1. 利用Mininet仿真平台构建如下图所示的网络拓扑,配置主机h1和h2的IP地址,测试两台主机之间的网络连通性


2. 利用Wireshark工具,捕获拓扑中交换机与控制器之间的通信数据,对OpenFlow协议类型的各类报文进行分析,对照wireshark截图写出分析内容。
先运行Wireshark然后选择any后再进行拓扑连接
hello
控制器与交换机建立连接时由其中某一方发起Hello消息,双方协调协议版本号。Hello消息只有openflow包头,没有主体部分。头部结构如下:
/* Header on all OpenFlow packets. */
struct ofp_header {
uint8_t version; /*版本*/
uint8_t type; /*消息类型*/
uint16_t length; /*消息总长度,包含头部*/
uint32_t xid; /*事件ID,同一件事件的ID号一致如feature_request和对应的feature_reply就使用同一个Transaction id,但是两个hello消息的Transaction id并不相同,不过据实验结果看两个id一般是两个相邻的数字。*/
};
OFP_ASSERT(sizeof(struct ofp_header) == 8);
交换机42914端口最高支持1.3版本,控制器6633端口
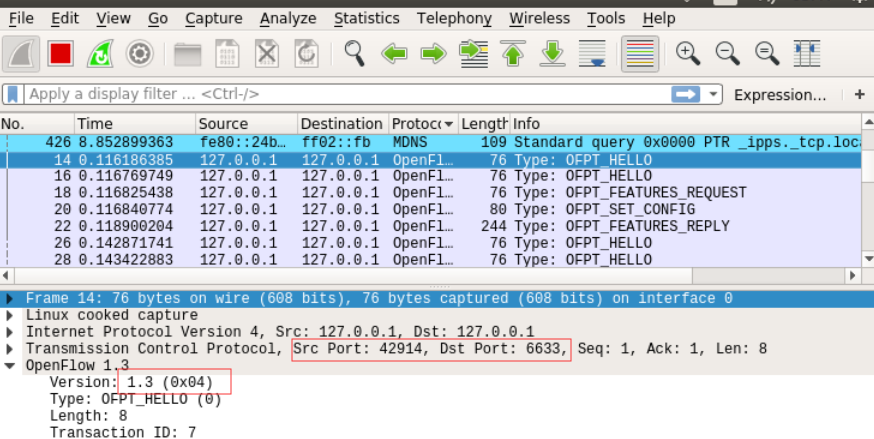
控制器6633端口最高支持1.0版本,交换机42914端口

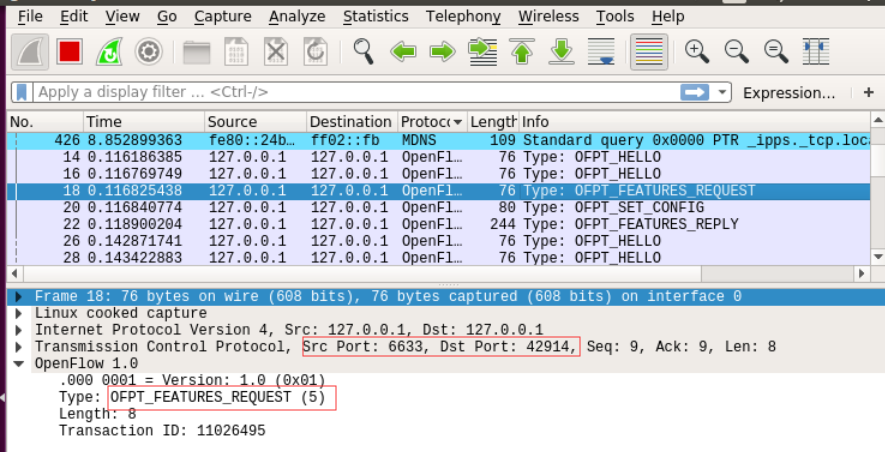
features
OpenFlow 连接建立之后,控制器就会向交换机发送一个ofpt_feature_request消息,该消息只有openflow包头。交换机会回复一条ofpt_feature_reply消息。知道了交换机的特性之后就要配置交换机了。OpenFlow 交换机只有两个属性需要控制器配置:
第一个属性为 flags,用来指示交换机如何才处理 IP 分片数据包。
第二个属性为 miss_send_len,用来指示当一个交换机无法处理的数据包到达时,将数据包发给控制器的最大字节数。
Features 消息包括的 OpenFlow Header 和 Features Reply Message对照Features Reply Message结构如下:
struct ofp_switch_features{
struct ofp_header header;
uint64_t datapath_id; /*唯一标识 id 号*/
uint32_t n_buffers; /*交缓冲区可以缓存的最大数据包个数*/
uint8_t n_tables; /*流表数量*/
uint8_t pad[3]; /*align to 64 bits*/
uint32_t capabilities; /*支持的特殊功能,具体见 ofp_capabilities*/
uint32_t actions; /*支持的动作,具体见 ofp_actions_type*/
struct ofp_phy_port ports[0]; /*物理端口描述列表,具体见 ofp_phy_port*/
};
结果如下:
features request:控制器向交换机发送请求交换机的特征信息
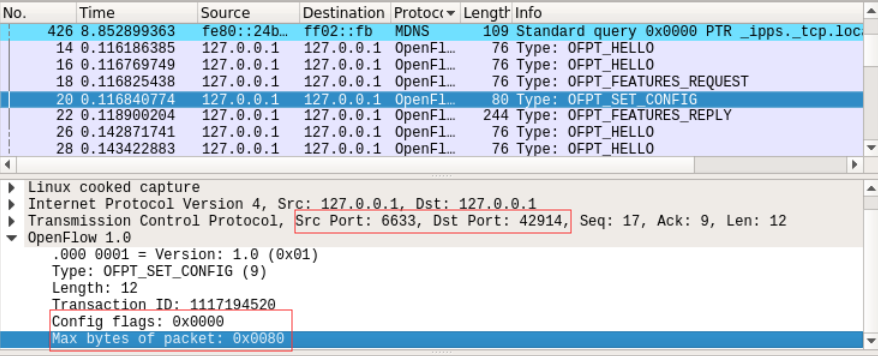
set config:控制器让交换机按自己设置的flag和 max bytes of packet进行配置
features reply:交换机向控制器发送自己的特征信息
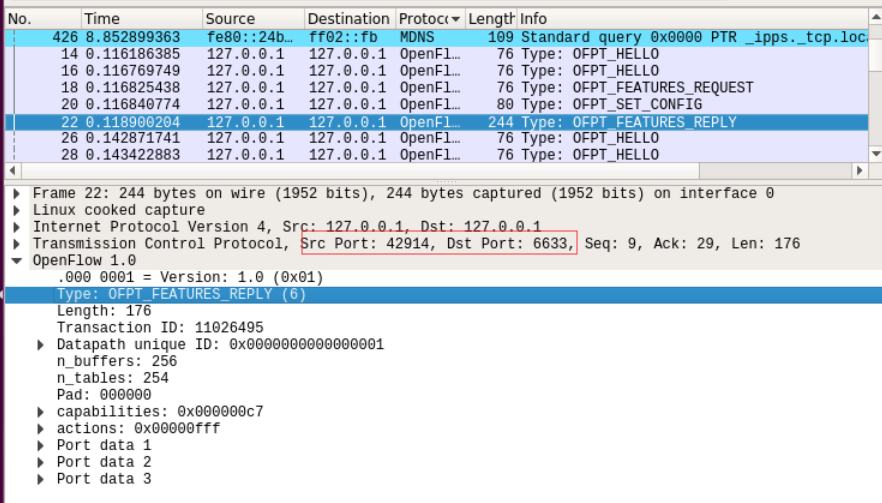
对应到抓取到的报文,逐项查看报文内容
Frame 22: 244 bytes on wire (1952 bits), 244 bytes captured (1952 bits) on interface 0
Linux cooked capture
