Object Literal Extensions.md
var price = 4.20, quantity = 20;
var invoiceData = {
price: price,
quantity: quantity
};
console.log(invoiceData);
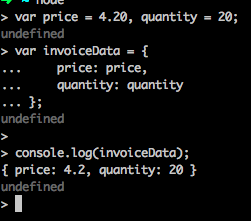
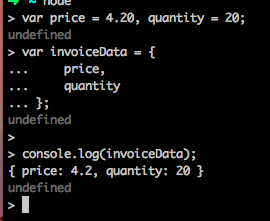
Declaring price and quantity twice is kind of redundant,but es6 provides a shorthand making writing this simpler.
var price = 4.20, quantity = 20;
var invoiceData = {
price,
quantity
};
console.log(invoiceData);
ES6 also gives us a short notation to wirte functions in an object literal.
const price = 4.20,quantity = 20;
const invoiceData = {
price,
quantity,
calculateTotal(){
return this.price * this.quantity;
}
};
console.log(invoiceData.calculateTotal());
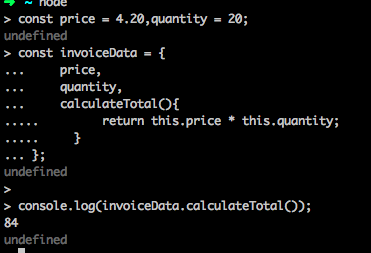
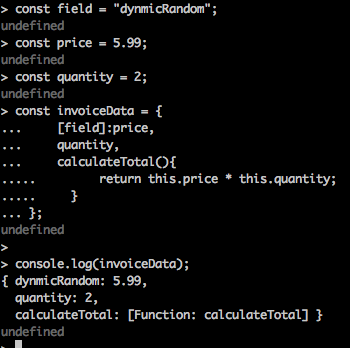
*In the above shorthand notation, you no longer need the keyword function.When we use the shorthand within an object literal, this refers to the context of the code just like an arrow funtion.It does not refer to the object that contains the function.It behaves exactly like an arrow function. *
const field = "dynmicRandom";
const price = 5.99;
const quantity = 2;
const invoiceData = {
[field]:price,
quantity,
calculateTotal(){
return this.price * this.quantity;
}
};
console.log(invoiceData);
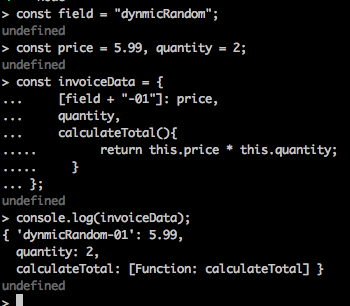
const field = "dynmicRandom";
const price = 5.99, quantity = 2;
const invoiceData = {
[field + "-01"]: price,
quantity,
calculateTotal(){
return this.price * this.quantity;
}
};
console.log(invoiceData);
Template Literals and Delimiters
ES6 Template Literals which provide you a way to defined strings with addational functionalities like
String interpolation
Embedded expressions
Multiline strings without hacks
String formatting
let user = `Kevin`;
console.log(`Hi ${user}!`);
let a = 10;
let b = 20;
console.log(`Sum of ${a} and ${b} is ${a+b}`);
console.log(`I am line one
I am line two`);
output `Hi, my name is ${name} and I love ${language}`;
1.Array of literal strings, that is ["Hi,my name is ","and I love", ""]
2.Substitutions,that is, name, language.
output(["Hi,my name is", "and I love", ""],name, language)
function output(literals, ...substitutions){
let result= "";
for(let i = 0 ;i < substitutions.length; i++) {
result += literals[i] + substitutions[i];
}
result += literals[literals.length - 1];
return result;
}
const name = "John",
language = "Javascript";
let text = output `Hi,my name is ${name} and I love {language}`
console.log(text);
Iterating with for...of
let names = ['matt','smith','jack'];
for(let i = 0; i<names.length; i++) {
console.log(name[i]);
}
let names = ["matt", "smith", "jack"];
for(let names of names){
console.log(name);
}
for(let char of "Bye"){
console.log(char);
}