- 正如标题所示:这篇复习带有指针类型成员的class
设计类
考虑到会有以下操作,来设计类
1 { 2 String s1(); 3 String s2("hello"); 4 String s3(s1); 5 cout << s3 << endl; 6 s3 = s2; 7 cout << s3 << endl; 8 }
函数体内第二行和第三行都是构造函数,一个含参数,一个不含参数。第四行创建一个以s1为初值的对象s3,是一个拷贝的动作,需要一个拷贝构造函数,之后会讲到;下一行是输出,需要一个操作符重载。第六行是一个赋值的操作,是一个拷贝的动作,这样第四行和第六行都是拷贝动作,所以这两个操作需要的是不同的函数,第六行需要的是拷贝赋值操作。如果,我们自己不写,编译器会给出默认的这两个操作函数,像上个复数的例子,就使用编译器给的,而这个string的例子,使用默认的就会出现不好的,想象一下,我们现在有个指针对象,指向一个地址,现在又创建一个新的对象,若只是拷贝,把指针拷贝过来,指向了同一个地方去,这并不是真正的拷贝,所以,只要class中含有带指针的成员,就不要使用默认的拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值操作。so,string类的大致设计如下:
1 class String { 2 public: 3 String(const char* cstr = 0);//construct func 4 //if only the calss with pointer pamater(s),we need design two functions as follow 5 String(const String& str);//copy construct func,the parameter type is itsown type 6 String& operator=(const String& str);//copy assign,the parameter is itsown type 7 8 ~String(); 9 char* get_c_str()const { return m_data; } 10 private: 11 char* m_data;//因为字符串长度不定,所以设置成动态的数组-指针 12 };
设计类内函数
构造函数和析构函数
1 inline 2 String::String(const char* cstr = 0) 3 { 4 if (cstr) {//有初值 5 m_data = new char[strlen(cstr + 1)]; 6 strcpy(m_data, cstr); 7 } 8 else { 9 m_data = new char[1]; 10 *m_data = '�'; 11 } 12 } 13 14 inline 15 String::~String() 16 { 17 delete[] m_data;//clean up 18 }
使用上述函数
{ String s1(); String s2("hello"); String* p = new String("hello"); delete p;//离开前,释放掉 }
前面两个,离开时会自动释放掉,也是调用析构函数,所以上述函数作用域内离开时会调用三次析构函数
先前的复数类,不需要清理,因为它们本来就要死亡了,所以不必要,但是,这里是动态分配内存,如果不释放的,就是内存泄漏了。so ,Note:如果class中含指针成员,多半要动态分配内存,那么对象死亡之前,就是析构函数调用时,将动态分配的内存释放掉
拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值操作
class with pointer member(s),一定要这样做,看下面的图片(来源于侯捷老师的课件)
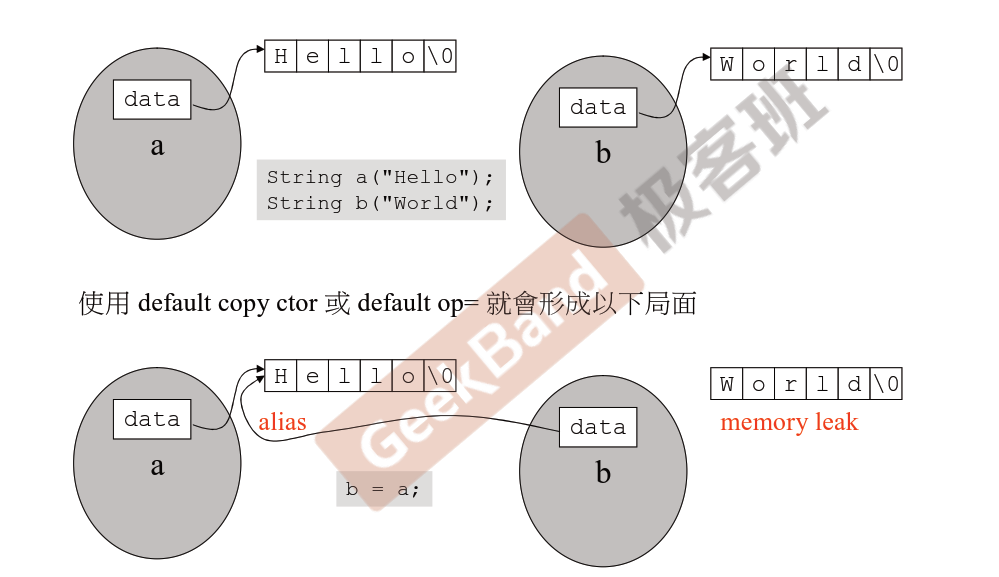
首先,看第一种情况(第二幅图),使用default copy construct function,对象的data是指针,至于指针中的内容(‘hello’)是不属于这个指针的,在做copy动作的时候,b也也只是指针,所以两个指针指向同一块内容了。虽然a和b 也有相同内容了,但是b中内容,没有指针指向它了,而此处‘hello‘’所在的内存块,有两个指针同时指向它了,将来若改变a,b指向的内容也会被改变。,着就是浅拷贝;与之对应的就是深拷贝,就是我们自己写的函数要做的操作.下面看看什么是深拷贝
//copy construct fuction inline String::String(const String& str) { m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1]; strcpy(m_data, str.m_data); }
使用:
String s3(s1);
这里s3也是新创建出来的对象,就要调用构造函数,先开辟足够的空间,然后将要拷贝的内容拷贝进来,这就是深拷贝,如果使用编译器默认的拷贝构造函数,只是把指针拷贝过来
拷贝赋值操作操作
要把右边的东西赋值给左边(Note:左右都有东西),正常思路就是先把左边清空,然后创建出与右边一样大的空间,再将右边内容拷贝给左边,so,实现如下:
inline String& String::operator=(const String& str) { if (this == &str)//self assignment or not return *this; delete[] m_data;//kill m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1]; strcpy(m_data, str.m_data); return *this; } //使用 String s4=s1;
output 函数
#include <iostream> #include "string.h" using namespace std; ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const String& str) { os << str.get_c_str(); return os; } //使用 String s1("Hello"); cout<<s1;
output 函数,必须为全域函数,这样才能保证是左边调用“<<”
总结
下面,我们回顾一下String 类的设计,设计一个class,首先,我们考虑class中需要什么样的数据,这里是字符串,我们字符串中会存放很多字符,当然,我们很容易想到使用数组存放,但是,对于设计字符串却不是一个好的选择,因为,数组声明时必须要指定数组大小,所以,我们选择指针,将来放多大的内容,使用new的方式动态分配大小,在32位系统中,一个指针占4个byte,所以不管字符串多大,字符串这个对象本身就是4byte;Then,考虑设计哪些函数,构造函数,前面讲过了,这里不多讲;上面讲过了,因为成员是指针,所以需要设计拷贝构造函数、拷贝赋值操作函数,析构函数(Big Three),设计完这三个函数后,再思考还需要设计哪些函数,由于,我们需要输出字符串,即需要cout,,所以,我们需要取出m_data中的字符,cout是可以接收这种东西的,所以,设计 char* get_c_str() const {return m_data;} ,只是返回,不改变,所以设计成const型的。
下面是完整的String类的设计的头文件

1 #pragma once 2 #ifndef __STRING__ 3 #define __STRING__ 4 #include <cstring> 5 class String { 6 public: 7 String(const char* cstr = 0);//construct func 8 //if only the calss with pointer pamater(s),we need design two functions as follow 9 String(const String& str);//copy construct func,the parameter type is itsown type 10 String& operator=(const String& str);//copy assign,the parameter is itsown type 11 12 ~String(); 13 char* get_c_str()const { return m_data; } 14 private: 15 char* m_data;//因为字符串长度不定,所以设置成动态的数组-指针 16 }; 17 18 inline 19 String::String(const char* cstr = 0) 20 { 21 if (cstr) {//有初值 22 m_data = new char[strlen(cstr + 1)]; 23 strcpy(m_data, cstr); 24 } 25 else { 26 m_data = new char[1]; 27 *m_data = '�'; 28 } 29 } 30 31 inline 32 String::~String() 33 { 34 delete[] m_data;//clean up 35 } 36 //copy construct fuction 37 inline 38 String::String(const String& str) 39 { 40 m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1]; 41 strcpy(m_data, str.m_data); 42 } 43 44 inline 45 String& String::operator=(const String& str)//String&:& is reference 46 { 47 if (this == &str)//self assignment or not,&str:& is getting address 48 return *this; 49 delete[] m_data;//kill 50 m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1]; 51 strcpy(m_data, str.m_data); 52 return *this; 53 } 54 #endif