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 127.0.0.1, Dst: 127.0.0.1
Transmission Control Protocol, Src Port: 42914, Dst Port: 6633, Seq: 9, Ack: 29, Len: 176
OpenFlow 1.0
.000 0001 = Version: 1.0 (0x01)
Type: OFPT_FEATURES_REPLY (6)
Length: 176
Transaction ID: 11026495
Datapath unique ID: 0x0000000000000001
n_buffers: 256
n_tables: 254
Pad: 000000
capabilities: 0x000000c7
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...1 = Flow statistics: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ..1. = Table statistics: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... .1.. = Port statistics: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... 0... = Group statistics: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... = Can reassemble IP fragments: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .1.. .... = Queue statistics: True
.... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... .... = Switch will block looping ports: False
actions: 0x00000fff
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...1 = Output to switch port: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ..1. = Set the 802.1q VLAN id: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... .1.. = Set the 802.1q priority: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... 1... = Strip the 802.1q header: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... ...1 .... = Ethernet source address: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... ..1. .... = Ethernet destination address: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... .1.. .... = IP source address: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... 1... .... = IP destination address: True
.... .... .... .... .... ...1 .... .... = IP ToS (DSCP field, 6 bits): True
.... .... .... .... .... ..1. .... .... = TCP/UDP source port: True
.... .... .... .... .... .1.. .... .... = TCP/UDP destination port: True
.... .... .... .... .... 1... .... .... = Output to queue: True
Port data 1
Port number: 65534
HW Address: e6:71:03:75:a0:41 (e6:71:03:75:a0:41)
Port Name: s1
Config flags: 0x00000001
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...1 = Port is administratively down: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. = Disable 802.1D spanning tree on port: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. = Drop all packets except 802.1D spanning tree packets: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... 0... = Drop received 802.1D STP packets: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... = Do not include this port when flooding: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... = Drop packets forwarded to port: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. .... = Do not send packet-in msgs for port: False
State flags: 0x00000001
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...1 = No physical link present: True
Current features: 0x00000000
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 = 10 Mb half-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. = 10 Mb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. = 100 Mb half-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... 0... = 100 Mb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... = 1 Gb half-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... = 1 Gb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. .... = 10 Gb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... 0... .... = Copper medium: False
.... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... .... = Fiber medium: False
.... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... .... = Auto-negotiation: False
.... .... .... .... .... .0.. .... .... = Pause: False
.... .... .... .... .... 0... .... .... = Asymmetric pause: False
Advertised features: 0x00000000
Features supported: 0x00000000
Features advertised by peer: 0x00000000
Port data 2
Port number: 1
HW Address: 3a:31:3c:b1:0f:f1 (3a:31:3c:b1:0f:f1)
Port Name: s1-eth1
Config flags: 0x00000000
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 = Port is administratively down: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. = Disable 802.1D spanning tree on port: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. = Drop all packets except 802.1D spanning tree packets: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... 0... = Drop received 802.1D STP packets: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... = Do not include this port when flooding: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... = Drop packets forwarded to port: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. .... = Do not send packet-in msgs for port: False
State flags: 0x00000000
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 = No physical link present: False
Current features: 0x000000c0
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 = 10 Mb half-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. = 10 Mb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. = 100 Mb half-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... 0... = 100 Mb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... = 1 Gb half-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... = 1 Gb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .1.. .... = 10 Gb full-duplex rate support: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... 1... .... = Copper medium: True
.... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... .... = Fiber medium: False
.... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... .... = Auto-negotiation: False
.... .... .... .... .... .0.. .... .... = Pause: False
.... .... .... .... .... 0... .... .... = Asymmetric pause: False
Advertised features: 0x00000000
Features supported: 0x00000000
Features advertised by peer: 0x00000000
Port data 3
Port number: 2
HW Address: f2:aa:52:77:ab:74 (f2:aa:52:77:ab:74)
Port Name: s1-eth2
Config flags: 0x00000000
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 = Port is administratively down: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. = Disable 802.1D spanning tree on port: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. = Drop all packets except 802.1D spanning tree packets: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... 0... = Drop received 802.1D STP packets: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... = Do not include this port when flooding: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... = Drop packets forwarded to port: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. .... = Do not send packet-in msgs for port: False
State flags: 0x00000000
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 = No physical link present: False
Current features: 0x000000c0
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 = 10 Mb half-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. = 10 Mb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... .0.. = 100 Mb half-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .... 0... = 100 Mb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... = 1 Gb half-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... = 1 Gb full-duplex rate support: False
