MyBaits
1.简介
1.1 什么是Mybaits
MyBatis 本是apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年这个项目由apache software foundation 迁移到了google code,并且改名为MyBatis,是一个基于Java的持久层框架。
- 持久层: 可以将业务数据存储到磁盘,具备长期存储能力,只要磁盘不损坏,在断电或者其他情况下,重新开启系统仍然可以读取到这些数据。
- 优点: 可以使用巨大的磁盘空间存储相当量的数据,并且很廉价
- 缺点:慢(相对于内存而言)
1.2 如何获取
-
maven
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.5</version> </dependency> -
github
github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/releases
1.3 优点
- 简单易学:本身就很小且简单。没有任何第三方依赖
- 灵活,sql写在xml里,便于统一管理和优化。通过sql语句可以满足操作数据库的所有需求。
- 解除sql与程序代码的耦合:通过提供DAO层,将业务逻辑和数据访问逻辑分离。sql和代码的分离,提高了可维护性。
- 提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库的orm字段关系映射
- 提供对象关系映射标签,支持对象关系组建维护
- 提供xml标签,支持编写动态sql。
2.第一个Mybaits程序
2.1 搭建一个maven项目
导入依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>mrh</groupId>
<artifactId>Mybaits</artifactId>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<modules>
<module>Mybaits_Demon01</module>
</modules>
<!--父工程-->
<!--导入依赖-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2.2 编写代码
-
实体类
-
Dao接口
-
接口实现(由原来的UserImp转变为一个xml配置文件)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!--namesapace指定一个Dao/Mapper接口--> <mapper namespace="mrh.dao.UserDao"> <!--查询语句--> <select id="getUserList" resultType="mrh.pojo.User"> select * from test2.user </select> </mapper> -
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test2?userSSL=true&userUnicode=true&characterEncode=UTF-8"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="991024"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!--注册mapper,注意这里文件夹之间不能用 . 只能用 / --> <mappers> <mapper resource="mrh/dao/UserMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration> -
测试
package mrh.dao; import mrh.pojo.User; import mrh.util.MybaitsUtil; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.List; /** * @ClassName UserDaoTest * @Description TODO * @Author m * @Version 1.0 */ public class UserDaoTest { @Test public void test(){ //1.获取sqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = MybaitsUtil.getSqlSession(); //getMapper UserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class); List<User> userList = userDao.getUserList(); for (User user : userList) { System.out.println(user.toString()); } sqlSession.close(); } }问题1:
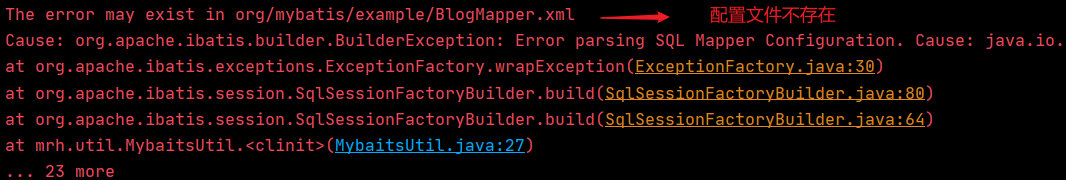
原因1:
由于Maven约定大于配置,我们之后写的配置文件可能存在无法导出的问题
解决方案:
<build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>true</filtering> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>true</filtering> </resource> </resources> </build>
2.3 CRUD
增删改需要提交事务
1.编写接口
package mrh.dao;
import mrh.pojo.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper {
//查询全部用户
List<User> getUserList();
//通过Id查找用户
User getUserById(int id);
//添加用户
int addUser(User user);
//修改用户
int updateUser(User user);
//删除用户
int deleteUser(int id);
}
2.编写对应的Mappersql语句(不要忘了在mybaits-config.xml中注册)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namesapace指定一个Dao/Mapper接口-->
<mapper namespace="mrh.dao.UserMapper">
<!--查询语句-->
<select id="getUserList" resultType="mrh.pojo.User">
select * from test2.user
</select>
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="mrh.pojo.User">
select * from test2.user where id = #{id};
</select>
<!--添加-->
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="mrh.pojo.User">
insert into test2.user(username ,password) value (#{userName} ,#{password});
</insert>
<!--修改-->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="mrh.pojo.User">
update test2.user set username = #{userName}, password = #{password} where id = #{id};
</update>
<!--删除-->
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int">
delete from test2.user where id = #{id};
</delete>
</mapper>
3.测试
package mrh.dao;
import mrh.pojo.User;
import mrh.util.MybaitsUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @ClassName UserDaoTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author m
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class UserDaoTest {
@Test
public void testGetAll(){
//1.获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybaitsUtil.getSqlSession();
//获取所有用户
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> userList = userMapper.getUserList();
