概述
- Protobuf是一种高效轻便的结构化数据存储方式,可用于(数据)通信协议、数据存储等
- Protobuf用于 RPC 系统和持续数据存储系统
- 可用于通讯协议、数据存储等领域的语言无关、平台无关、可扩展的序列化结构数据格式
- 目前提供了 C++、Java、Python 三种语言的 API
特点
- 平台无关、语言无关
- 二进制、数据自描述
- 提供了完整详细的操作API
- 高性能,比xml要快20-100倍
- 尺寸小,比xml要小3-10倍,高可扩展性、
- 数据自描述、前后兼容
基本类型
| proto类型 | Java类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| double | double | 双精度浮点型 |
| float | float | 单精度浮点型 |
| int32 | int | 使用可变长编码方式,编码负数的时候不够高效。如果编码负数,建议使用sint32 |
| int64 | long | 使用可变长编码方式。编码负数的时候不够高效。如果包含负数,建议使用sint64 |
| uint32 | 对应于无符号整数int | |
| uint64 | 对应于无符号整数long | |
| sint32 | int | 使用可变长编码方式。编码通常比int32高效 |
| sint64 | long | 使用可变长编码方式。编码通常比int64高效 |
| fixed32 | int | 固定4个字节。如果数值比228大的话,用此方式比较高效 |
| fixed64 | long | 固定8个字节。如果数值比256大的话,用此方式比较高效 |
| sfixed32 | int | 固定4个字节 |
| sfixed64 | long | 固定8个字节 |
| bool | boolean | 布尔值 |
| string | String | 字符串 |
| bytes | ByteString | 字节序列 |
复杂类型
| Proto类型 | Java类型 |
|---|---|
| message | class |
| enum | enum |
| map | Map |
| service | RPC interface |
Protobuf的使用
1.序列化和反序列化
1.1.安装Protobuf插件
1.2.创建maven工程
1.3.在pom.xml中配置相关依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.blb</groupId> <artifactId>proto</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>proto</name> <!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --> <url>http://www.example.com</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!--protobuf相关start--> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.protobuf/protobuf-java-util --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-java-util</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.grpc/grpc-all --> <dependency> <groupId>io.grpc</groupId> <artifactId>grpc-all</artifactId> <version>1.11.0</version> </dependency> <!--protobuf相关end--> </dependencies> <!-- 先创建<build></build>在里面创建<extensions></extensions>--> <build> <extensions> <extension> <groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId> <artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>1.5.0.Final</version> </extension> </extensions> <!-- //之后再创建<plugins></plugins>--> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>0.5.0</version> <configuration> <protocArtifact> com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.1.0:exe:${os.detected.classifier} </protocArtifact> <pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId> <pluginArtifact> io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.11.0:exe:${os.detected.classifier} </pluginArtifact> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>compile</goal> <goal>compile-custom</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
1.4.创建.proto文件
message xxx { // 字段规则:required -> 字段只能也必须出现 1 次 // 字段规则:optional -> 字段可出现 0 次或1次 // 字段规则:repeated -> 字段可出现任意多次(包括 0) // 类型:int32、int64、sint32、sint64、string、32-bit .... // 字段编号:0 ~ 536870911(除去 19000 到 19999 之间的数字) 字段规则 类型 名称 = 字段编号; }
package com.blb; message Person{ //定义int类型的属性id //required表示该属性是必须属性 required int32 id = 1; //定义String类型的属性name required string name = 2; //定义int类型的属性age //optional表示可选属性 optional int32 age = 3; }
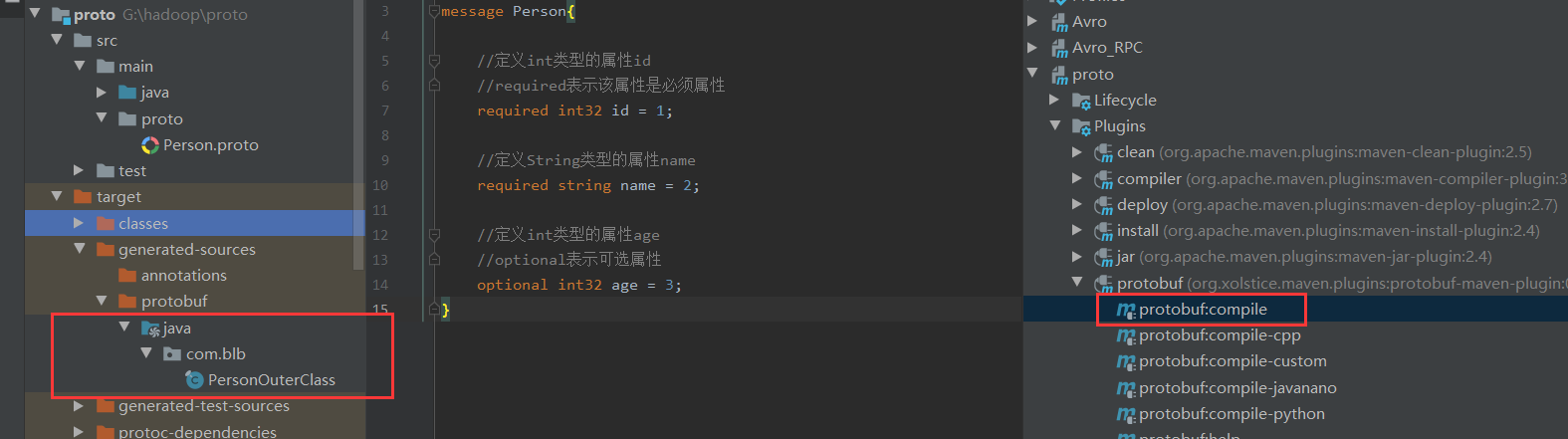
1.5.将proto文件转化为java文件
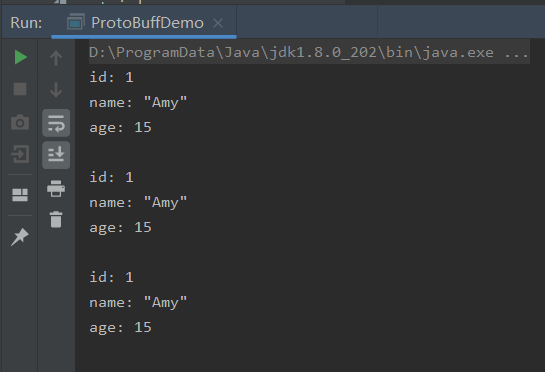
1.6.开始序列化和反序列化操作