.... .... .... .... .... .... .1.. .... = 10 Gb full-duplex rate support: True
.... .... .... .... .... .... 1... .... = Copper medium: True
.... .... .... .... .... ...0 .... .... = Fiber medium: False
.... .... .... .... .... ..0. .... .... = Auto-negotiation: False
.... .... .... .... .... .0.. .... .... = Pause: False
.... .... .... .... .... 0... .... .... = Asymmetric pause: False
Advertised features: 0x00000000
Features supported: 0x00000000
Features advertised by peer: 0x00000000
packet_in消息
当交换机碰到新数据包不知道如何处理,或者action要求发送给控制器,那么交换机就会用packet_in消息发送给控制器。一般将数据包缓存在交换机中,将有效的数据包信息(默认的128字节,如果原因是 “send to controller” action,那么长度由action_out的max_len决定;如果是原因table miss,那么长度由set_config消息中的miss_send_len决定。)和缓存id发送给控制器,不过,如果交换机不支持缓存或者内存用光了,那么就把整个数据包放在数据部分发给控制器,并且缓存id为-1。
packet_in消息结构如下:
struct ofp_packet_in {
struct ofp_header header;
uint32_t buffer_id; /*Packet-in消息所携带的数据包在交换机缓存区中的ID*/
uint16_t total_len; /*data字段的长度*/
uint16_t in_port; /*数据包进入交换机时的端口号*/
uint8_t reason; /*发送Packet-in消息的原因,具体见 ofp_packet_in_reason*/
uint8_t pad;
uint8_t data[0]; /*携带的数据包*/
};
结果如下:
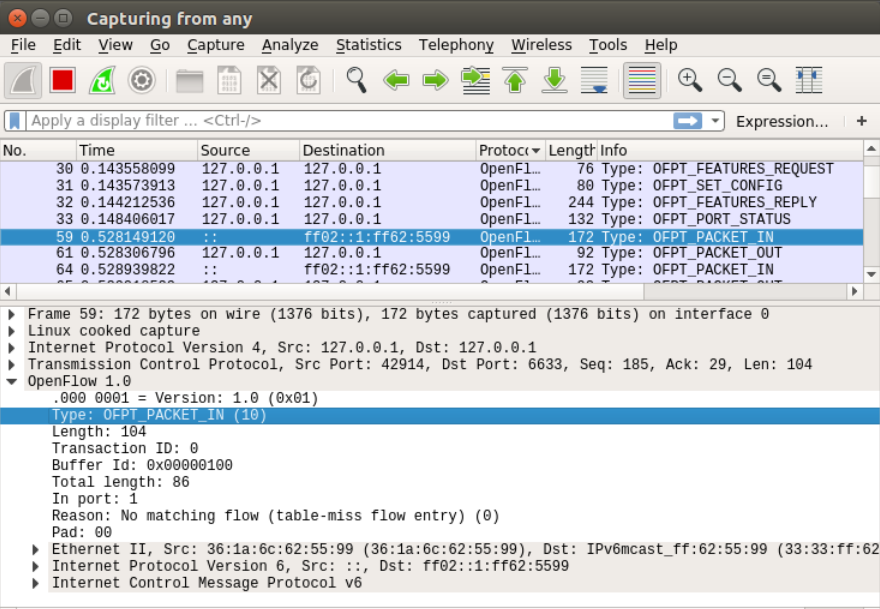
分析抓取的数据包,可以发现是因为交换机发现此时自己并没有匹配的流表(Reason: No matching flow (table-miss flow entry) (0)),所以要问控制器如何处理
Frame 59: 172 bytes on wire (1376 bits), 172 bytes captured (1376 bits) on interface 0
Linux cooked capture
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 127.0.0.1, Dst: 127.0.0.1
Transmission Control Protocol, Src Port: 42914, Dst Port: 6633, Seq: 185, Ack: 29, Len: 104
OpenFlow 1.0
.000 0001 = Version: 1.0 (0x01)
Type: OFPT_PACKET_IN (10)
Length: 104
Transaction ID: 0
Buffer Id: 0x00000100
Total length: 86
In port: 1
Reason: No matching flow (table-miss flow entry) (0)
Pad: 00