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testGetUserById(){
//1.获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybaitsUtil.getSqlSession();
//获取用户
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = userMapper.getUserById(2);
System.out.println(user.toString());
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testAddUser(){
User user = new User(2, "hahah", "123456");
//1.获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybaitsUtil.getSqlSession();
//添加用户
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
userMapper.addUser(user);
//增删改数据必须提交
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testUpdateUser(){
User user = new User(2, "rhma", "123456");
//1.获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybaitsUtil.getSqlSession();
//添加用户
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
userMapper.updateUser(user);
//增删改数据必须提交
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testDeleteUser(){
//1.获取sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybaitsUtil.getSqlSession();
//添加用户
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
userMapper.deleteUser(9);
//增删改数据必须提交
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
3.配置文件
3.1 属性优化
configuration(配置)
- properties(属性)
- settings(设置)
- typeAliases(类型别名)
- typeHandlers(类型处理器)
- objectFactory(对象工厂)
- plugins(插件)
- environments(环境配置)
- environment(环境变量)
- transactionManager(事务管理器)
- dataSource(数据源)
- environment(环境变量)
- databaseIdProvider(数据库厂商标识)
- mappers(映射器)
这些属性都是可以在整个配置文件中用来替换需要动态配置的属性值
<properties resource="org/mybatis/example/config.properties">
<property name="username" value="dev_user"/>
<property name="password" value="F2Fa3!33TYyg"/>
</properties>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
引用优先级问题:
3.2 别名优化
- 类型别名可为 Java 类型设置一个缩写名字。
- 仅用于 XML 配置
- 意在降低冗余的全限定类名书写。
例如:
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/>
<typeAlias alias="Blog" type="domain.blog.Blog"/>
<typeAlias alias="Comment" type="domain.blog.Comment"/>
<typeAlias alias="Post" type="domain.blog.Post"/>
<typeAlias alias="Section" type="domain.blog.Section"/>
<typeAlias alias="Tag" type="domain.blog.Tag"/>
</typeAliases>
当这样配置时,Blog 可以用在任何使用 domain.blog.Blog 的地方。
除了类名,包名也可以设置别名
MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean,比如:
<typeAliases>
<package name="domain.blog"/>
</typeAliases>
每一个在包 domain.blog 中的 Java Bean,在没有注解的情况下,会使用 Bean 的首字母小写的非限定类名来作为它的别名。 比如 domain.blog.Author 的别名为 author;若有注解,则别名为其注解值。见下面的例子:
@Alias("author")
public class Author {
...
}
3.3 映射器
方式一:推荐使用
<!-- 使用相对于类路径的资源引用 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
方式二:
<!-- 使用映射器接口实现类的完全限定类名 -->
<mappers>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.BlogMapper"/>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.PostMapper"/>
</mappers>
注意点:
-
接口必须和注册文件同名
-
接口必须和注册文件在同一包下
方式三:
<!-- 将包内的映射器接口实现全部注册为映射器 -->
<mappers>
<package name="org.mybatis.builder"/>
</mappers>
注意点:
- 接口必须和注册文件同名
- 接口必须和注册文件在同一包下
这些配置会告诉 MyBatis 去哪里找映射文件,剩下的细节就应该是每个 SQL映射文件了
4.数据库字段与实体类中属性名不一致问题
会导致不一致的字段返回值为null
原理:
select * from user;
-- 类型处理器后变为:
select id, username, pwd from user
-- id, username, pwd为绑定的实体类中的属性
-- 当名称不一致时导致最终执行的sql语句查询不到对应的字段,返回null
解决方法
1.起别名
select id, username, pwd as password from user;
2.resultMap(结果集映射)
5.日志
5.1 日志工厂
意义:方便查错
设置:
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
-
STDOUT_LOGGING
-
LOG4J
-
Log4j是Apache的一个开源项目,通过使用Log4j,我们可以控制日志信息输送的目的地是控制台、文件、GUI组件,甚至是套接口服务器、NT的事件记录器、UNIX Syslog守护进程等
-
可以通过一个配置文件来灵活地进行配置,而不需要修改应用的代码
-
配置文件
### 设置### log4j.rootLogger = debug,console,D ### 输出信息到控制抬 ### log4j.appender.console = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.console.Target = System.out log4j.appender.console.Threshold = DEBUG log4j.appender.console.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern = [%c]-%m%n ### 输出DEBUG 级别以上的日志到=E://logs/error.log ### log4j.appender.D=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender log4j.appender.D.File = ./logs/log.log #-----------------------------------文件的最大尺寸 log4j.appender.D.MaxFileSize=500KB log4j.appender.D.append=true log4j.appender.D.Threshold = DEBUG log4j.appender.D.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.D.layout.ConversionPattern = [%p][%d{yy-MM-dd}][%c]-%m%n ### 日志输出级别 ### log4j.logger.org.mybatis=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
-
