引用自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a8fa72e708d3
引出:
使用Handler的时候,其必须要跟一个Looper绑定。在UI线程可直接初始化Handler来使用。但是在非主线程中直接new Handler() 会报错: E/AndroidRuntime( 6173): Uncaught handler: thread Thread-8 exiting due to uncaught exception E/AndroidRuntime( 6173): java.lang.RuntimeException: Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()
原因是非主线程中默认没有创建Looper对象,需要先调用Looper.prepare()启用Looper。 当初始化Handler的时候,其会通过Looper来获取当前的Looper,代码如下:
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) { //省略 mLooper = Looper.myLooper(); if (mLooper == null) { throw new RuntimeException( "Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()"); } //省略 }
那么,问题来了,为什么在子线程中,通过Looper.myLooper()方法获取的就是为空呢?如果有人回答了Looper是线程相绑定的,那它是如何做到绑定的? 如果还知道答案的话,那就可以跳过本篇文章了。
代码分析
1. Looper的myLooper方法
public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() { return sThreadLocal.get(); }
此方法只是通过从变量sThreadLocal中取出一个值。那么它的值是哪里来的呢?
2. Looper的prepare方法
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) { if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread"); } sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed)); }
可以看出的是调用了这个方法之后,会在sThreadLocal中存在一个新建的Looper对象。那么看看这个sThreadLocal是什么东西呢?
ThreadLocal分析:
1. 定义 (本地线程副本变量工具类)
先看一下官方的解释:
Implements a thread-local storage, that is, a variable for which each thread has its own value. All threads share the same {@code ThreadLocal} object, but each sees a different value when accessing it, and changes made by one thread do not affect the other threads. The implementation supports {@code null} values.
这段话的意思是实现了一个线程相关的存储,即每个线程都有自己独立的变量。所有的线程都共享着这一个ThreadLocal对象,
并且当一个线程的值发生改变之后,不会影响其他的线程的值。
threadlocal是一个范型类,这标志着threadlocal可以存储所有数据,作为存储数据来说,我们首先想到的是会对外提供set(),get(),remove(),等方法,顺着我们的想法来看源码,果然如此。
2. 核心机制
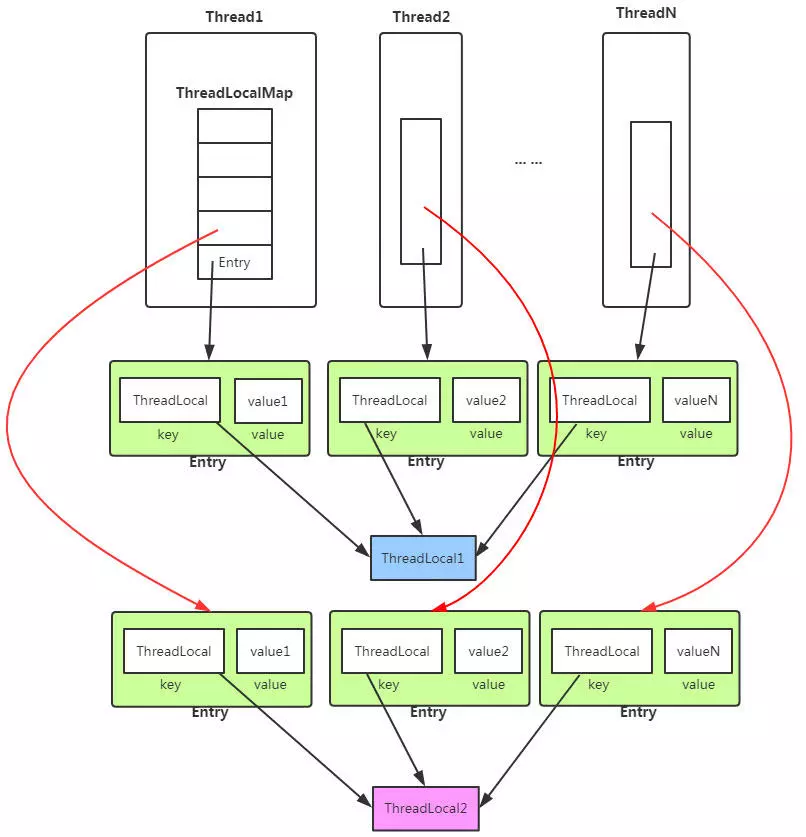
ThreadLocal的核心机制:
- 每个Thread线程内部都有一个Map。
- Map里面存储线程本地对象(key)和线程的变量副本(value)
- 但是,Thread内部的Map是由ThreadLocal维护的,由ThreadLocal负责向map获取和设置线程的变量值。
3. 实现
ThreadLocal的类定义使用了泛型ThreadLocal<T>,其中T指代的是在线程中存取值的类型。(对应Android中使用的ThreadLocal, T则存放的类型为Looper)
- set方法
/** * Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable * to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to * override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue} * method to set the values of thread-locals. * * @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of * this thread-local. */ public void set(T value) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); } ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; } void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); }
步骤:
1.获取当前线程的成员变量map
2.map非空,则重新将ThreadLocal和新的value副本放入到map中。
3.map空,则对线程的成员变量ThreadLocalMap进行初始化创建,并将ThreadLocal和value副本放入map中。
- get方法
/** * Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this * thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the * current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned * by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method. * * @return the current thread's value of this thread-local */ public T get() { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) { ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) return (T)e.value; } return setInitialValue(); } ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; } private T setInitialValue() { T value = initialValue(); Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); return value; } protected T initialValue() { return null; }
1.获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象threadLocals
2.从map中获取线程存储的K-V Entry节点。
3.从Entry节点获取存储的Value副本值返回。
4.map为空的话返回初始值null,即线程变量副本为null,在使用时需要注意判断NullPointerException。
remove()方法
public void remove() { ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread()); if (m != null) m.remove(this); } ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; }
---------------------
public class Thread implements Runnable { /* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained * by the ThreadLocal class. */ ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null; }
总结
举例:
package test; import test.*; public class Test { static final ThreadLocal<ThreadValue> mThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<ThreadValue>(); /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub ThreadValue threadValue = new ThreadValue("主线程"); mThreadLocal.set(threadValue); System.out.print("in main thread : mThreadLocal:" + mThreadLocal +" "); System.out.print("in main thread : 名字:" + mThreadLocal.get().name +" "); mThreadLocal.get().print(); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { ThreadValue childThreadValue = new ThreadValue("子线程"); mThreadLocal.set(childThreadValue); System.out.print("in child thread : mThreadLocal:" + mThreadLocal +" "); System.out.print("in child thread : 名字:" + mThreadLocal.get().name +" "); mThreadLocal.get().print(); } }).start(); } } package test; public class ThreadValue { String name; public ThreadValue() { } public ThreadValue(String name) { this.name=name; } public void print() { System.out.print("this = " + this+" "); } }
结果:
然后编译:javac test/*.java 运行:java test.Test 输出: in main thread : mThreadLocal:java.lang.ThreadLocal@788bf135 in main thread : 名字:主线程 this = test.ThreadValue@2b890c67 in child thread : mThreadLocal:java.lang.ThreadLocal@788bf135 in child thread : 名字:子线程 this = test.ThreadValue@4f93b604
可以看出由于mThreadLocal定义为静态最终变量,所以在主线程和子线程中,mThreadLocal都是同一个实例。
但是在两个线程中调用mThreadLocal.get(),得到的ThreadValue对象却并不相同。
这是因为mThreadLocal.get(),取到的对象是线程内的局部变量,相互之间并不干扰。
---------------------
作者:??-D-Luffy
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/zyfzhangyafei/article/details/64927617
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!