1.前期工作准备
1.首先从GitHub上下载models 网址:https://github.com/tensorflow/models,将object detection文件夹整个复制到python安装目录中的pythonpython3.5.2Libsite-packages下(目的是为了防止之后的代码发生找不到包的问题)
2.protobuf下载,我下载的是protoc-3.3.0-win32.zip 网址:https://github.com/google/protobuf/releases
3.将其解压到第一步下载的models文件夹中的research文件夹下,CMD cd到research文件夹下输入
protoc ./object_detection/protos/*.proto --python_out=.
我在这里发生了报错:(这里转载并参考了https://blog.csdn.net/xingwei_09/article/details/79161221的解决方法)
解决方法就是在Libsite-packages文件夹下(无论是python还是anaconda),找到tensorflow_model.pth文件,没有就新建一个,输入下方路径:

之后就Ok啦!
2.首先准备好图片以及xml文件

(说明:这里的XML文件是需要使用labelImg软件进行批注,但是我的数据中原来已经完成批注,所以这里不再解释)
3.创建文件目录

说明:其中data文件夹中存放的是之后要进行生成的train.csv,eval.csv , train.record,eval.record等文件;
1.output文件夹存放训练后的输出路径;
2.pretrained_model中存放的是从GitHub上下载解压的ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_2018_01_28文件中的内容,下载网址: https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/object_detection/g3doc/detection_model_zoo.md
3.train与test分别存放训练与检测的图片与XML文件;
4.training中存放从object_detection文件夹中复制来的ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config;
下面用到的文件说明(未说到的没用):
1.xml_to_cvs.py是将XML文件转换为CSV文件的代码;
2.cvs_to_tfrecord.py、generate_tfrecord.py分别是使用pycharm、CMD两种方法将CSV转换为TFRECORD文件的代码
4.进行XML到CSV文件的转换
代码:
import os
import glob
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def xml_to_csv(path):
xml_list = []
# 读取注释文件
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall('object'):
# value=(root.find('filename').test + '.jpg',
#这里要注意,如果生成的filename中没有.jpg文件,就在这里修改
value = (root.find('filename').text,
int(root.find('size')[0].text),
int(root.find('size')[1].text),
member[0].text,
int(member[4][0].text),
int(member[4][1].text),
int(member[4][2].text),
int(member[4][3].text)
)
xml_list.append(value)
column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
# 将所有数据分为样本集和验证集,一般按照3:1的比例
train_list = xml_list[0: int(len(xml_list) * 0.67)]
eval_list = xml_list[int(len(xml_list) * 0.67) + 1: ]
# 保存为CSV格式
train_df = pd.DataFrame(train_list, columns=column_name)
eval_df = pd.DataFrame(eval_list, columns=column_name)
train_df.to_csv('D:\software\pycharm\pycharmproject\imagerecognition\models-master\models-master\research\securityhattest\data\train.csv', index=None)
eval_df.to_csv('D:\software\pycharm\pycharmproject\imagerecognition\models-master\models-master\research\securityhattest\data\eval.csv', index=None)
def main():
path = 'D:\software\pycharm\pycharmproject\imagerecognition\models-master\models-master\research\securityhattest\data\train'
xml_to_csv(path)
print('Successfully converted xml to csv.')