Ethernet II, Src: 36:1a:6c:62:55:99 (36:1a:6c:62:55:99), Dst: IPv6mcast_ff:62:55:99 (33:33:ff:62:55:99)
Destination: IPv6mcast_ff:62:55:99 (33:33:ff:62:55:99)
Address: IPv6mcast_ff:62:55:99 (33:33:ff:62:55:99)
.... ..1. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Locally administered address (this is NOT the factory default)
.... ...1 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Group address (multicast/broadcast)
Source: 36:1a:6c:62:55:99 (36:1a:6c:62:55:99)
Address: 36:1a:6c:62:55:99 (36:1a:6c:62:55:99)
.... ..1. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Locally administered address (this is NOT the factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Type: IPv6 (0x86dd)
Internet Protocol Version 6, Src: ::, Dst: ff02::1:ff62:5599
0110 .... = Version: 6
.... 0000 0000 .... .... .... .... .... = Traffic Class: 0x00 (DSCP: CS0, ECN: Not-ECT)
.... 0000 00.. .... .... .... .... .... = Differentiated Services Codepoint: Default (0)
.... .... ..00 .... .... .... .... .... = Explicit Congestion Notification: Not ECN-Capable Transport (0)
.... .... .... 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 = Flow Label: 0x00000
Payload Length: 32
Next Header: ICMPv6 (58)
Hop Limit: 255
Source: ::
Destination: ff02::1:ff62:5599
Internet Control Message Protocol v6
Type: Neighbor Solicitation (135)
Code: 0
Checksum: 0x5cd0 [correct]
[Checksum Status: Good]
Reserved: 00000000
Target Address: fe80::341a:6cff:fe62:5599
ICMPv6 Option (Nonce)
Type: Nonce (14)
Length: 1 (8 bytes)
Nonce: 303f81c51438
packet_out
当控制器希望交换机发送某个数据包或指定一个数据包的处理方法时,就使用packet_out
packet_out消息结构如下:
struct ofp_packet_out {
struct ofp_header header;
uint32_t buffer_id; /*交换机缓存区id,如果为-1则指定的为packet-out消息携带的data字段*/
uint16_t in_port; /*如果buffer_id为‐1,并且action列表中指定了Output=TABLE的动作,in_port将作为data段数据包的额外匹配信息进行流表查询*/
