自然数幂和:
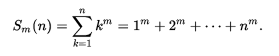
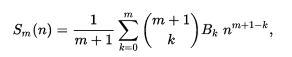 (1)
(1)
伯努利数的递推式:
B0 = 1

(要满足(1)式,求出Bn后将B1改为1 /2)
参考:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bernoulli_number
http://blog.csdn.net/acdreamers/article/details/38929067
使用分数类,代入求解
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<utility>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 25, INF = 0x3F3F3F3F;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
while(b){
LL t = a % b;
a = b;
b = t;
}
return a;
}
LL lcm(LL a, LL b){
return a / gcd(a, b) * b;
}
struct frac{
LL x, y;
frac(){
x = 0;
y = 1;
}
frac(LL x1, LL y1){
x = x1;
y = y1;
}
frac operator*(const frac &tp)const{
LL a = x * tp.x;
LL b = y * tp.y;
LL d = gcd(a, b);
a /= d;
b /= d;
if(a >= 0 && b < 0){
a = -a;
b = -b;
}
return frac(a, b);
}
frac operator+(const frac &tp)const{
LL a = x * tp.y + tp.x * y;
LL b = y * tp.y;
LL d = gcd(a, b);
a /= d;
b /= d;
if(a >= 0 && b < 0){
a = -a;
b = -b;
}
return frac(a, b);
}
}ans[N][N], bo[N];
LL cm[N][N];
void init(){
memset(cm, 0, sizeof(cm));
cm[0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){
cm[i][0] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++){
cm[i][j] = cm[i - 1][j - 1] + cm[i - 1][j];
}
}
bo[0].x = 1, bo[0].y = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){
bo[i].x = 0;
bo[i].y = 1;
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
bo[i] = bo[i] + frac(cm[i + 1][j], 1) * bo[j];
}
bo[i] = bo[i] * frac(-1, i + 1);
}
bo[1].x = 1; bo[1].y = 2;
for(int m = 0; m < N; m++){
for(int k = 0; k <= m; k++){
ans[m][m + 1 - k] = frac(cm[m + 1][k], 1) * bo[k] * frac(1, m + 1);
}
LL lc = ans[m][0].y;
for(int k = 1; k <= m; k++){
lc = lcm(ans[m][k].y, lc);
}
for(int k = 0; k <= m + 1; k++){
LL d = lc / ans[m][k].y;
ans[m][k].x *= d;
ans[m][k].y *= d;
}
}
}
int main(){
init();
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int n;
cin >>n;
printf("%lld ", ans[n][0].y);
for(int i = n + 1; i >= 0; i--){
if(i == 0){
printf("%lld
", ans[n][i].x);
}else{
printf("%lld ", ans[n][i].x);
}
}
if(t){
printf("
");
}
}
return 0;
}