main()5.将生成的CSV文件转换为tfrecord文件
方法一:在pycharm中直接运行 cvs_to_tfrecord.py
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
from __future__ import absolute_import
import os
import io
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
# from object_detection.utils import dataset_util
from object_detection.utils import dataset_util
from collections import namedtuple, OrderedDict
flags = tf.app.flags
flags.DEFINE_string('csv_input', '', 'Path to the CSV input')
flags.DEFINE_string('output_path', '', 'Path to output TFRecord')
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
# 将分类名称转成ID号
#这里要修改成你的分类ID,打开之前的CVS文件可以看到
def class_text_to_int(row_label):
if row_label == 'hat':
return 1
elif row_label == 'person':
return 2
else:
print('NONE: ' + row_label)
# None
def split(df, group):
data = namedtuple('data', ['filename', 'object'])
gb = df.groupby(group)
return [data(filename, gb.get_group(x)) for filename, x in zip(gb.groups.keys(), gb.groups)]
def create_tf_example(group, path):
print(os.path.join(path, '{}'.format(group.filename)))
with tf.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(path, '{}'.format(group.filename)), 'rb') as fid:
encoded_jpg = fid.read()
encoded_jpg_io = io.BytesIO(encoded_jpg)
image = Image.open(encoded_jpg_io)
width, height = image.size
filename = (group.filename + '.jpg').encode('utf8')
#这里要注意,很多网上的代码都是filename =group.filename.encode('utf8'),我直接运行会产生段错误
image_format = b'jpg'
xmins = []
xmaxs = []
ymins = []
ymaxs = []
classes_text = []
classes = []
for index, row in group.object.iterrows():
xmins.append(row['xmin'] / width)
xmaxs.append(row['xmax'] / width)
ymins.append(row['ymin'] / height)
ymaxs.append(row['ymax'] / height)
classes_text.append(row['class'].encode('utf8'))
classes.append(class_text_to_int(row['class']))
tf_example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/height': dataset_util.int64_feature(height),
'image/width': dataset_util.int64_feature(width),
'image/filename': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/source_id': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/encoded': dataset_util.bytes_feature(encoded_jpg),
'image/format': dataset_util.bytes_feature(image_format),
'image/object/bbox/xmin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmins),
'image/object/bbox/xmax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmaxs),
'image/object/bbox/ymin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymins),
'image/object/bbox/ymax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymaxs),
'image/object/class/text': dataset_util.bytes_list_feature(classes_text),
'image/object/class/label': dataset_util.int64_list_feature(classes),
}))
return tf_example
def main(csv_input, output_path, imgPath):
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(output_path)
path = imgPath
examples = pd.read_csv(csv_input)
grouped = split(examples, 'filename')
for group in grouped:
tf_example = create_tf_example(group, path)
writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
print('Successfully created the TFRecords: {}'.format(output_path))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# imgPath = 'E:dataImages'存放的图片的路径
imgPath = r'D:softwarepycharmpycharmprojectimagerecognitionmodels-mastermodels-master
esearchsecurityhattestimages rain'
# 生成train.record文件
output_path = 'data/train.tfrecord'#输出路径
csv_input = 'data/train.csv'#存放的csv文件路径
main(csv_input, output_path, imgPath)
# 生成验证文件 eval.record
output_path = 'data/eval.tfrecord'
csv_input = 'data/eval.csv'
main(csv_input, output_path, imgPath)
方法二:在CMD中CD到该项目文件夹下,我这里是images文件夹下,输入下列命令,运行generate_tfrecord.py:
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/train.csv --output_path=data/train.record
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/eval.csv --output_path=eval.record输出Successfully created the TFRecords即表示完成。
(小小提醒:开始没发现,我的数据集中XML文件中的图片名称有的是JPEG格式,而对应的图片全是JPG格式,导致PY代码中出现段错误,提醒大家多多注意这中坑…………)
6.新建自己的pbtxt文件
在自己项目中的data文件夹中新建label_map.pbtxt文件,我的是hatlabel_map.pbtxt,输入:
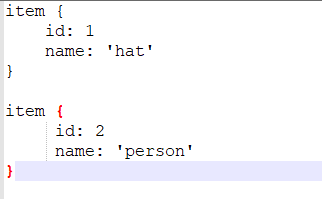
数字要与cvs_to_tfrecord.py、generate_tfrecord.py中的class_text_to_int函数一致对应
7.修改自己的ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config文件
代码:
