作者:小土豆biubiubiu
掘金:https://juejin.im/user/58c61b4361ff4b005d9e894d
简书:https://www.jianshu.com/u/cb1c3884e6d5
微信公众号:土豆妈的碎碎念(扫码关注,一起吸猫,一起听故事,一起学习前端技术)
码字不易,点赞鼓励哟~
一.前言
上一篇文章《Vuex入门实践(上)》,我们一共实践了vuex的这些内容:
1.在state中定义共享属性,在组件中可使用[$store.state.属性名]访问共享属性
2.在mutations可中定义修改共享数据的方法,在组件中可使用[$store.commit('方法名')]同步修改共享属性
3.在actions中可定义异步修改共享数据的方法,在组件中可使用[$store.dispatch('方法名')]异步修改共享属性
4.在getters中可定义共享数据的计算属性,在组件中可使用[$store.getters.计算属性名]访问共享数据的计算属性
这篇文章接着实践和探究vuex的奥秘。
二.创建多个store模块
前面的文章中,我们在vuex的实例方法Store上分别创建了state、mutations、actions和getters这几个配置选项。
可以思考一下,当我们的应用程序愈加复杂时,组件之间需要共享的数据也在持续增加,那么state、mutations、actions和getters配置项里面的代码会愈加庞大。
因此为解决此问题,vuex支持每个模块定义自己的state、mutations、actions和getters。
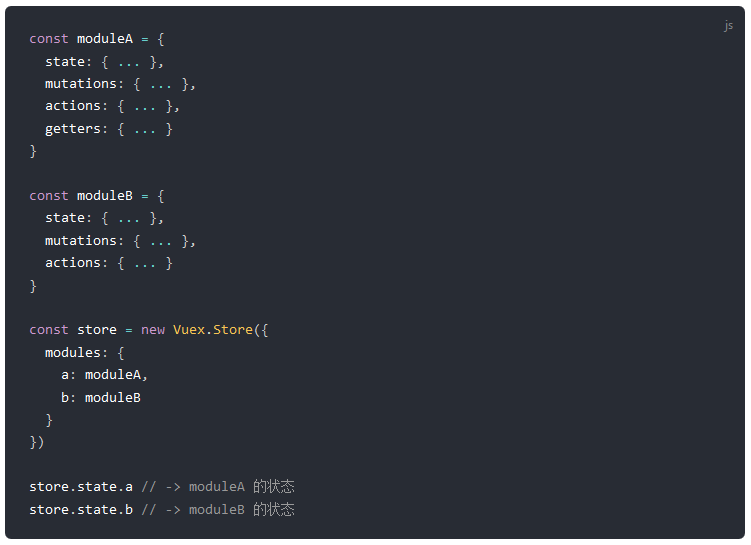
1.多个Module配置
现在我们来实践一下多个module。首先我们在E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuex目录下新建两个文件:moduleA.js和moduleB.js。
现在,我们分别编辑这两个文件的state、mutations、actions和getters配置项。
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleA.js
const moduleA = {
state:{
counter: 100
},
mutations: {
//递增
increase(state) {
state.counter++
},
//递减
decrement(state) {
state.counter--
}
},
actions: {
increaseAction(context) {
setTimeout(function(){
//action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态
context.commit('increase');
},3000)
},
decrementAction(context){
setTimeout(function(){
//action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态
context.commit('decrement');
},3000)
}
},
getters: {
doubleCounter(state) {
return state.counter*state.counter
}
}
}
export default moduleA
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleB.js
const moduleB = {
state:{
counter: 5
},
mutations: {
//递增
increase(state) {
state.counter++
},
//递减
decrement(state) {
state.counter--
}
},
actions: {
increaseAction(context) {
setTimeout(function(){
//action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态
context.commit('increase');
},3000)
},
decrementAction(context){
setTimeout(function(){
//action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态
context.commit('decrement');
},3000)
}
},
getters: {
doubleCounter(state){
return state.counter*state.counter
}
}
}
export default moduleB
可以看到每个module定义自己的state、mutations、actions和getters和直接写在store.js中的语法相差无几,只是单个module无需将这些选项挂载到vuex实例的Store方法上。
接着我们在store.js中编写该模块的state、mutations、actions和getters,并且配置这两个module
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexstore.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import moduleA from './moduleA'