uint16_t actions_len; /*action列表的长度,可以用来区分actions和data段*/
struct ofp_action_header actions[0]; /*动作列表*/
uint8_t data[0]; /*数据缓存区,可以存储一个以太网帧,可选*/
}
结果如下:
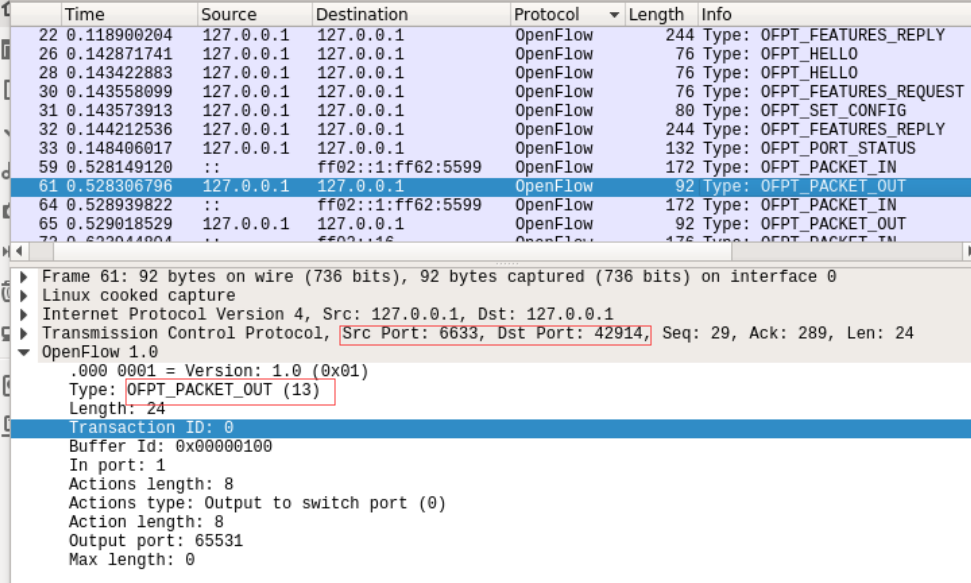
分析报文内容可知,控制器告诉交换机输出到65531端口
Frame 61: 92 bytes on wire (736 bits), 92 bytes captured (736 bits) on interface 0
Linux cooked capture
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 127.0.0.1, Dst: 127.0.0.1
Transmission Control Protocol, Src Port: 6633, Dst Port: 42914, Seq: 29, Ack: 289, Len: 24
OpenFlow 1.0
.000 0001 = Version: 1.0 (0x01)
Type: OFPT_PACKET_OUT (13)
Length: 24
Transaction ID: 0
Buffer Id: 0x00000100
In port: 1
Actions length: 8
Actions type: Output to switch port (0)
Action length: 8
Output port: 65531
Max length: 0
另一台交换机与控制器的交互过程

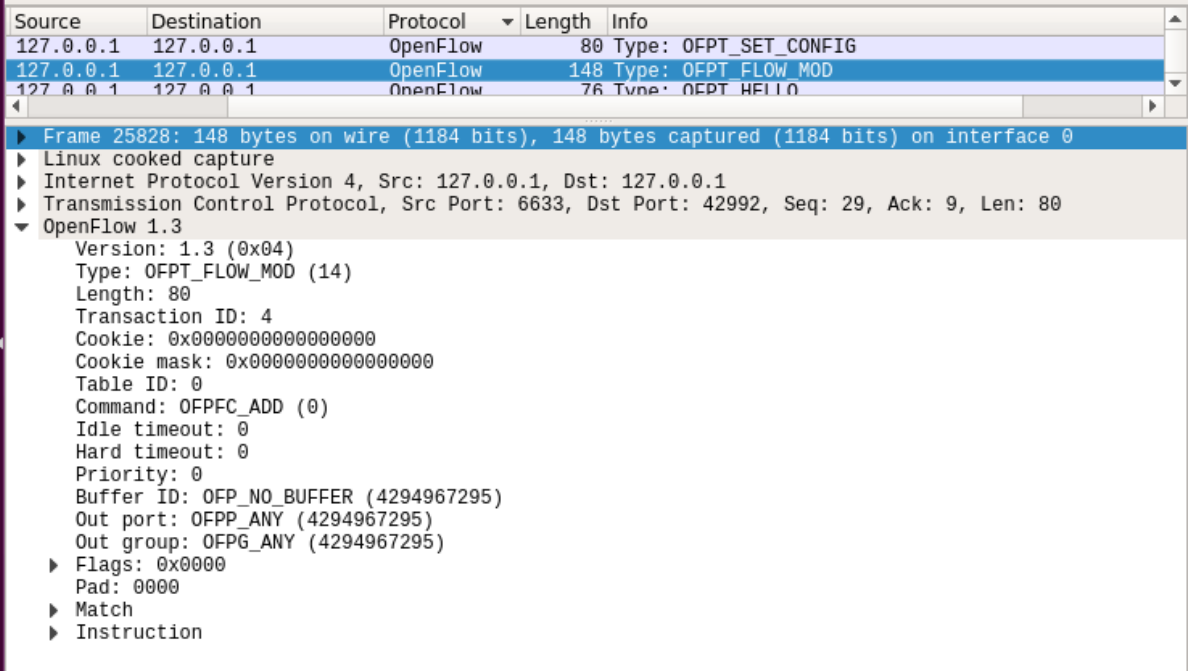
flow-mod
flow-mod消息结构如下:
struct ofp_flow_mod {
struct ofp_header header;
struct ofp_match match; /*流表的匹配域*/
uint64_t cookie; /*流表项标识符*/
uint16_t command; /*可以是ADD,DELETE,DELETE-STRICT,MODIFY,MODIFY-STRICT*/
uint16_t idle_timeout; /*空闲超时时间*/
uint16_t hard_timeout; /*最大生存时间*/
uint16_t priority; /*优先级,优先级高的流表项优先匹配*/
uint32_t buffer_id; /*缓存区ID ,用于指定缓存区中的一个数据包按这个消息的action列表处理*/
uint16_t out_port; /*如果这条消息是用于删除流表则需要提供额外的匹配参数*/
uint16_t flags; /*标志位,可以用来指示流表删除后是否发送flow‐removed消息,添加流表时是否检查流表重复项,添加的流表项是否为应急流表项。*/
struct ofp_action_header actions[0]; /*action列表*/
};
h1 ping h2
使用命令
h1 ping -c 3 h2
抓包结果如下:
控制器通过6633端口向交换机45646端口,交换机42914端口下发流表项,指导数据的转发处理
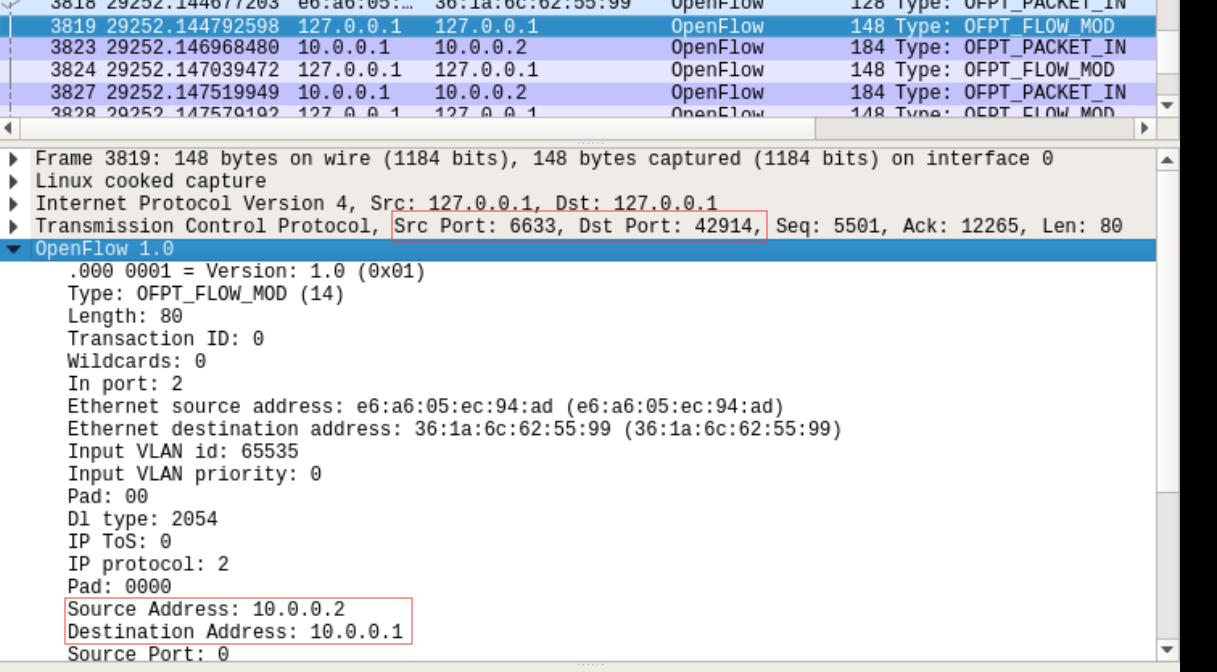
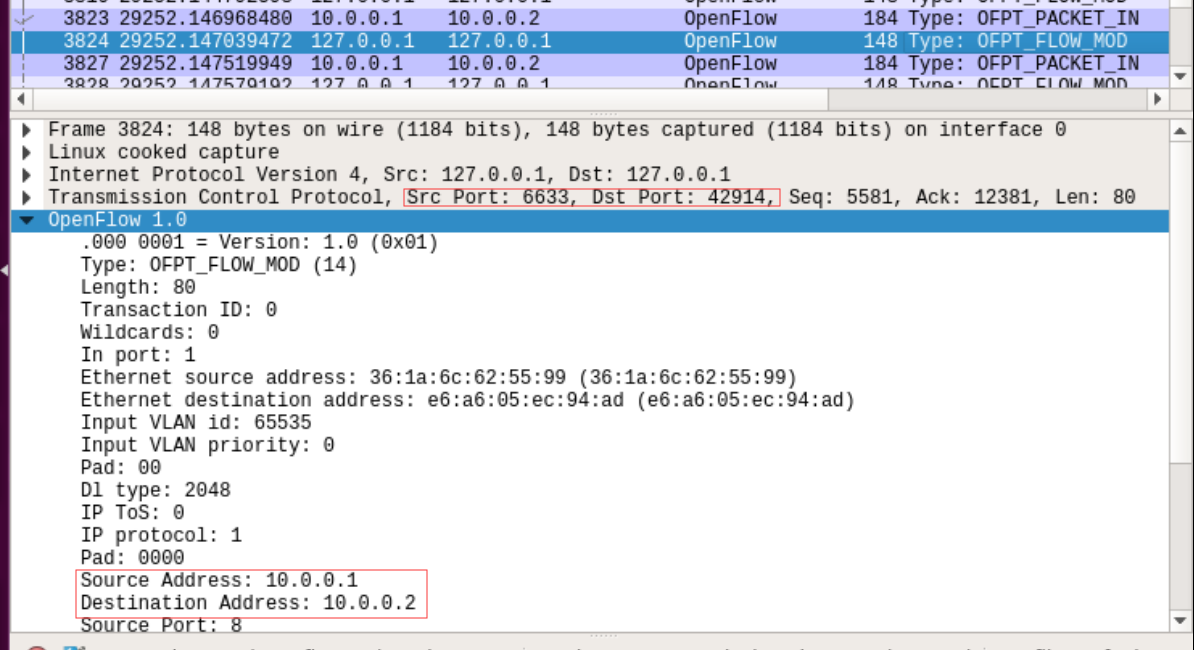
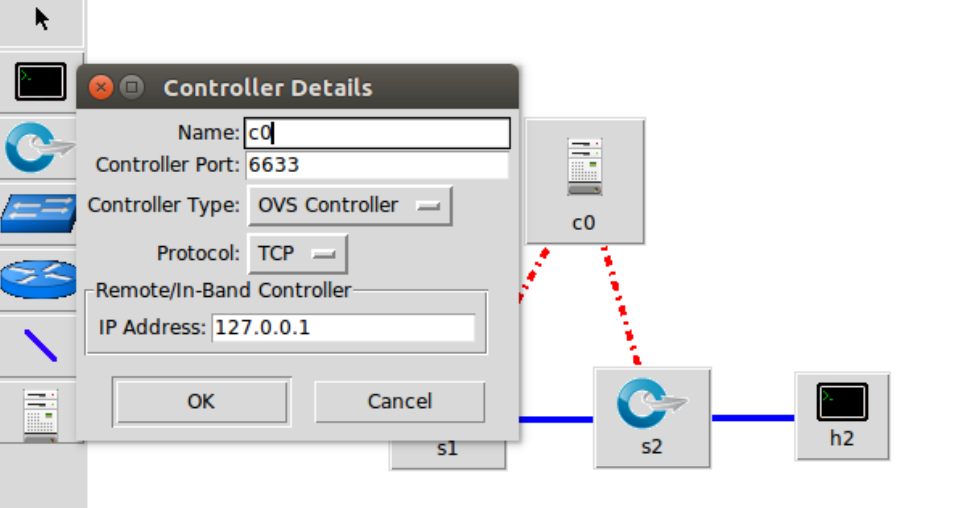
把控制器从openflow reference改成ovs controller
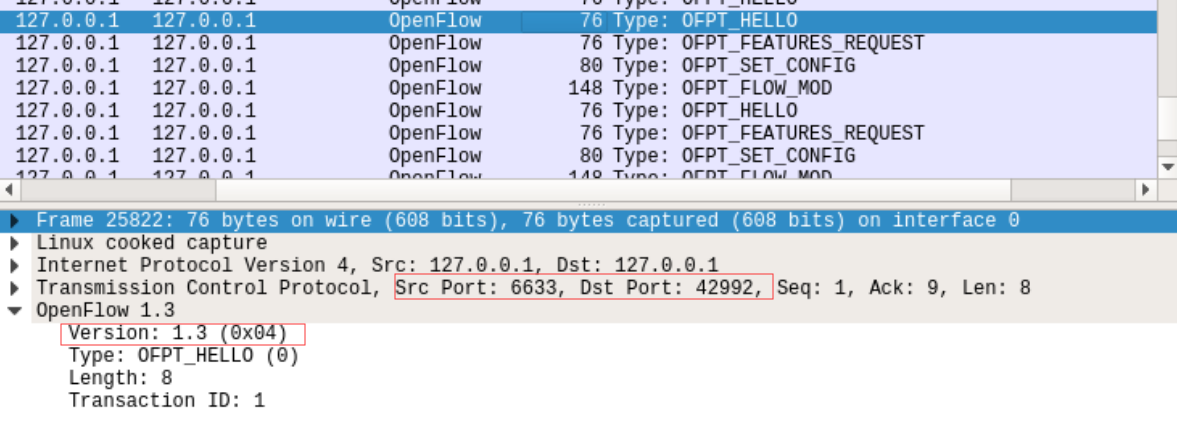
在hello报文中可以发现控制器支持的OpenFlow版本从1.0变成了1.3,因此,经过协商交换机和控制器之间将通过1.3版本的OpenFlow协议进行通信

low_mod