






/** * 暴力解法 * 1.创建数组,存放所有的请求 * 整型数组,存放10000个元素 * 2.把当前请求存入数组 * 记录最后一次存入的索引,从0开始 * 3.统计距离此次请求前3000毫秒之间的请求次数 * 从最后一次存放位置倒序遍历 * * @param t 时长为 t(单位:毫秒) 的请求 * @return 过去3000毫秒内有多少次请求:[t-3000, t] */ public int ping(int t) { // 2.把当前请求存入数组 int end = 0; for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { if (array[i] == 0) { // 细节:数组元素是0,该位置没有存过请求 array[i] = t; end = i; // 记录最近一次请求存放的索引 break; } } // 3.统计距离此次请求前3000毫秒之间的请求次数 int count = 0; // 计数器 while (array[end] >= t - 3000) { count++; if (--end < 0) { // 防止越界 break; } } return count; }




// 1.创建数组,存放所有的请求 // int[] array = new int[10000]; int[] array = new int[3002]; // 2.记录起止索引,从0开始 int start = 0, end = 0; /** * 优化解法:双指针 * 1.创建数组存放请求:int[3002] * 2.额外定义开始指针 * start=0,end=0,记录起止索引 * 3.存放请求后,更新起止索引 * end++; 从上次的开始索引(start)向后查找 * 直到新的合法的起始位置 * 4.通过end与start差值计算请求次数 * * @param t 时长为 t(单位:毫秒) 的请求 * @return 过去3000毫秒内有多少次请求:[t-3000, t] */ public int ping(int t) { // 3.存放请求后,更新起止索引 array[end++] = t; // 存放最近一次请求,结束索引加 1 end = end == array.length ? 0 : end; // 越界后,从0开始 // 从start位置开始,正向查找符合要求的请求次数 while (array[start] < t - 3000) { // 过滤掉所有不符合要求的数据 start ++; start = start == array.length ? 0 : start; } // 4.通过end与start差值计算请求次数 if (start > end) { // 请求次数超过数组容量,发生了溢出 return array.length - (start - end); } // 此时,end为最新一次请求 + 1 的索引,start是3000毫秒前的第一次合法请求索引 return end - start; }




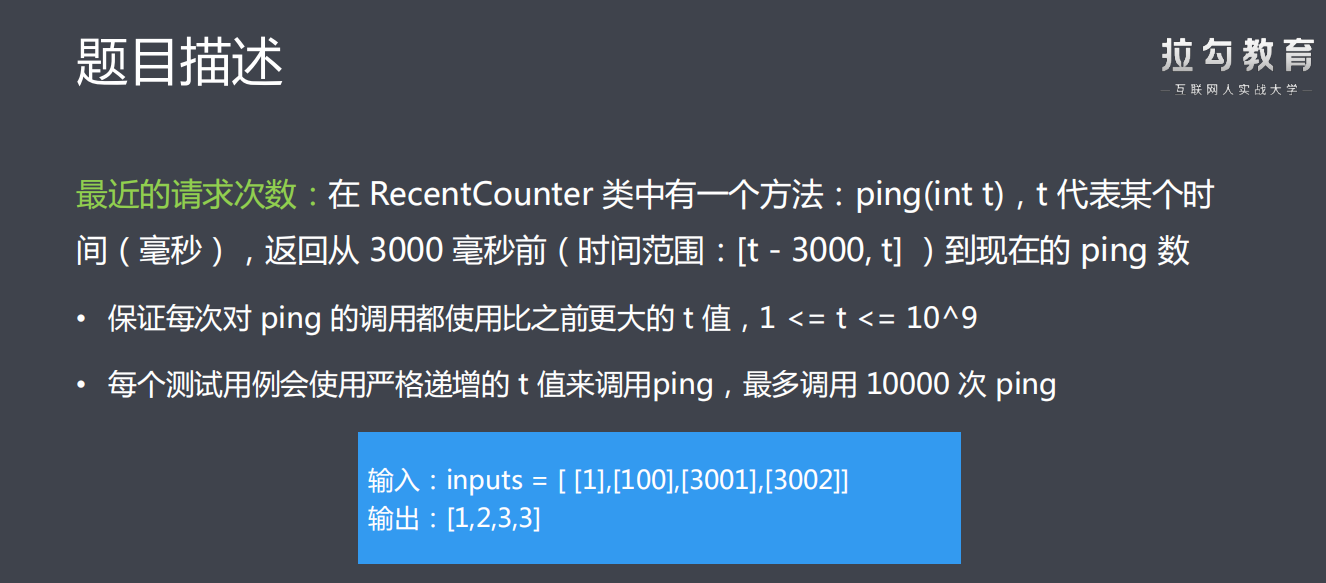
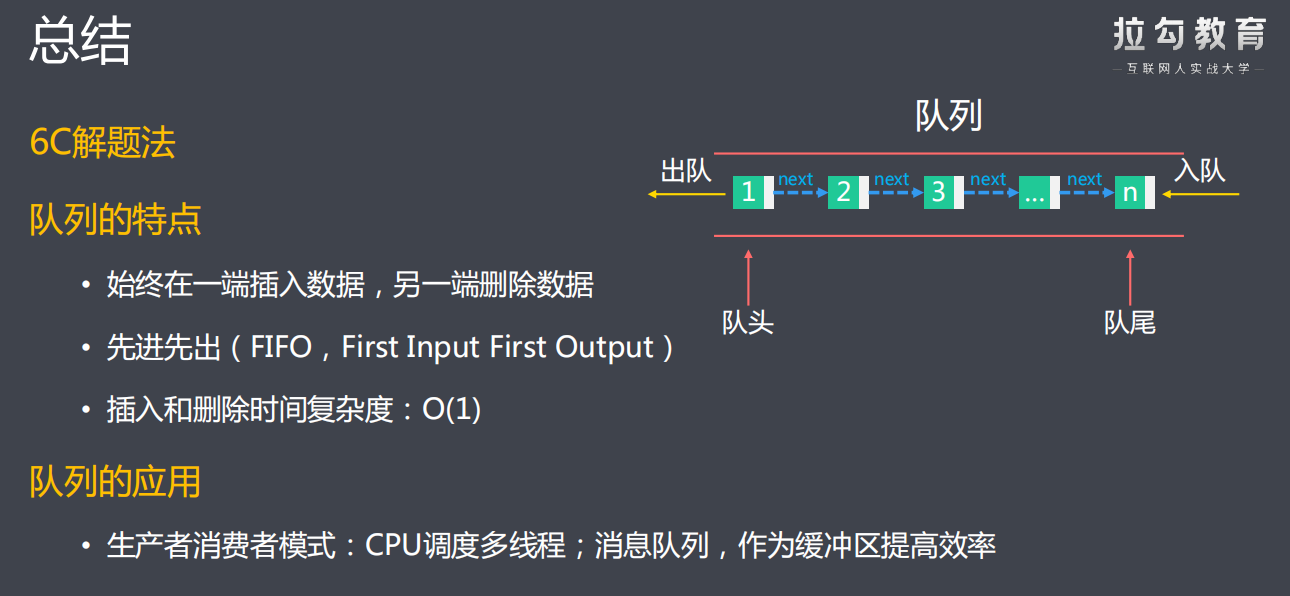