# SSD with Mobilenet v1 configuration for MSCOCO Dataset.
# Users should configure the fine_tune_checkpoint field in the train config as
# well as the label_map_path and input_path fields in the train_input_reader and
# eval_input_reader. Search for "PATH_TO_BE_CONFIGURED" to find the fields that
# should be configured.
model {
ssd {
num_classes: 2#这里是你的种类数
box_coder {
faster_rcnn_box_coder {
y_scale: 10.0
x_scale: 10.0
height_scale: 5.0
width_scale: 5.0
}
}
matcher {
argmax_matcher {
matched_threshold: 0.5
unmatched_threshold: 0.5
ignore_thresholds: false
negatives_lower_than_unmatched: true
force_match_for_each_row: true
}
}
similarity_calculator {
iou_similarity {
}
}
anchor_generator {
ssd_anchor_generator {
num_layers: 6
min_scale: 0.2
max_scale: 0.95
aspect_ratios: 1.0
aspect_ratios: 2.0
aspect_ratios: 0.5
aspect_ratios: 3.0
aspect_ratios: 0.3333
}
}
image_resizer {
fixed_shape_resizer {
height: 300
300
}
}
box_predictor {
convolutional_box_predictor {
min_depth: 0
max_depth: 0
num_layers_before_predictor: 0
use_dropout: false
dropout_keep_probability: 0.8
kernel_size: 1
box_code_size: 4
apply_sigmoid_to_scores: false
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
}
feature_extractor {
type: 'ssd_mobilenet_v1'
min_depth: 16
depth_multiplier: 1.0
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
loss {
classification_loss {
weighted_sigmoid {
}
}
localization_loss {
weighted_smooth_l1 {
}
}
hard_example_miner {
num_hard_examples: 3000
iou_threshold: 0.99
loss_type: CLASSIFICATION
max_negatives_per_positive: 3
min_negatives_per_image: 0
}
classification_weight: 1.0
localization_weight: 1.0
}
normalize_loss_by_num_matches: true
post_processing {
batch_non_max_suppression {
score_threshold: 1e-8
iou_threshold: 0.6
max_detections_per_class: 100
max_total_detections: 100
}
score_converter: SIGMOID
}
}
}
train_config: {
batch_size: 2
optimizer {
rms_prop_optimizer: {
learning_rate: {
exponential_decay_learning_rate {
initial_learning_rate: 0.004
decay_steps: 800720
decay_factor: 0.95
}
}
momentum_optimizer_value: 0.9
decay: 0.9
epsilon: 1.0
}
}
#这里修改
fine_tune_checkpoint: "D:/software/pycharm/pycharmproject/imagerecognition/models-master/models-master/research/securityhattest/images/pretrained_model/model.ckpt"
from_detection_checkpoint: true
# Note: The below line limits the training process to 200K steps, which we
# empirically found to be sufficient enough to train the pets dataset. This
# effectively bypasses the learning rate schedule (the learning rate will
# never decay). Remove the below line to train indefinitely.
num_steps: 40000
data_augmentation_options {
random_horizontal_flip {
}
}
data_augmentation_options {
ssd_random_crop {
}
}
}
#下方4个路径修改
train_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "D:/software/pycharm/pycharmproject/imagerecognition/models-master/models-master/research/securityhattest/images/data/train.record"
}
label_map_path: "D:/software/pycharm/pycharmproject/imagerecognition/models-master/models-master/research/securityhattest/images/data/hatlabel_map.pbtxt"
}
eval_config: {
num_examples: 48#这里要修改
# Note: The below line limits the evaluation process to 10 evaluations.
# Remove the below line to evaluate indefinitely.
max_evals: 10
}
eval_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "D:/software/pycharm/pycharmproject/imagerecognition/models-master/models-master/research/securityhattest/images/data/eval.record"
}
label_map_path: "D:/software/pycharm/pycharmproject/imagerecognition/models-master/models-master/research/securityhattest/images/data/label_map.pbtxt"
shuffle: false
num_readers: 1
}
8.开始训练
我是直接打开researchobject_detectionlegacy下的train.py文件,修改后直接运行
代码:
# Copyright 2017 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
r"""Training executable for detection models.
This executable is used to train DetectionModels. There are two ways of
configuring the training job:
1) A single pipeline_pb2.TrainEvalPipelineConfig configuration file
can be specified by --pipeline_config_path.
Example usage:
./train
--logtostderr
--train_dir=path/to/train_dir
--pipeline_config_path=pipeline_config.pbtxt
2) Three configuration files can be provided: a model_pb2.DetectionModel
configuration file to define what type of DetectionModel is being trained, an
input_reader_pb2.InputReader file to specify what training data will be used and
a train_pb2.TrainConfig file to configure training parameters.
Example usage:
./train
--logtostderr
--train_dir=path/to/train_dir
--model_config_path=model_config.pbtxt
--train_config_path=train_config.pbtxt
--input_config_path=train_input_config.pbtxt
"""
import functools
import json
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib import framework as contrib_framework
from object_detection.builders import dataset_builder
from object_detection.builders import graph_rewriter_builder
from object_detection.builders import model_builder
from object_detection.legacy import trainer
from object_detection.utils import config_util
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO)
flags = tf.app.flags
flags.DEFINE_string('master', '', 'Name of the TensorFlow master to use.')
flags.DEFINE_integer('task', 0, 'task id')
flags.DEFINE_integer('num_clones', 1, 'Number of clones to deploy per worker.')
flags.DEFINE_boolean('clone_on_cpu', False,
'Force clones to be deployed on CPU. Note that even if '
'set to False (allowing ops to run on gpu), some ops may '
'still be run on the CPU if they have no GPU kernel.')
flags.DEFINE_integer('worker_replicas', 1, 'Number of worker+trainer '
'replicas.')
flags.DEFINE_integer('ps_tasks', 0,
'Number of parameter server tasks. If None, does not use '
'a parameter server.')