6.分页
分页能够减少数据处理量
语法:
select *from user limit 起始位置, 每页大小;
7.使用注解CRUD
#{}和${}的区别
- ${}使用字符串直接拼接,不能防止sql注入
- #{}会将字符串中的特殊字符转义,能防止sql注入
8.多对一的处理
1.查询嵌套的处理思想
<mapper namespace="mrh.dao.StudentMapper">
<!--
1.查询所有的学生
2.根据查到的tid查找对应的老师
-->
<select id="getAllStudent" resultMap="student2Teacher">
select * from student;
</select>
<!--结果集映射-->
<resultMap id="student2Teacher" type="student">
<result column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--对于复杂的属性,我们需要单独处理 对象:association 集合:collection-->
<association column="tid" property="teacher" javaType="Teacher" select="getTeacher"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="teacher">
select * from teacher where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
2.结果嵌套的思想
<select id="getAll" resultMap="student2Teacher2">
select s.id sid, s.name sname, s.tid stid, t.id tid, t.name tname from student s, teacher t
where s.tid = t.id;
</select>
<!--将查询的结果映射为类-->
<resultMap id="student2Teacher2" type="student">
<result column="sid" property="id"/>
<result column="sname" property="name"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher">
<result column="tid" property="id"/>
<result column="tname" property="name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
9.一对多的处理
1.查询嵌套的处理思想
<select id="getTeacherById2" parameterType="_int" resultMap="teacher2Student2">
select * from teacher;
</select>
<resultMap id="teacher2Student2" type="teacher">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<collection property="students" column="" ofType="student" select="getStudent"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getStudent" parameterType="_int" resultType="student">
select * from studen where id = #{sid}
</select>
2.结果嵌套的思想
<select id="getTeacherById" parameterType="_int" resultMap="teacher2Student">
select t.id tid, t.name tname, s.id sid, s.name sname, s.tid stid
from teacher t, student s
where t.id = s.tid and t.id = #{id};
</select>
<resultMap id="teacher2Student" type="teacher">
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<collection property="students" ofType="student">
<result column="sid" property="id"/>
<result column="sname" property="name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
一对多和多对于区别:
一个使用association,一个使用collection
注意点:
- 保证sql的可读性
- 注意属性名和字段的问题
- 建议使用日志工厂排错
面试高频:
- Mysql引擎
- InnoDB底层
- 索引及其优化
10.动态sql
动态sql:即根据不同的条件生产不同的语言
可容易实现sql的复用
if
choose (when, otherwise)
trim (where, set)
foreach
if
<select id="queryBlog" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
</where>
</select>
trim(where, set)
<update id="updateBlog" parameterType="map" >
update blog
<set>
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title},
</if>
<if test="author != null">
author = #{author},
</if>
<if test="creat_time != null">
creat_time = #{creat_time},
</if>
<if test="views !=null">
views = #{views}
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
set 元素会动态地在行首插入 SET 关键字,并会删掉额外的逗号(这些逗号是在使用条件语句给列赋值时引入的)。
where 元素只会在子元素返回任何内容的情况下才插入 “WHERE” 子句。而且,若子句的开头为 “AND” 或 “OR”,where 元素也会将它们去除。
以上两者本质都是通过trim过滤字符
说明:如果where没有添加过,则自动添加where,并且如果拼接的字符串前缀是"and"或"or"则自动去除
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR ">
...
</trim>
说明:如果set没有添加过,则自动添加set,并且如果拼接的字符串后缀是","则自动去除
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
...
</trim>
choose(when … otherwise)
与if语句不同的是:
if语句会对满足条件的语句进行拼接choose语句只会选择满足条件的第一个语句,对应java中的swith语句
<select id="queryBlog" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null">
author = #{author}
</when>
<otherwise>
views = 998
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
sql片段
用于将某些sql片段提取,方便复用
<sql id="sql-if">
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
</sql>
<select id="queryBlog" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<include refid="sql-if"></include>
</where>
</select>
foreach
<select id="selectPostIn" resultType="domain.blog.Post">
SELECT *
FROM POST P
WHERE ID in
<foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
</select>
foreach 元素的功能非常强大,它允许你指定一个集合,声明可以在元素体内使用的集合项(item)和索引(index)变量。它也允许你指定开头与结尾的字符串以及集合项迭代之间的分隔符。这个元素也不会错误地添加多余的分隔符,看它多智能!