/** * 最优解:队列解法 * 1.使用链表实现一个队列 * 定义属性:队头-head、队尾-tail、长度-size * 定义方法:添加节点-add(int)、移除节点-poll() 、队列长度-size() * 定义内部类:Node,封装每次入队的请求数据和指向下一个节点的指针 * 2.每次请求向队列尾部追加节点 * 3.循环检查队头数据是否合法 * 不合法则移除该节点 * 4.返回队列长度 * @param t * @return */ public int ping(int t) { // 2.每次请求向队列尾部追加节点 q.add(t); // 3.循环检查队头数据是否合法 while (q.head.getVal() < t - 3000){ q.poll();
} // 4.返回队列长度 return q.size(); }
/** * 最优解:队列解法 * 1.使用链表实现一个队列 * 定义属性:队头-head、队尾-tail、长度-size * 定义方法:添加节点-add(int)、移除节点-poll() 、队列长度-size() * 定义内部类:Node,封装每次入队的请求数据和指向下一个节点的指针 * 2.每次请求向队列尾部追加节点 * 3.循环检查队头数据是否合法 * 不合法则移除该节点 * 4.返回队列长度 * @param t * @return */ public int ping(int t) { // 2.每次请求向队列尾部追加节点 q.add(t); // 3.循环检查队头数据是否合法 while (q.head.getVal() < t - 3000){ q.poll();
} // 4.返回队列长度 return q.size(); }
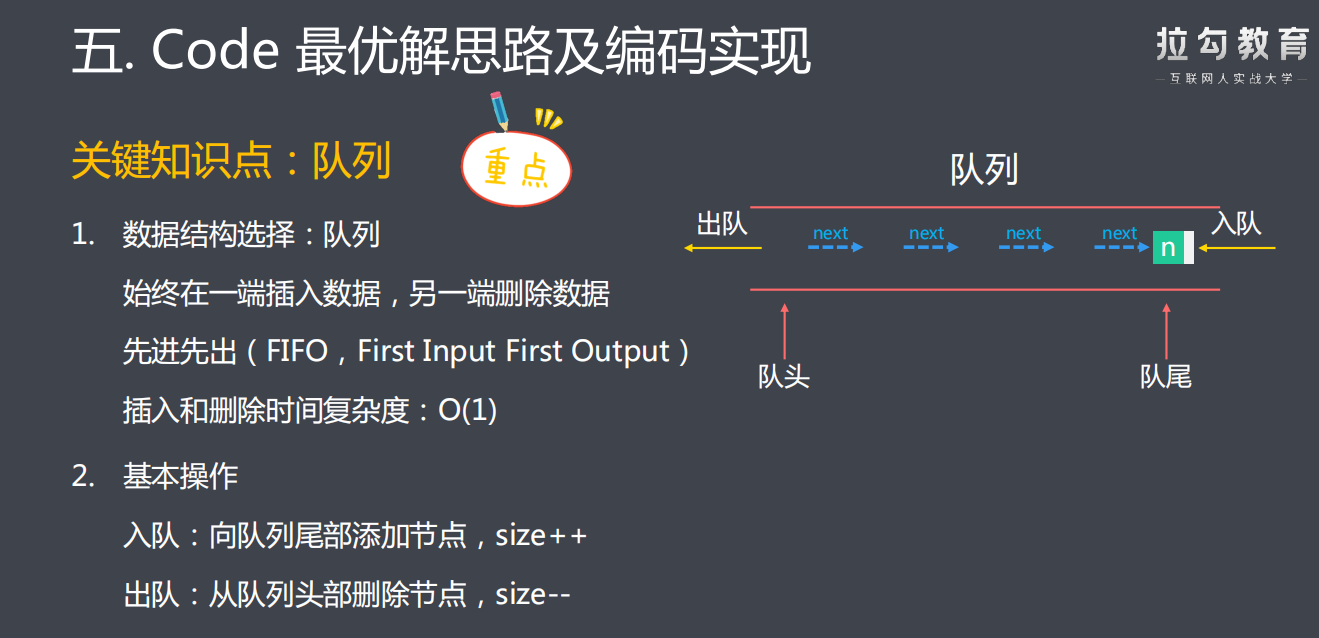
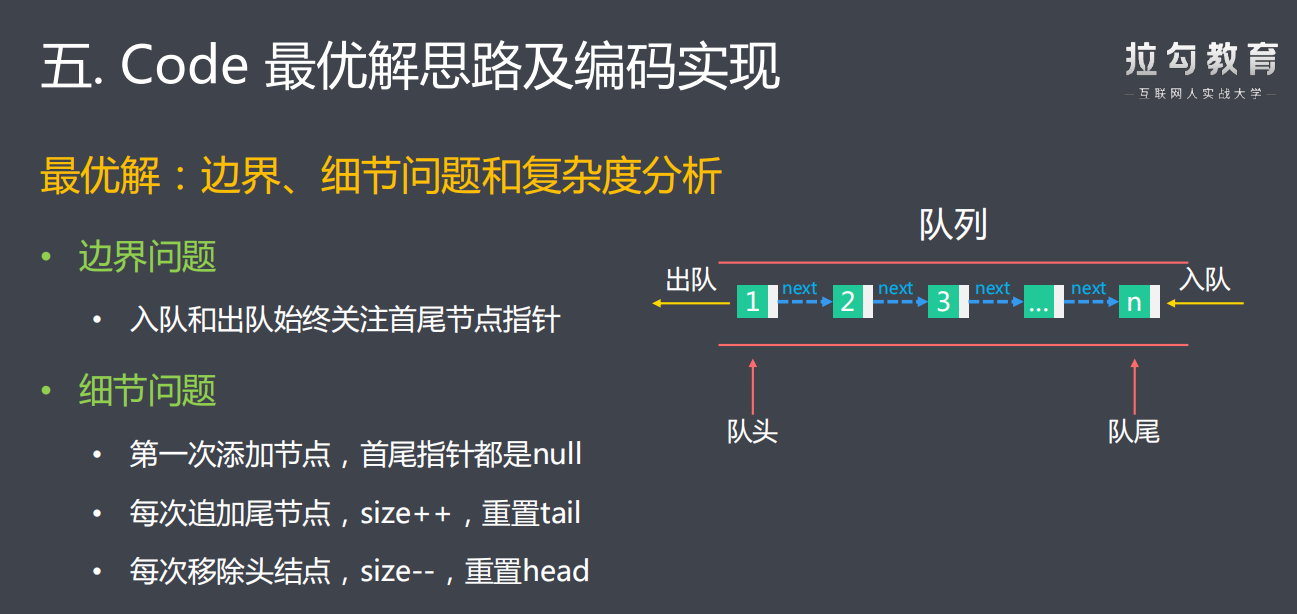
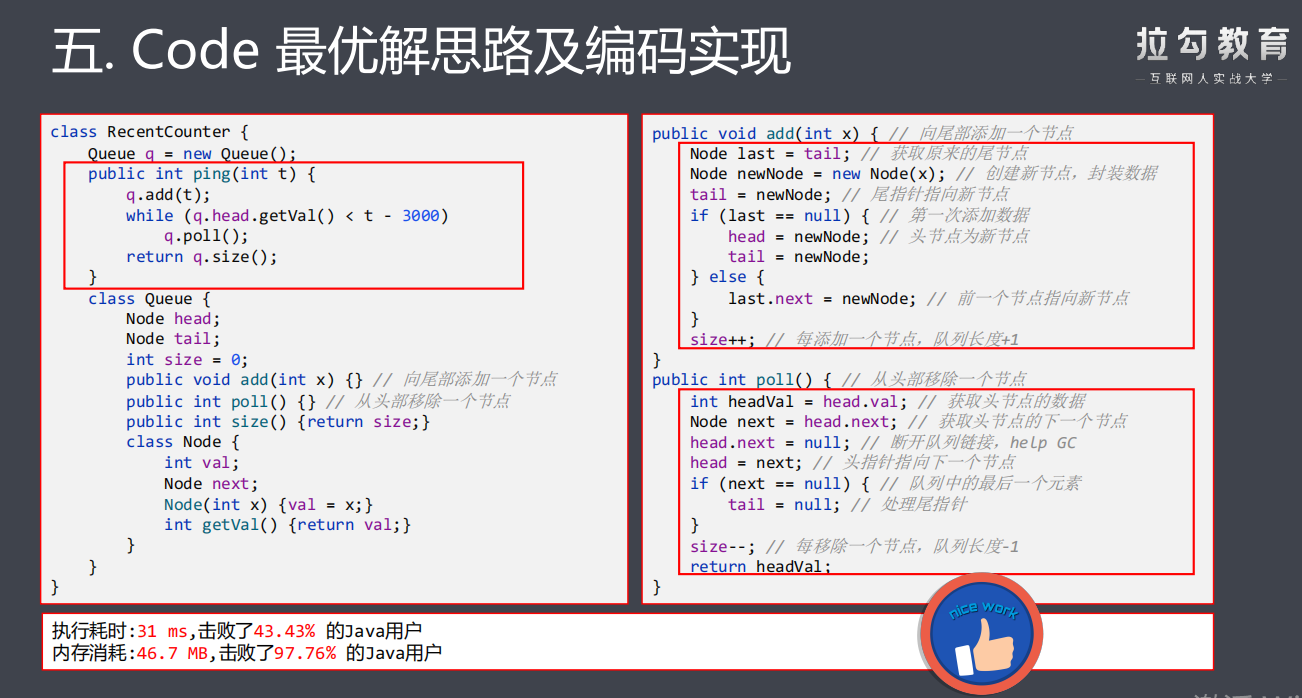
队列实现代码:
Queue q; public RecentCounter() { q = new Queue(); } class Queue { // 1.使用链表实现一个队列 Node head; Node tail; int size = 0; public Queue() { } public void add(int x) { // 向尾部添加一个节点 Node last = tail; Node newNode = new Node(x); tail = newNode; // 尾指针指向新节点 if (last == null) { // 第一次添加数据 head = newNode; tail = newNode; } else { last.next = newNode; // 前一个节点指向新节点 } size++; // 每添加一个节点,队列长度+1 } public int poll() { // 从头部移除一个节点 int headVal = head.val; // 获取头节点的数据 Node next = head.next; head.next = null; // 链表第一个节点断开 head = next; // head指针指向后一个节点 if (next == null) { // 队列中的最后一个元素 tail = null; // 处理尾指针 } size--; // 每移出一个节点,队列长度减1 return headVal; } public int size() { return size; } class Node { // 队列节点:链表结构 int val; Node next; Node(int x) { val = x; } int getVal() { return val; } } }
