Mybatis
八、复杂查询处理
1、复杂环境准备
- 创建表tb_teacher和tb_student
- pom.xml中依赖包【数据库驱动包、Mybatis依赖包、测试包Junit、Lombok】
- 实现SqlSessionUtil工具类
- 编写实体类dto【Teacher和Student】
- 编写数据持久层dao【mapper接口和mapper.xml配置文件】
- 测试
2、一对多实现
问题描述:查询某个老师以及他所教的学生信息
Student
@Data
public class Student {
private int sid;
private String sname;
private int tid;
}
Teacher
@Data
public class Teacher {
private int tid;
private String tname;
private List<Student> students;
}
TeacherMapper
public interface TeacherMapper {
//问题:查询某个老师以及他所教的学生信息
Teacher queryByTid(int tid);
Teacher queryByTid2(int tid);
}
TeacherMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.TeacherMapper">
<!-- 方式一:使用联合查询 -->
<resultMap id="ts" type="teacher">
<!-- 将结果中的字段与实体类中的属性对应 -->
<result property="tid" column="tid" ></result>
<result property="tname" column="tname" ></result>
<!-- 试题类中有集合,使用collection映射
property:属性名
ofType:对应着集合中泛型所限定的类【List<Student>】
-->
<collection property="students" ofType="student">
<result property="tid" column="tid" ></result>
<result property="sid" column="sid"></result>
<result property="sname" column="sname"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="queryByTid" resultMap="ts">
select sid, sname, t.tid as tid, tname
from tb_teacher t, tb_student s
where t.tid = s.tid
and t.tid = #{tid};
</select>
<!-- 方式二:子查询的方式进行查询 -->
<select id="queryByTid2" resultMap="ts2">
select tid, tname from tb_teacher where tid = #{tid};
</select>
<resultMap id="ts2" type="teacher">
<!-- 将查询的结果的字段名和实体类中的属性名做映射 -->
<result property="tid" column="tid" ></result>
<!-- collection实体类中存在集合
property:实体类中的集合属性名
javaType:集合属性所对应的类型【可以省略不写】
ofType:集合中泛型所限定的类型【List<Student>】
select:对应的子查询的唯一标识id
column:子查询中所需要用到的参数
-->
<collection property="students" javaType="ArrayList" ofType="student" select="queryStudent" column="tid"></collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="queryStudent" resultType="student">
select sid, sname from tb_student where tid = #{tid};
</select>
</mapper>
3、多对一实现
问题描述:查询某个老师以及他所教的学生信息
Student
@Data
public class Student {
private int sid;
private String sname;
private Teacher teacher;
}
Teacher
@Data
public class Teacher {
private int tid;
private String tname;
}
StudentMapper
public interface StudentMapper {
//查询所有的学生以及对应的授课老师
List<Student> getAll();
List<Student> getAll2();
}
StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.ch.dao.StudentMapper">
<!-- 方式一: 使用联合查询的方式查询 -->
<resultMap id="st" type="student">
<!-- 将查询的结果字段与实体类的属性一一映射 -->
<result property="sid" column="sid"></result>
<result property="sname" column="sname"></result>
<!-- 实体类中包含teacher对象,使用association将它与Teacher实体类中的属性映射
property:对应的属性名
javaType:属性名对应的类型
-->
<association property="teacher" javaType="teacher">
<result property="tid" column="tid"></result>
<result property="tname" column="tname"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getAll" resultMap="st">
select sid, sname, t.tid tid, tname
from tb_teacher t, tb_student s
where t.tid = s.tid;
</select>
<!-- 方式二: 使用子查询的方式查询 -->
<select id="getAll2" resultMap="st2">
select sid, sname, tid from tb_student;
</select>
<resultMap id="st2" type="student">
<!-- 将查询的结果字段与实体类的属性一一映射 -->
<result property="sid" column="sid"></result>
<result property="sname" column="sname"></result>
<!-- 实体类中包含teacher对象,使用association将它与Teacher实体类中的属性映射
property:对应的属性名
javaType:属性名对应的类型【可以省略】
column:需要传入子查询的参数
select:子查询对应的唯一标识id
-->
<association property="teacher" javaType="teacher" column="tid" select="queryTeacher"></association>
</resultMap>
<select id="queryTeacher" resultType="teacher">
select tid,tname from tb_teacher where tid = #{tid};
</select>
</mapper>
九、动态SQL
理解什么是动态SQL?