提示 你可以将任何可迭代对象(如 List、Set 等)、Map 对象或者数组对象作为集合参数传递给 foreach。当使用可迭代对象或者数组时,index 是当前迭代的序号,item 的值是本次迭代获取到的元素。当使用 Map 对象(或者 Map.Entry 对象的集合)时,index 是键,item 是值。
11.缓存
1.什么是缓存
【1】缓存就是数据交换的缓冲区(称作:Cache),当某一硬件要读取数据时,会首先从缓存汇总查询数据,有则直接执行,不存在时从内存中获取。由于缓存的数据比内存快的多,所以缓存的作用就是帮助硬件更快的运行。
【2】缓存往往使用的是RAM(断电既掉的非永久存储),所以在用完后还是会把文件送到硬盘等存储器中永久存储。电脑中最大缓存就是内存条,硬盘上也有16M或者32M的缓存。
【3】高速缓存是用来协调CPU与主存之间存取速度的差异而设置的。一般CPU工作速度高,但内存的工作速度相对较低,为了解决这个问题,通常使用高速缓存,高速缓存的存取速度介于CPU与主存之间。系统将一些CPU在最近几个时间段经常访问的内容存在高速缓存,这样就在一定程度上缓解了由于主存速度低造成的CPU“停工待料”的情况。
【4】缓存就是把一些外存上的数据保存在内存上而已,为什么保存在内存上,我们运行的所有程序里面的变量都是存放在内存中的,所以如果想将值放入内存上,可以通过变量的方式存储。在JAVA中一些缓存一般都是通过Map集合来实现的。
▁▂▃▅▆ **:**缓存在不同的场景下,作用是不一样的具体举例说明:
✔ 操作系统磁盘缓存 ——> 减少磁盘机械操作。
✔ 数据库缓存——>减少文件系统IO。
✔ 应用程序缓存——>减少对数据库的查询。
✔ Web服务器缓存——>减少应用服务器请求。
✔ 客户端浏览器缓存——>减少对网站的访问。
2.一级缓存(本地缓存)
相同的sql语句执行两次
public void testQuery(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybaitsUtil.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("title", "高等数学");
map.put("author","M");
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.queryBlog(map);
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
System.out.println(blog.toString());
}
blogs = mapper.queryBlog(map);
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
System.out.println(blog.toString());
}
sqlSession.close();
}
可以看到,实际上sql语句只执行了一次:
第一次查询后将sql语句和查询到的数据存储在缓存中,第二次查询是匹配到相同的sql语句直接取出对应的数据(类似于Map)
缓存失效的情况:
-
增删改操作
-
查询不同语句
-
手动清除缓存
sqlSession.clearCache(); // 手动清除缓存- 一级缓存默认开启,即只在一次sql中有效,sql关闭连接就失效
3.二级缓存(全局缓存)
MyBatis 内置了一个强大的事务性查询缓存机制,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。 为了使它更加强大而且易于配置,我们对 MyBatis 3 中的缓存实现进行了许多改进。
默认情况下,只启用了本地的会话缓存,它仅仅对一个会话中的数据进行缓存。 要启用全局的二级缓存,只需要在你的 SQL 映射文件中添加一行:
MyBatis 内置了一个强大的事务性查询缓存机制,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。 为了使它更加强大而且易于配置,我们对 MyBatis 3 中的缓存实现进行了许多改进。
默认情况下,只启用了本地的会话缓存,它仅仅对一个会话中的数据进行缓存。 要启用全局的二级缓存,只需要在你的 SQL 映射文件中添加一行:
<cache/>
- 映射语句文件中的所有 select 语句的结果将会被缓存。
- 映射语句文件中的所有 insert、update 和 delete 语句会刷新缓存。
- 缓存会使用最近最少使用算法(LRU, Least Recently Used)算法来清除不需要的缓存。
- 缓存不会定时进行刷新(也就是说,没有刷新间隔)。
- 缓存会保存列表或对象(无论查询方法返回哪种)的 1024 个引用。
- 缓存会被视为读/写缓存,这意味着获取到的对象并不是共享的,可以安全地被调用者修改,而不干扰其他调用者或线程所做的潜在修改。
问题:我们使用二级缓存时,需要将实体类序列化,否则会报错
查询顺序:
- 查询二级缓存,有记录则返回, 找不到往下走
- 查询一级缓存,有记录则返回, 找不到往下走
- 查询数据库,返回结果,并存入一级缓存
小结:
- 开启了二级缓存后,在同一个Mapper下就有效
- 所有数据会先放在一级缓存中,当一级缓存失效时,会将数据存到二级缓存中
4.Ehcache
EhCache 是一个
纯Java的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精干等特点,是Hibernate中默认CacheProvider。Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存。主要面向通用缓存,Java EE和轻量级容器。它具有内存和磁盘存储,缓存加载器,缓存扩展,缓存异常处理程序,一个gzip缓存servlet过滤器,支持REST和SOAP api等特点。