辅助数据结构:队列。代码如下:
class Queue { // 1.使用链表实现一个队列 Node head; Node tail; int size = 0; public Queue() { } public void add(int x) {} public int poll() {} public int size() {} class Node { // 队列节点:链表结构 int val; Node next; Node(int x) { val = x; } int getVal() { return val; } } }
输入:inputs = [[1],[100],[3001],[3002]]
输出:[1,2,3,3]


1/4 用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列的支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
你只能使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
进阶:
你能否实现每个操作均摊时间复杂度为 O(1) 的队列?换句话说,执行 n 个操作的总时间复杂度为 O(n) ,即使其中一个操作可能花费较长时间。
示例:
输入:
["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
提示:
1 <= x <= 9
最多调用 100 次 push、pop、peek 和 empty
假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用 pop 或者 peek 操作)
/** * 入队(push): * 新元素总是压入 s1 的栈顶,同时我们会把 s1 中压入的第一个元素赋值给作为队首元素的 front 变量 * 出队(pop): * 根据栈 LIFO 的特性,s1 中第一个压入的元素在栈底。为了弹出 s1 的栈底元素,我们得把 s1 中所有的元素全部弹出, * 再把它们压入到另一个栈 s2 中,这个操作会让元素的入栈顺序反转过来。通过这样的方式,s1 中栈底元素就变成了 s2 的栈顶元素, * 这样就可以直接从 s2 将它弹出了。一旦 s2 变空了,我们只需把 s1 中的元素再一次转移到 s2 就可以了 * * 入队 - O(1),出队 - 摊还复杂度 O(1) */ public class MyQueue { private Stack<Integer> s1;//入栈 private Stack<Integer> s2;//出栈 //构造方法 public MyQueue(){ s1 = new Stack<>(); s2 = new Stack<>(); } //入栈 public void push(int x) { /* 1.首先给s1入栈 */ s1.push(x); } public int pop() { /* 1.如果s2为空,则将s1(是否为空)全部的值先移动到s2 2.