import moduleB from './moduleB'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
counter: 1000
},
mutations: {
//递增
increase(state) {
state.counter++
},
//递减
decrement(state) {
state.counter--
}
},
actions: {
increaseAction(context) {
setTimeout(function(){
//action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态
context.commit('increase');
},3000)
},
decrementAction(context){
setTimeout(function(){
//action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态
context.commit('decrement');
},3000)
}
},
getters: {
doubleCounter(state) {
return state.counter*state.counter
}
},
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.js中对多个module的配置语法也比较简单,即在modules中以字典的形式【模块名:模块引用】写入即可。其余配置state、mutations、actions和getters的方法和前面的一模一样。
vuex多个module的配置完成,现在我们分别按顺序访问store模块、a模块和b模块的共享数据、同步/异步修改共享数据以及计算属性访问。
2.多个Module-共享数据访问
多个Module这种情况下,state中共享数据的访问被绑定在模块上(模块内部的state是局部的,只属于模块本身),因此我们需要使用【$store.state.模块名称】去访问不同模块的共享数据。
而对于store.js这个根模块配置的state数据,直接使用【$store.state】访问即可。
那么访问store根模块counter的逻辑:$store.state.counter;访问a模块counter的逻辑为:$store.state.a.counter;访问b模块的counter的逻辑为:$store.state.b.counter。
现在我们分别在App.vue组件中访问store.js这个根模块的counter和a模块的counter数据,在Index.vue组件中访问b模块的counter数据。
(在那个组件中访问那个模块的state无所谓,也可以舍弃Index.vue,将所有代码都写在App.vue组件中)
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcApp.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<!-- 获取共享数据 -->
<h1>这里是App组件</h1>
<h3> App组件获取共享数据 </h3>
<h3>访问根模块counter——$store.state.counter : {{ $store.state.counter }} </h3>
<h3>访问a模块counter——$store.state.a.counter : {{ $store.state.a.counter }} </h3>
<hr/>
<Index></Index>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Index from './components/Index'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { Index }
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrccomponentsIndex.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>这里是Index.vue组件</h1>
<h3>Index组件获取共享数据 </h3>
<h3>访问b模块counter——$store.state.b.counter :{{ $store.state.b.counter }}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Index'
}
</script>
最后我们启动项目查看一下结果

可以看到,我们已经成功的访问到了根模块的counter数据、a模块的counter数据以及b模块的counter数据。
3.多个Module-同步修改共享数据
现在,我们需要在App.vue组件中同步修改store根模块的数据和a模块的数据,在Index.vue组件中同步修改b模块的数据。
前面我们说了state绑定在模块上,那mutations它并没有和模块绑定。
那么根据《vuex入门实践(上)》这一篇文章中的总结,能想到触发counter递增的方法为$store.commit(‘increase’)。
由于根store模块、a模块、b模块中使counter递增和递减的mutation方法名都是一模一样的,那会出现什么样的结果呢?
我们来试一下。
首先在根store模块、a模块、b模块中的mutation increase中添加打印console.log的打印信息,其余代码沿用前面的保存不变
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexstore.js