package com.blb; import com.google.protobuf.InvalidProtocolBufferException; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class ProtoBuffDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建一个Person对象 //注意:该创建方式是建造者模式 PersonOuterClass.Person amy = PersonOuterClass.Person.newBuilder().setId(1).setName("Amy").setAge(15).build(); System.out.println(amy); //序列化和反序列化 /** * 方式一:转化为数组 */ byte[] bytes = amy.toByteArray(); PersonOuterClass.Person person = PersonOuterClass.Person.parseFrom(bytes); System.out.println(person); /** * 方式二:利用流写出或者读取 */ amy.writeTo(new FileOutputStream("person.data")); PersonOuterClass.Person person1 = PersonOuterClass.Person.parseFrom(new FileInputStream("person.data")); System.out.println(person1); } }
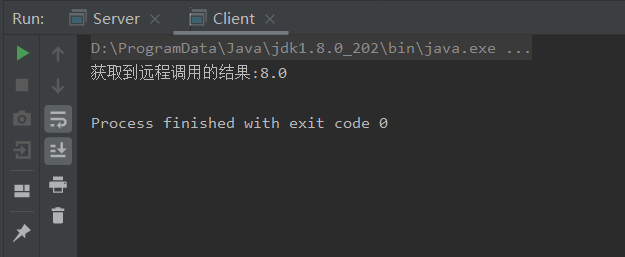
2.RPC调用
2.1.编写.proto文件
package com.blb.rpc; option java_generic_services=true; //开启rpc //定义请求参数 message Req{ required double num1 = 1; required double num2 = 2; required string name = 3; }; //定义返回结果 message Resp{ required double result = 1; }; //定义要执行的方法 service CalcService{ rpc add(Req) returns (Resp); };
2.2.将.proto文件转换为java文件
同上操作
2.3.实现客户端
package com.blb.rpc; import com.google.protobuf.*; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.Socket; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 获取要调用的远程对象的本地存根 * 该存根和远程的方法一致 * 调用莨的任何方法,在底层都会调用传入的RPChannel中的callMethod方法 * 所以需要自己来实习那callMethod方法来实现其中真正远程调用 */ Calc.CalcService.Stub stub = Calc.CalcService.newStub(new RpcChannel() { @Override public void callMethod(Descriptors.MethodDescriptor methodDescriptor, RpcController rpcController, Message req, Message resp, RpcCallback<Message> cb) { Socket socket = new Socket(); try { socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080)); //获取指向远程服务器的输出流 OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream(); //序列化请求对象 byte[] bytes = req.toByteArray(); //进行发送 out.write(bytes); socket.shutdownOutput(); //获取返回结果 Calc.Resp resp1 = Calc.Resp.parseFrom(socket.getInputStream()); socket.shutdownInput(); //调用回调对象 cb.run(resp1); socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); //准备请求对象 Calc.Req add = Calc.Req.newBuilder().setNum1(3).setNum2(5).setName("add").build(); //调用方法 stub.add(null, add, new RpcCallback<Calc.Resp>() { @Override public void run(Calc.Resp resp) { System.out.println("获取到远程调用的结果:"+resp.getResult()); } }); } }
2.4.实现服务端
package com.blb.rpc; import com.google.protobuf.*; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ServiceException { //创建服务端对象 ServerSocket socket = new ServerSocket(8080); Socket s = socket.accept(); //获取请求参数 Calc.Req req = Calc.Req.parseFrom(s.getInputStream()); s.shutdownInput(); //创建真正的远程调用对象,用于处理客户端发送的调用请求 ClacServiceImpl calc = new ClacServiceImpl(); //包装calc对象,可以便捷的实现利用方法名来调用真正的方法 BlockingService service = Calc.CalcService.newReflectiveBlockingService(calc); //获取方法名和对应的实际方法 Descriptors.MethodDescriptor descriptor = service.getDescriptorForType().findMethodByName(req.getName()); //执行方法 Calc.Resp resp = (Calc.Resp) service.callBlockingMethod(descriptor, null, req); //写出数据 resp.writeTo(s.getOutputStream()); s.shutdownOutput(); //关流 socket.close(); } static class ClacServiceImpl implements Calc.CalcService.BlockingInterface{ @Override public Calc.Resp add(RpcController controller, Calc.Req request) throws ServiceException { //计算结果 Calc.Resp resp = Calc.Resp.newBuilder().setResult(request.getNum1() + request.getNum2()).build(); return resp; } } }