如果s2有值,则直接弹出 */ if (s2.empty()){ while(!s1.empty()){ s2.push(s1.pop()); } } //这个判断条件就是去除s1为空,从而导致s2也为空的情况 if (!s2.empty()){ return s2.pop(); } return -1; } public int peek() { if (s2.empty()){ while(!s1.empty()){ s2.push(s1.pop()); } } if (!s2.empty()){ return s2.peek(); } return -1; } public boolean empty() { if (s1.empty() && s2.empty()){ return true; } return false; } } /** * Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: * MyQueue obj = new MyQueue(); * obj.push(x); * int param_2 = obj.pop(); * int param_3 = obj.peek(); * boolean param_4 = obj.empty(); */
用两个栈实现一个队列。队列的声明如下,请实现它的两个函数 appendTail 和 deleteHead ,
分别完成在队列尾部插入整数和在队列头部删除整数的功能。(若队列中没有元素,deleteHead 操作返回 -1 )
示例 1:
输入:
["CQueue","appendTail","deleteHead","deleteHead"]
[[],[3],[],[]]
输出:
[null,null,3,-1]
示例 2:
输入:
["CQueue","deleteHead","appendTail","appendTail","deleteHead","deleteHead"]
[[],[],[5],[2],[],[]]
输出:
[null,-1,null,null,5,2]
提示:
1 <= values <= 10000
最多会对 appendTail、deleteHead 进行 10000 次调用
// 思路同上一个题 public class CQueue { Stack<Integer> stack1; Stack<Integer> stack2; public CQueue() { stack1 = new Stack<>(); stack2 = new Stack<>(); } public void appendTail(int value) { stack1.push(value); } public int deleteHead() { // 如果第二个栈为空,把第一个栈中的数据一次入栈到第二个栈 if (stack2.isEmpty()) { while (!stack1.isEmpty()) { stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } } //从第二个栈中出数据 if (stack2.isEmpty()) { return -1; } else { int deleteItem = stack2.pop(); return deleteItem; } } }
3/4 用队列实现栈
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈
pop() -- 移除栈顶元素
top() -- 获取栈顶元素
empty() -- 返回栈是否为空
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
/** * 入栈操作时,首先获得入栈前的元素个数 n,然后将元素入队到队列, * 再将队列中的前 n个元素(即除了新入栈的元素之外的全部元素)依次出队并入队到队列, * 此时队列的前端的元素即为新入栈的元素,且队列的前端和后端分别对应栈顶和栈底。 * * 由于每次入栈操作都确保队列的前端元素为栈顶元素,因此出栈操作和获得栈顶元素操作都可以简单实现。 * 出栈操作只需要移除队列的前端元素并返回即可,获得栈顶元素操作只需要获得队列的前端元素并返回即可(不移除元素)。 * 由于队列用于存储栈内的元素,判断栈是否为空时,只需要判断队列是否为空即可。 */ public class MyStack { Queue<Integer> queue; /** 初始化数据结构. */ public MyStack() { queue = new LinkedList<Integer>(); } public void push(int x) { int n = queue.size(); queue.offer(x); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { queue.offer(queue.poll()); } } public int pop() { return queue.poll(); } public int top() { return queue.peek(); } public boolean empty() { return queue.isEmpty(); } } /** * Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such: * MyStack obj = new MyStack(); * obj.push(x); * int param_2 = obj.pop(); * int param_3 = obj.top(); * boolean param_4 = obj.empty(); */
返回 A 的最短的非空连续子数组的长度,该子数组的和至少为 K 。
如果没有和至少为 K 的非空子数组,返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入: A = [1], K = 1
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: A = [1,2], K = 4
输出: -1
示例 3:
输入: A = [2,-1,2], K = 3
输出: 3
提示:
1 <= A.length <= 50000
-10 ^ 5 <= A[i] <= 10 ^ 5
1 <= K <= 10 ^ 9