flags.DEFINE_string('train_dir', r'D:softwarepycharmpycharmprojectimagerecognitionmodels-mastermodels-master
esearchsecurityhattestimagesoutput',
'Directory to save the checkpoints and training summaries.')
flags.DEFINE_string('pipeline_config_path', r'D:softwarepycharmpycharmprojectimagerecognitionmodels-mastermodels-master
esearchsecurityhattestimages rainingssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config',
'Path to a pipeline_pb2.TrainEvalPipelineConfig config '
'file. If provided, other configs are ignored')
flags.DEFINE_string('train_config_path', '',
'Path to a train_pb2.TrainConfig config file.')
flags.DEFINE_string('input_config_path', '',
'Path to an input_reader_pb2.InputReader config file.')
flags.DEFINE_string('model_config_path', '',
'Path to a model_pb2.DetectionModel config file.')
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
@contrib_framework.deprecated(None, 'Use object_detection/model_main.py.')
def main(_):
assert FLAGS.train_dir, '`train_dir` is missing.'
if FLAGS.task == 0: tf.gfile.MakeDirs(FLAGS.train_dir)
if FLAGS.pipeline_config_path:
configs = config_util.get_configs_from_pipeline_file(
FLAGS.pipeline_config_path)
if FLAGS.task == 0:
tf.gfile.Copy(FLAGS.pipeline_config_path,
os.path.join(FLAGS.train_dir, 'pipeline.config'),
overwrite=True)
else:
configs = config_util.get_configs_from_multiple_files(
model_config_path=FLAGS.model_config_path,
train_config_path=FLAGS.train_config_path,
train_input_config_path=FLAGS.input_config_path)
if FLAGS.task == 0:
for name, config in [('model.config', FLAGS.model_config_path),
('train.config', FLAGS.train_config_path),
('input.config', FLAGS.input_config_path)]:
tf.gfile.Copy(config, os.path.join(FLAGS.train_dir, name),
overwrite=True)
model_config = configs['model']
train_config = configs['train_config']
input_config = configs['train_input_config']
model_fn = functools.partial(
model_builder.build,
model_config=model_config,
is_training=True)
def get_next(config):
return dataset_builder.make_initializable_iterator(
dataset_builder.build(config)).get_next()
create_input_dict_fn = functools.partial(get_next, input_config)
env = json.loads(os.environ.get('TF_CONFIG', '{}'))
cluster_data = env.get('cluster', None)
cluster = tf.train.ClusterSpec(cluster_data) if cluster_data else None
task_data = env.get('task', None) or {'type': 'master', 'index': 0}
task_info = type('TaskSpec', (object,), task_data)
# Parameters for a single worker.
ps_tasks = 0
worker_replicas = 1
worker_job_name = 'lonely_worker'
task = 0
is_chief = True
master = ''
if cluster_data and 'worker' in cluster_data:
# Number of total worker replicas include "worker"s and the "master".
worker_replicas = len(cluster_data['worker']) + 1
if cluster_data and 'ps' in cluster_data:
ps_tasks = len(cluster_data['ps'])
if worker_replicas > 1 and ps_tasks < 1:
raise ValueError('At least 1 ps task is needed for distributed training.')
if worker_replicas >= 1 and ps_tasks > 0:
# Set up distributed training.
server = tf.train.Server(tf.train.ClusterSpec(cluster), protocol='grpc',
job_name=task_info.type,
task_index=task_info.index)
if task_info.type == 'ps':
server.join()
return
worker_job_name = '%s/task:%d' % (task_info.type, task_info.index)
task = task_info.index
is_chief = (task_info.type == 'master')
master = server.target
graph_rewriter_fn = None
if 'graph_rewriter_config' in configs:
graph_rewriter_fn = graph_rewriter_builder.build(
configs['graph_rewriter_config'], is_training=True)
trainer.train(
create_input_dict_fn,
model_fn,
train_config,
master,
task,
FLAGS.num_clones,
worker_replicas,
FLAGS.clone_on_cpu,
ps_tasks,
worker_job_name,
is_chief,
FLAGS.train_dir,
graph_hook_fn=graph_rewriter_fn)
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()
修改内容:只是添加了train_dir、pipeline_config_path的路径
9.打开tensorboard查看训练过程
1.CMD CD到images文件夹中的output文件夹,输入tensorboard --logdir ./

10.训练完成,导出训练模型
CMD CD到object_detection文件夹,输入:
python export_inference_graph.py --input_type image_tensor
--pipeline_config_path=D://software//pycharm//pycharmproject//imagerecognition//models-master//models-master//research//securityhattest//images//training//ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config
--trained_checkpoint_prefix=D://software//pycharm//pycharmproject//imagerecognition//models-master//models-master//research//securityhattest//images//output//model.ckpt-10374
--output_directory=D://software//pycharm//pycharmproject//imagerecognition//models-master//models-master//research//securityhattest//images//finished
报错:ValueError: The passed save_path is not a valid checkpoint:
原因是项目所在的文件导入路径的字符太长
将--trained_checkpoint_prefix的路径改的短一点就可以了
之后的模型检验借鉴了https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33624802/article/details/82384117
11.模型检验
安装了anaconda的大家可以使用jupyter打开object_detection中的object_detection_tutorial.ipynb,如果使用的是python可以使用下面的代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import os
import pylab
import tensorflow as tf
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
#下面的两个导入根据你PY文件的路径进行修改,我的是在object——detection文件夹下
from utils import label_map_util
from utils import visualization_utils as vis_util
# What model to download.刚才训练模型的输出路径
MODEL_NAME = 'D:\software\pycharm\pycharmproject\imagerecognition\models-master\models-master\research\securityhattest\images\finished'
