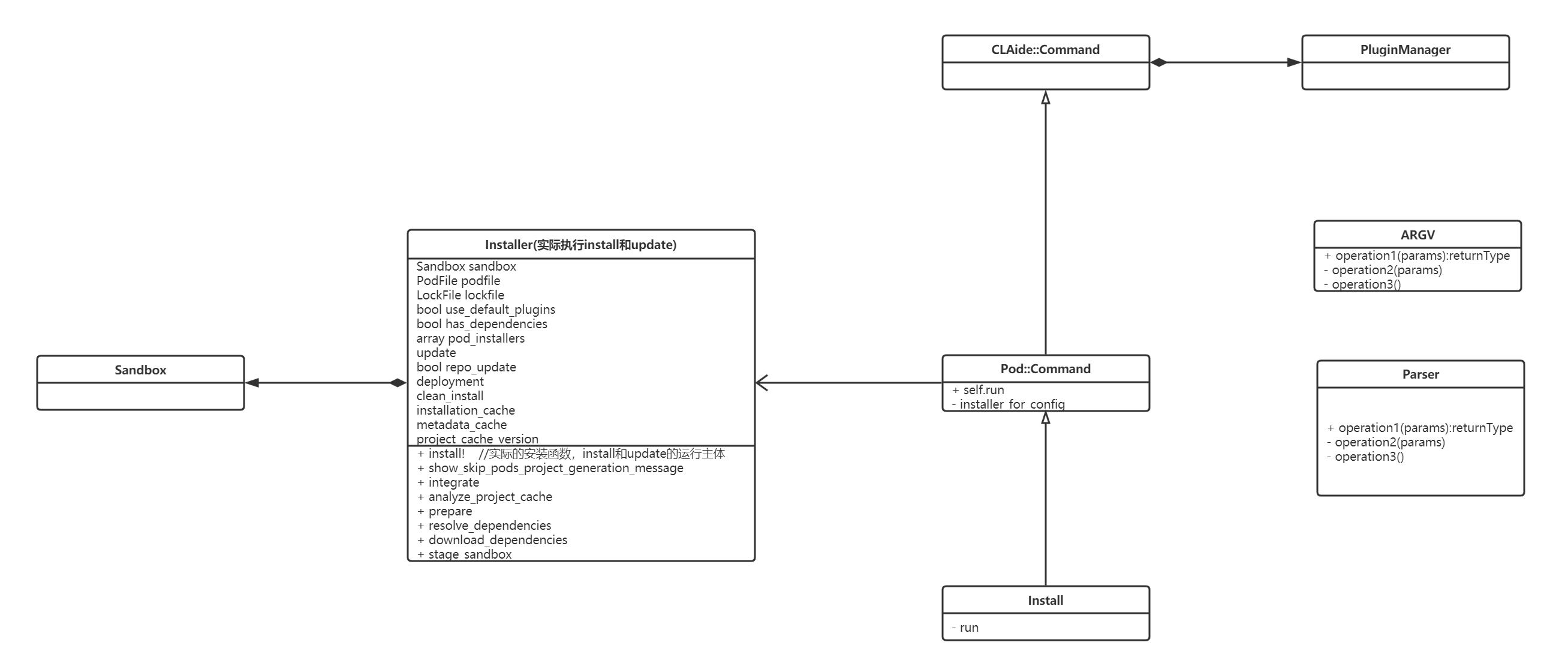
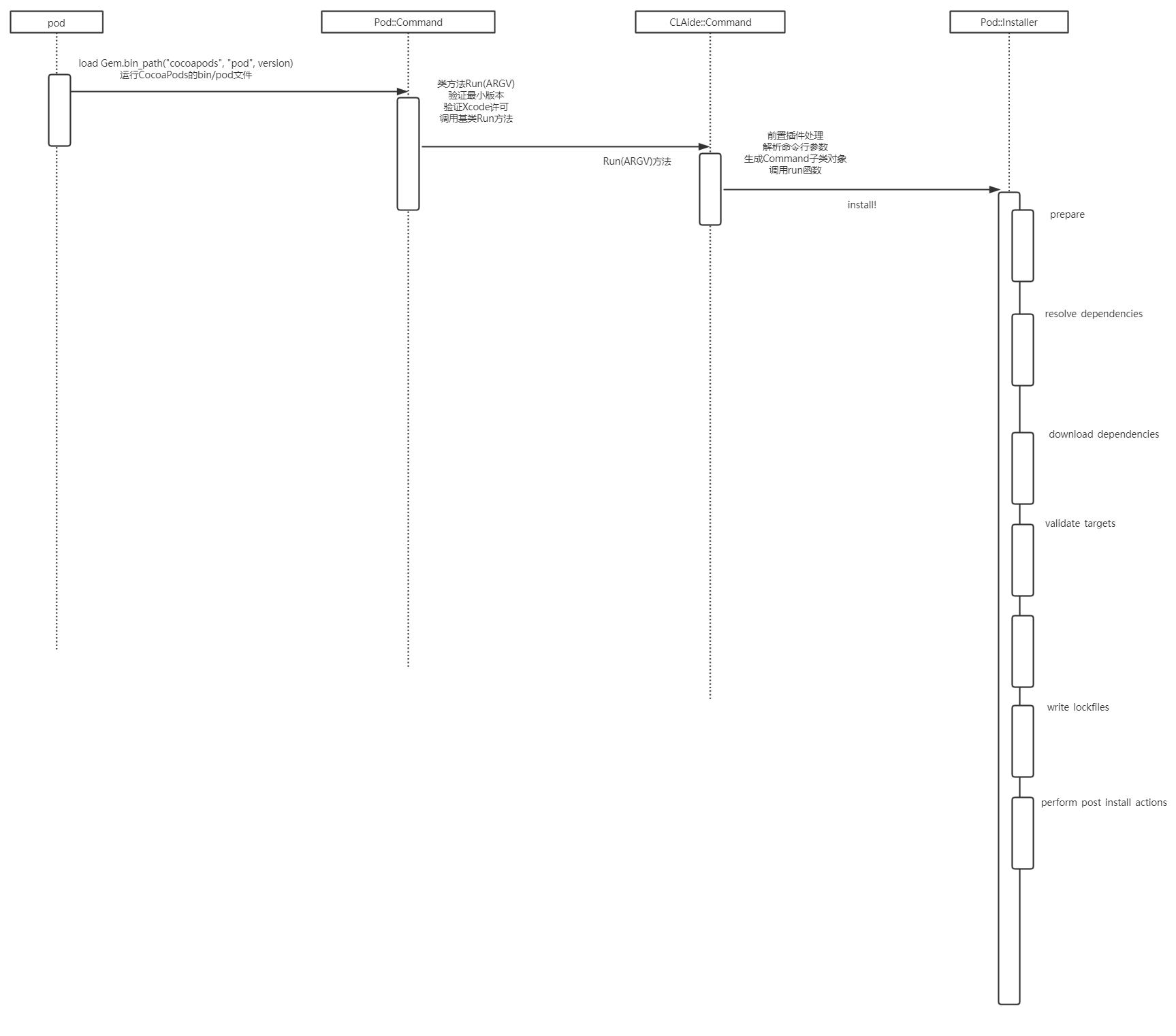
写在后面的话
- 鉴于篇幅已较长,为了有较好的阅读体验(避免文章分析过长,很多读者其实都没有耐心看下去),而且自己也不能一下子完全捋清楚,所以第一篇到此为止。
- 后续会从该篇的节点继续往下分析
- 后续还需要分析的点
- Installer类中的update属性如何使用?如何具体地区别install和update两种场景?
- PodFile.lock文件有何作用?
- Pod如何解析PodFile文件的?
- Pod.spec文件有何作用?
- Pod是如何集成Xcode工程的?