//通过维持一个队列,从头到尾遍历。对于每个y,找出满足,P[y]-P[x]>=K的最大的x。如果y-x比之前的长度要小就记录新的最小值 class Solution { //先计算前缀和p数组 // 通过维持一个队列,从头到尾遍历。对于每个y,找出满足,p[y]-p[x]>=K的最大的x。 // 计算的就是 ((0...y-1) - (0....x-1) )=(x....y-1) 长度为y-1-x+1=y-x // 如果y-x比之前的长度要小就记录新的最小值 // 细节问题:要注意负数的情况 public int shortestSubarray(int[] A, int K) { int size = A.length; long[] p = new long[size + 1]; //前缀和preSum //一次累加每一个值 p[y]存放的是 A数组中从0加到y-1位置 for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) p[i + 1] = p[i] + (long) A[i]; int result = size + 1;//最小长度 Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList();//存放下标 滑动窗口 for (int y = 0; y < p.length; y++) { //p[y]表示A[y]之前的数字和(A数组中从0加到y-1位置) while (!queue.isEmpty() && p[y] <= p[queue.getLast()]) {//存在负数的情况,在队列尾部删除元素 queue.removeLast(); } //当前队列头到y的范围内元素和大于K,需要判断是否比之前的长度更小 while (!queue.isEmpty() && p[y] >= p[queue.getFirst()] + K) { result = Math.min(result, y - queue.removeFirst()); } //加到队列尾部 queue.addLast(y); } return result < size + 1 ? result : -1; } //滑动窗口 public int shortestSubarray2(int[] A, int K) { int size = A.length; int left = 0, right = 0; //双指针 int sum = 0;//当前子序列和 int result = size + 1; while (right < size) {//右指针未到边界 sum = sum + A[right];//累加 if (sum <= 0) {//出现负值的情况,双指针都后移到当前右指针的下一个位置 left = right + 1; right = right + 1; sum = 0; continue; } int i = right; while (A[i] < 0) {//将负数变为0,同时在上一个元素加上这负数 A[i - 1] += A[i]; A[i] = 0; i--; } if (sum >= K) {//尝试缩小窗口 while (left <= right && sum - A[left] >= K) { sum = sum - A[left]; left++; } if (right - left + 1 < result) { result = right - left + 1; if (result == 1) { //最短为1个,发现最短直接返回,提前终止 return result; } } } right++; } return result < size + 1 ? result : -1; } }