//递增
increase(state) {
console.log("store-increase")
state.counter++
}
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleA.js
//递增
increase(state) {
console.log("moduleA-increase")
state.counter++
},
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleB.js
//递增
increase(state) {
console.log("moduleB-increase")
state.counter++
},
接着编写App.vue和Index.vue的代码
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcApp.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<!-- 获取共享数据 -->
<h1>这里是App组件</h1>
<h3> App组件获取共享数据 </h3>
<h3>访问根模块counter——$store.state.counter : {{ $store.state.counter }} </h3>
<h3>访问a模块counter——$store.state.a.counter : {{ $store.state.a.counter }} </h3>
<h3>同步修改根模块counter:<button @click="$store.commit('increase')">同步修改根模块counter</button></h3>
<h3>同步修改a模块counter:<button @click="$store.commit('increase')">同步修改a模块counter</button></h3>
<hr/>
<Index></Index>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Index from './components/Index'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { Index }
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrccomponentsIndex.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>这里是Index.vue组件</h1>
<h3>Index组件获取共享数据 </h3>
<h3>访问b模块counter——$store.state.b.counter :{{ $store.state.b.counter }}</h3>
<h3>同步修改b模块counter:<button @click="$store.commit('increase')">同步修改b模块counter</button></h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Index'
}
</script>
最后我们来看下效果
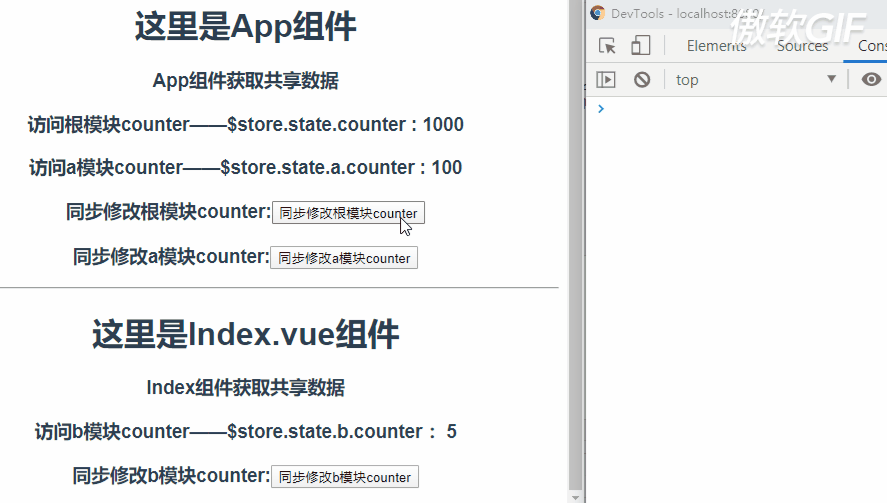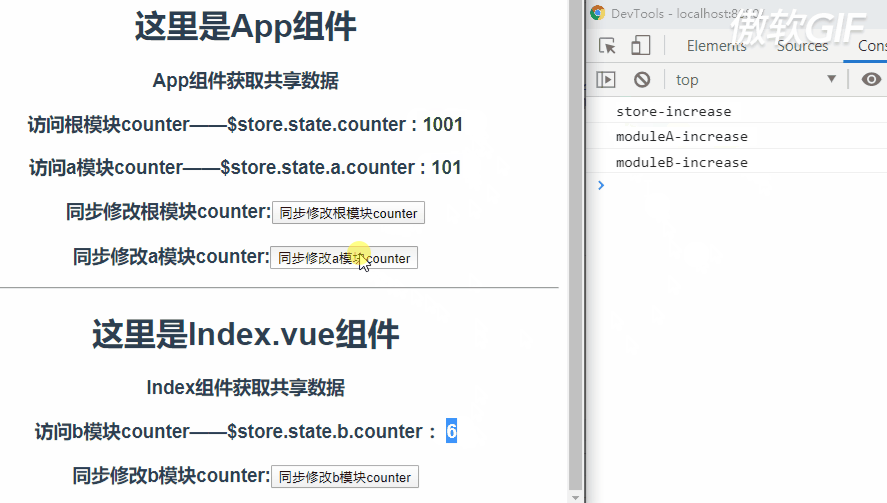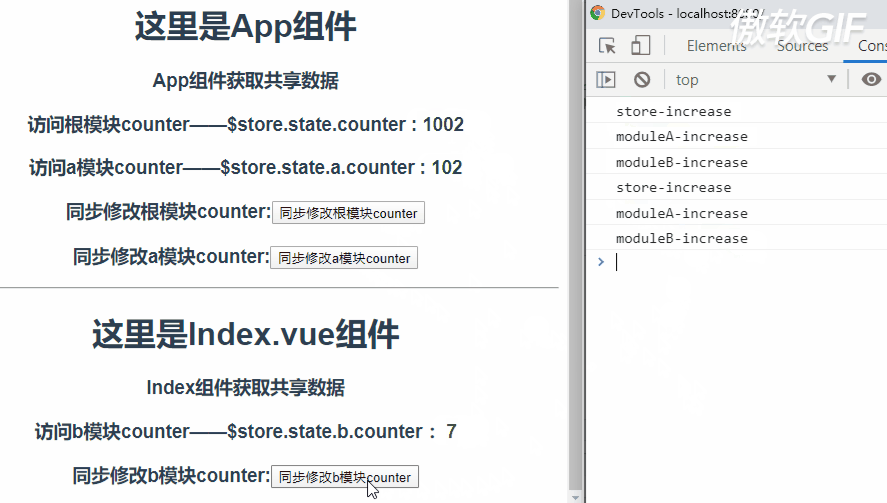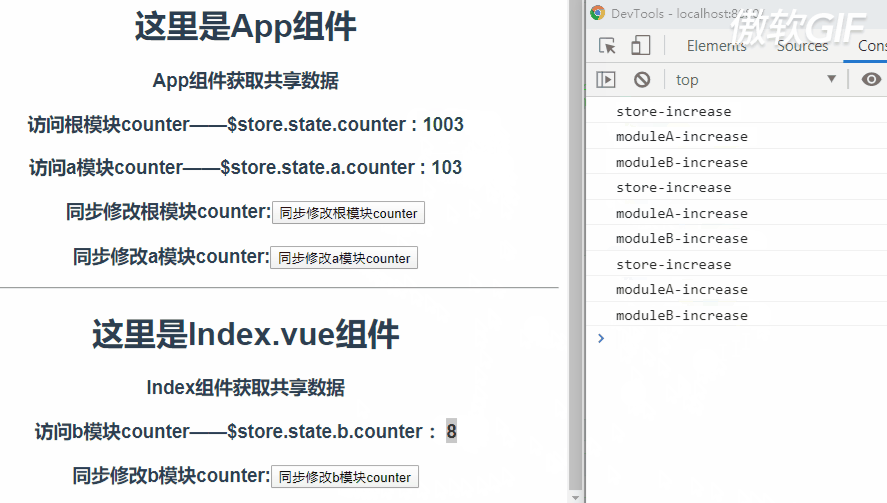
那么现象就是,执行一次$store.commit('increase')会依次触发store根模块、a模块和b模块mutation中increase的执行。
所以看到当点击button时这三个模块的counter都会加1。
关于触发increase的顺序呢,先是根模块,然后是根据根模块中modules的配置顺序决定的。
这个操作呢只是我自己的一个小尝试,真正多模块的mutation也不会这样去使用。
那么想避免上面问题的出现,我们可以避免多个模块中的mutation方法的重名。
我们来实践一下,store模块中mutation的increase名称不做修改,只修改a、b这两个模块。
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleA.js
mutations: {
//递增
increaseA(state) {
console.log("moduleA-increase")
state.counter++
}
},
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleB.js
mutations: {
//递增
increaseB(state) {
console.log("moduleB-increase")
state.counter++
}
},
然后对应的需要修改App.vue和Index.vue中触发mutation的代码(只贴出修改部分代码)
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcApp.vue
<h3>同步修改a模块counter:<button @click="$store.commit('increaseA')">同步修改a模块counter</button></h3>
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrccomponentsIndex.vue
