实验程序:
package 实验九;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Point {
static int x;
static int y;
Point(int x,int y){
Point.x=x;
Point.y=y;
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
@SuppressWarnings({ "unused", "resource" })
Scanner shuru=new Scanner(System.in);
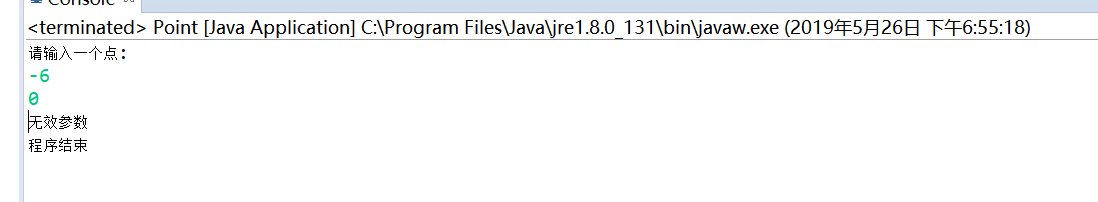
System.out.println("请输入一个点:");
int h=shuru.nextInt();
int a=shuru.nextInt();
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
Point s=new Point(h,a);
if(x>=0&&y>=0) {
System.out.println("x为:"+Point.x+"y为:"+Point.y);
}
else {
throw new Exception() {
public String toString() {
return "无效参数";
}
};
}
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("程序结束");
}
}
}
package 实验九;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Rectangle {
static int length;
static int width;
Rectangle(Point point1,int length,int width){
Rectangle.length=length;
Rectangle.width=width;
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
Scanner shuru=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个点:");
int h=shuru.nextInt();
int a=shuru.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入长方形的长:");
int b=shuru.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入长方形的宽:");
int c=shuru.nextInt();
Point p1=new Point(h,a);
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
Rectangle m=new Rectangle(p1,b,c);
if(length>=0&&width>=0) {
System.out.println("这是一个长为"+Rectangle.length+"宽为"+Rectangle.width+"的长方形" );
}
else {
throw new Exception() {
public String toString() {
return "无效参数";
}
};
}
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("程序结束");
}
}
}

package 实验九;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Polygon {
Polygon(Point[] points) {
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public static void main(String[] args) {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
Scanner shuru=new Scanner(System.in);
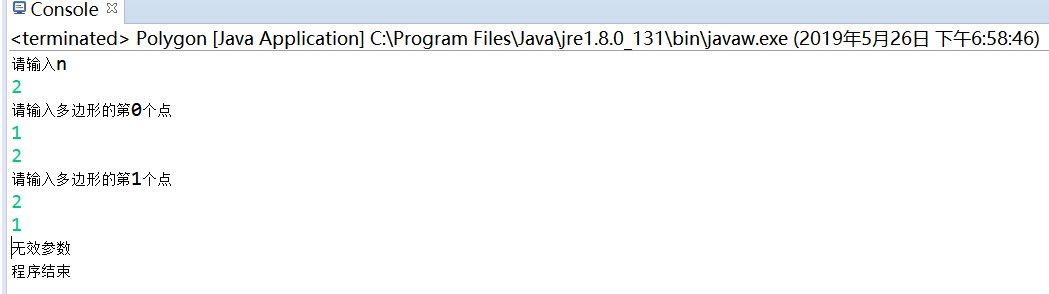
System.out.println("请输入n");
int n=shuru.nextInt();
int Point[]=new int[n];
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
System.out.println("请输入多边形的第"+i+"个点");
int h1=shuru.nextInt();
int a1=shuru.nextInt();
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
Point p2 = new Point(h1,a1);
}
try {
// Point s=new Point(-1,2);
if(Point.length>=3)
{
System.out.println("这可以构成一个多边形");
}
else {
throw new Exception() {
public String toString() {
return "无效参数";
}
};
}
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("程序结束");
}
}
}
package 实验九;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Triangle {
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private static final Point Point = null;
public Point point2,point3;
protected double a,b,c;
public Triangle(Point p1,Point p2,Point p3) {
//super("三角形",p1);
this.point2=p2;
this.point3=p3;
}
public Triangle() {
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
Scanner shuru=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个点:");
int h=shuru.nextInt();
int a=shuru.nextInt();
Point p1 = new Point(h,a);
System.out.println("请输入一个点:");
int h1=shuru.nextInt();
int a1=shuru.nextInt();
Point p2 = new Point(h1,a1);
System.out.println("请输入一个点:");
int h2=shuru.nextInt();
int a2=shuru.nextInt();
Point p3 = new Point(h2,a2);
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
Triangle s = new Triangle(p1, p2, p3);
double g=(h1-h)/(a1-a);
double p=(h2-h1)/(a2-a1);
if(g!=p) {
System.out.println("这三个点可以构成一个三角形");
}
else{
throw new Exception() {
public String toString() {
return "无效参数";
}
};
}
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("程序结束");
}
}
}

实验心得:通过本次实验我学习到了异常的抛出,捕获,并处理。程序通过try{}捕捉异常,try如果有异常发生,程序的运行便会中断,抛出“异常类所产生的对象”。try{}抛出的异常对象会进入catch()判断是否是括号内想要捕获的异常,如果是,就会进入catch{}代码块内进行异常的处理,程序继续往下运行,可以有多个catch(){},即可以有多个异常对象,按类处理异常。finally{}程序无论是否捕获异常都会执行,一般用来关闭对象。