# Path to frozen detection graph. This is the actual model that is used for the object detection.
PATH_TO_CKPT = MODEL_NAME + '/frozen_inference_graph.pb'
# List of the strings that is used to add correct label for each box.
#PATH_TO_LABELS = os.path.join('data', 'mscoco_label_map.pbtxt')
#你的label_map.pbtxt文件路径
PATH_TO_LABELS='D:\software\pycharm\pycharmproject\imagerecognition\models-master\models-master\research\securityhattest\images\data\hatlabel_map.pbtxt'
NUM_CLASSES = 2#分类个数
tf.reset_default_graph()
od_graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
with tf.gfile.GFile(PATH_TO_CKPT, 'rb') as fid:
serialized_graph = fid.read()
od_graph_def.ParseFromString(serialized_graph)
tf.import_graph_def(od_graph_def, name='')
label_map = label_map_util.load_labelmap(PATH_TO_LABELS)
categories = label_map_util.convert_label_map_to_categories(label_map, max_num_classes=NUM_CLASSES,
use_display_name=True)
category_index = label_map_util.create_category_index(categories)
def load_image_into_numpy_array(image):
(im_width, im_height) = image.size
return np.array(image.getdata()).reshape(
(im_height, im_width, 3)).astype(np.uint8)
#存放用于测试的图片路径,个数更改的话for i in range(1, 5)也要更改
PATH_TO_TEST_IMAGES_DIR = 'D:\software\pycharm\pycharmproject\imagerecognition\models-master\models-master\research\securityhattest\images\test'
TEST_IMAGE_PATHS = [os.path.join(PATH_TO_TEST_IMAGES_DIR, 'image{}.jpg'.format(i)) for i in range(1, 5)]
# Size, in inches, of the output images.
IMAGE_SIZE = (12, 8)
detection_graph = tf.get_default_graph()
with tf.Session(graph=detection_graph) as sess:
for image_path in TEST_IMAGE_PATHS:
image = Image.open(image_path)
# the array based representation of the image will be used later in order to prepare the
# result image with boxes and labels on it.
image_np = load_image_into_numpy_array(image)
# Expand dimensions since the model expects images to have shape: [1, None, None, 3]
image_np_expanded = np.expand_dims(image_np, axis=0)
image_tensor = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('image_tensor:0')
# Each box represents a part of the image where a particular object was detected.
boxes = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_boxes:0')
# Each score represent how level of confidence for each of the objects.
# Score is shown on the result image, together with the class label.
scores = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_scores:0')
classes = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_classes:0')
num_detections = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('num_detections:0')
# Actual detection.
(boxes, scores, classes, num_detections) = sess.run(
[boxes, scores, classes, num_detections],
feed_dict={image_tensor: image_np_expanded})
# Visualization of the results of a detection.
vis_util.visualize_boxes_and_labels_on_image_array(
image_np,
np.squeeze(boxes),
np.squeeze(classes).astype(np.int32),
np.squeeze(scores),
category_index,
use_normalized_coordinates=True,
line_thickness=8)
plt.figure(figsize=IMAGE_SIZE)
plt.imshow(image_np)
pylab.show()12.效果展示


我是使用自己电脑,设置训练40000次,等不上了10000就停了,而且数据量较小,所以有的图片识别效果不好,下一步就是扩大数据集,用服务器跑了~
输出详细信息:参见https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43599336/article/details/84112134