<h3>同步修改b模块counter:<button @click="$store.commit('increaseB')">同步修改b模块counter</button></h3>
现在在看下效果

可以看得到不同的按钮触发了不同的模块的mutation。
那么还有一个问题,当module特别多时,其实不可避免真的会有重名的mutation,那么此时vuex的命令命名空间就需要上场了。
命名空间也很简单,就是在模块中添加一个配置namespaced:true。
现在我们来实践一下分别给模块a和模块b添加命名空间的配置,同时在把mutation中递增的方法名称统一改回increase。
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleA.js
const moduleA = { namespaced: true, state:{ counter: 100 }, mutations: { //递增 increase(state) { console.log("moduleA-increase") state.counter++ }, //递减 decrement(state) { state.counter-- } }, actions: { increaseAction(context) { setTimeout(function(){ //action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态 context.commit('increase'); },3000) }, decrementAction(context){ setTimeout(function(){ //action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态 context.commit('decrement'); },3000) } }, getters: { doubleCounter(state) { return state.counter*state.counter } } } export default moduleA
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleB.js
const moduleB = { namespaced: true, state:{ counter: 5 }, mutations: { //递增 increase(state) { console.log("moduleB-increase") state.counter++ }, //递减 decrement(state) { state.counter-- } }, actions: { increaseAction(context) { setTimeout(function(){ //action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态 context.commit('increase'); },3000) }, decrementAction(context){ setTimeout(function(){ //action通过提交mutation改变共享数据状态 context.commit('decrement'); },3000) } }, getters: { doubleCounter(state){ return state.counter*state.counter } } } export default moduleB
当有了命令空间以后,触发mutation的方法也就有了变化: $store.commit('模块名/方法')
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcApp.vue
<h3>同步修改根模块counter:<button @click="$store.commit('increase')">同步修改根模块counter</button></h3> <h3>同步修改a模块counter:<button @click="$store.commit('a/increase')">同步修改a模块counter</button></h3>
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrccomponentsIndex.vue
<h3>同步修改b模块counter:<button @click="$store.commit('b/increase')">同步修改b模块counter</button></h3>
看下结果

可以看到命名空间的效果和前面修改mutation名称不重复是同样的效果。
那么关于多模块的mutation触发就总结完了。
4.多个Module-异步修改共享数据
异步修改共享数据的逻辑和前面同步修改的相同。
我们在actions中定义了异步同名的递增和递减方法,执行一次$store.dispatch('increaseAction'),会依次触发执行store、a模块和b模块的actions。
同样我们可以选择让不同模块的actions方法名称不重复,也可以使用命名空间去解决。
这里我们只演示命名空间的方式去触发不同module的actions。
store.js、moduleA.js和moduleB.js的代码沿用上一小节的不做修改。
只需要在App.vue和Index.vue中添加$store.dispatch('increaseAction')的逻辑即可。
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcApp.vue
