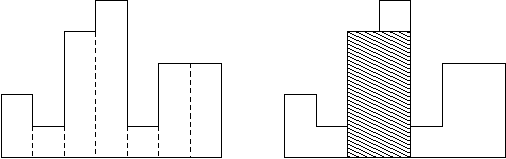
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
|
思路 |
题目大意:就是求最大的矩形面积。 解决方法:把i前面大于等于它的数下标记下来left[],把它后面比他大的数的下标记下来right[],在一次比较面积的大小。 |
|
源码 |
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> __int64 h[100005], left[100005], right[100005]; int main() { int i, j, k, n, temp; while(scanf("%d", &n)==1&&n) { memset(h, 0, sizeof(h)); memset(left, 0, sizeof(left)); memset(right, 0, sizeof(right)); for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { scanf("%I64d", &h[i]); left[i]=right[i]=i; } for(i=2; i<=n; i++) { temp=i; while(h[temp-1]>=h[i]&&temp>1) temp=left[temp-1]; left[i]=temp; } for(i=n-1; i>0; i--) { temp=i; while(h[temp+1]>=h[i]&&temp<n) temp=right[temp+1]; right[i]=temp; } __int64 area=0; for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { if((__int64)((right[i]-left[i]+1)*h[i])>area) area=(right[i]-left[i]+1)*h[i]; } printf("%I64d\n", area); } } |