- 动态SQL就是根据不同的条件生成不同的SQL语句。
- 动态SQL本质还是SQL,只是在SQL层面,添加一些逻辑代码
if
choose (when, otherwise)
trim (where, set)
foreach
if
//1、if
//如果传入sid,则根据sid查询,如果传入sname,则根据sname查询,如果都不穿,则查询所有
List<Student> queryByIf(Map<String, Object> map);
<!-- if测试 -->
<select id="queryByIf" resultType="com.ch.dto.Student" parameterType="map">
select * from tb_student where 1 = 1
<if test="sid != null">
and sid = #{sid};
</if>
<if test="sname != null ">
and sname = #{sname};
</if>
</select>
choose(when,otherwise)
//2、choose
//如果传入sname,则根据sname查询,否则就根据sid查询
List<Student> queryByChoose(Map<String, Object> map);
<!-- choose测试 -->
<select id="queryByChoose" resultType="com.ch.dto.Student" parameterType="map">
select * from tb_student where 1 = 1
<choose>
<when test="sid != null">
and sname = #{sname};
</when>
<otherwise>
and sid = #{sid};
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
trim(where,set)
显然写where 1 = 1是不安全的,所以使用where标签
where
- 动态添加where
- 自动判断是否需要添加或去掉and|or
//如果传入sid,则根据sid查询,如果传入sname,则根据sname查询,如果都传则两条件一起查询,如果都不传,则查询所有
List<Student> queryByWhere(Map<String, Object> map);
<!-- where测试 -->
<select id="queryByWhere" resultType="com.ch.dto.Student" parameterType="map">
select * from tb_student
<where>
<if test="sid != null">
sid = #{sid}
</if>
<if test="sname != null">
and sname = #{sname}
</if>
</where>
</select>
set
- 动态添加set
- 自动判断是否需要去掉多余的逗号“,”
//如果传入sname,则修改sname,如果传入tid,则修改tid,如果都传则两字段一起修改
int updateBySet(Map<String, Object> map);
<!-- set测试 -->
<update id="updateBySet" parameterType="map">
update tb_student
<set>
<if test="sid != null">
tid = #{tid}
</if>
<if test="sname != null">
, sname = #{sname}
</if>
</set>
where sid = #{sid};
</update>
foreach
//查询id = 1 or id = 2 or id = 3【不使用in】
List<Student> queryByForeach(List<Integer> list);
<!-- foreach测试 -->
<select id="queryByForeach" resultType="com.ch.dto.Student" parameterType="list">
select * from tb_student
<where>
<!-- foreach
collection:遍历我们所传递的集合
item:从我们集合中遍历出来的每一项
open:以...开始
close:以...结束
separator:分隔符是什么
-->
<foreach collection="list" item="sid" open="(" close=")" separator="or">
sid = #{sid}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
SQL片段
抽取一个公共的部分
- 最好是单表,简单的SQL语句
- 里面最好不使用where
<sql id="pub">
<if test="sid != null">
sid = #{sid}
</if>
<if test="sname != null">
and sname = #{sname}
</if>
</sql>
<!-- where测试 -->
<select id="queryByWhere" resultType="com.ch.dto.Student" parameterType="map">
select * from tb_student
<where>
<include refid="pub"></include>
<!-- <if test="sid != null">-->
<!-- sid = #{sid}-->
<!-- </if>-->
<!-- <if test="sname != null">-->
<!-- and sname = #{sname}-->
<!-- </if>-->
</where>
</select>
十、缓存
缓存有什么用?
在没有增删改的情况下,不需要去查询数据库,减轻数据库的压力
一级缓存
一级缓存默认是开启的
- 一级缓存是基于SqlSession级别的缓存,缓存在创建SqlSession到提交或者关闭期间有效
二级缓存
二级缓存需要手动开启
- 二级缓存是namespace级别的缓存,只要查询的是当前namespace下的数据,那么缓存均有效
如何开启?