<h3>异步修改根模块counter:<button @click="$store.dispatch('increaseAction')">异步修改根模块counter</button></h3> <h3>异步修改a模块counter:<button @click="$store.dispatch('a/increaseAction')">异步修改a模块counter</button></h3>
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrccomponentsIndex.vue
<h3>异步修改b模块counter:<button @click="$store.dispatch('b/increaseAction')">异步修改b模块counter</button></h3>
现在我们看下结果

可以看到已经成功的触发了不同模块的actions。
5.多个Module-计算属性访问
最后一部分就是多module的getters访问了。
首先这个需要说明的是getters也没有和模块进行绑定,在我们没有给a和b模块添加命名空间namespaced:true的配置前。
因为多个模块的getters存在重名属性,因此控制台可以看到一个错误信息。

后面我们在moduleA.js和moduleB.js中添加了命令空间的配置后该错误就不会在出现。
我自己也测试了一下,同样可以像前面那样,保证getters中的属性不重名,直接使用[$store.getters.属性名]去访问不同模块的getters。
下面还是来实践一下。
store.js中getters的属性名不做修改,依然是doubleCounter。
将moduleA.js中getters的属性名改为doubleCounterA;
将moduleB.js中getters的属性名改为doubleCounterB;
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleA.js
getters: { doubleCounterA(state) { return state.counter*state.counter } }
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcvuexmoduleB.js
getters: { doubleCounterB(state) { return state.counter*state.counter } }
接着就是在App.vue和Index.vue中访问store模块、a模块和b模块的计算属性。
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcApp.vue
<h3>访问根模块getters——$store.getters.doubleCounter : {{ $store.getters.doubleCounter }} </h3> <h3>访问a模块getters——$store.getters.doubleCounterA : {{ $store.getters.doubleCounterA }} </h3>
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrccomponentsIndex.vue
<h3>访问b模块getters——$store.getters.doubleCounterB : {{ $store.getters.doubleCounterB }} </h3>
浏览器查看结果:

可以看到已经成功的访问到不同模块的getters。
那么最后我们在尝试将a、b两个模块的getters属性名称在改回doubleCounter,使用命名空间的方式去访问。
这里不贴moduleA.js和moudleB.js的代码了,直接修改App.vue和Index.vue中使用命名控件访问getters的代码
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrcApp.vue
<h3>访问根模块getters——$store.getters.doubleCounter : {{ $store.getters.doubleCounter }} </h3>
<h3>访问a模块getters——$store.getters['a/doubleCounter'] : {{ $store.getters['a/doubleCounter'] }} </h3>
E:MyStudy estVueDemosrccomponentsIndex.vue
<h3>访问b模块getters——$store.getters[''b/doubleCounter'] : {{ $store.getters['b/doubleCounter'] }} </h3>
浏览器查看结果

可以看到命名空间访问成功。
注意:我们一直访问getters的逻辑代码为$store.getters.doubleCounter。
因此在尝试使用命名空间访问getters时我的代码为$store.getters.a.doubleCounter。
但是发现这种方法会报错,因此灵机一动把代码换成了$store.getters['a/doubleCounter'],最后访问成功。
三.总结
到此本篇文章要总结的内容就完成了。
篇幅比较长,但是也很简单。
vuex的前一篇文章和本篇文章,在访问state、mutations、actions和getters时均采用的是$store对象访问,因此下一篇文章将会介绍另外一种比较常用的访问方式。
关注博主不迷路,下次见