1、在mybatis-config.xml中开启全局缓存(二级缓存)
<!-- 开启全局缓存 -->
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
2、在需要使用二级缓存的mapper.xml中配置
<cache/>
或者自定义参数配置
<cache
eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size="512"
readOnly="true"/>
这个更高级的配置创建了一个 FIFO 缓存,每隔 60 秒刷新,最多可以存储结果对象或列表的 512 个引用,而且返回的对象被认为是只读的,因此对它们进行修改可能会在不同线程中的调用者产生冲突。
可用的清除策略有:
LRU– 最近最少使用:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。FIFO– 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。SOFT– 软引用:基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则移除对象。WEAK– 弱引用:更积极地基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则移除对象。
默认的清除策略是 LRU。
flushInterval(刷新间隔)属性可以被设置为任意的正整数,设置的值应该是一个以毫秒为单位的合理时间量。 默认情况是不设置,也就是没有刷新间隔,缓存仅仅会在调用语句时刷新。
size(引用数目)属性可以被设置为任意正整数,要注意欲缓存对象的大小和运行环境中可用的内存资源。默认值是 1024。
readOnly(只读)属性可以被设置为 true 或 false。只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。 因此这些对象不能被修改。这就提供了可观的性能提升。而可读写的缓存会(通过序列化)返回缓存对象的拷贝。 速度上会慢一些,但是更安全,因此默认值是 false。
特别注意:实体类都应该实现序列化接口,不然二级缓存使用的时候会报错........
缓存原理
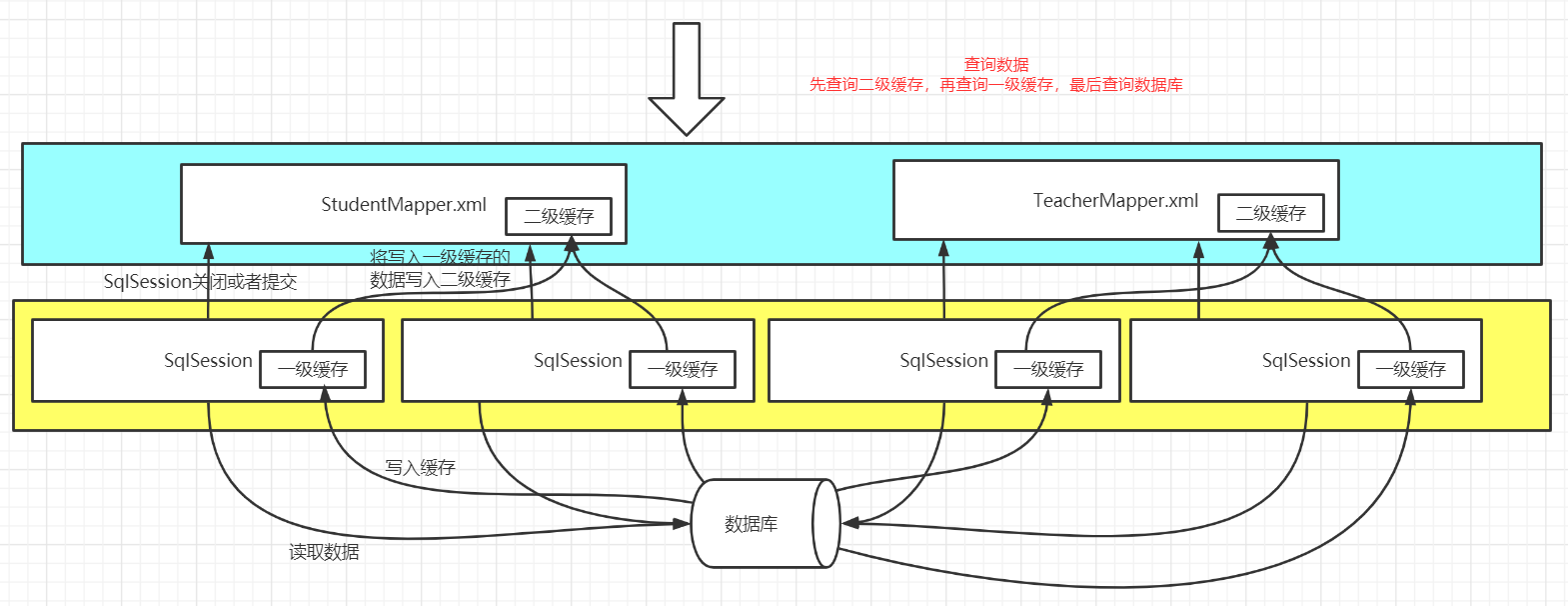
- 数据缓存先缓存到一级缓存
- SqlSession提交或者关闭后,则将一级缓存的数据放到二级缓存中