JSON functions in SQL Server enable you to analyze and query JSON data, transform JSON to relational format, and export SQL query results as JSON text.
If you have JSON text, you can extract data from JSON or verify that JSON is properly formatted using built-in functions JSON_VALUE, JSON_QUERY, and ISJSON. For more advanced querying and analysis, the OPENJSON function can transform an array of JSON objects into a set of rows. Any SQL query can be executed on the returned result set. Finally, there is the FOR JSON clause that enables you to format query results as JSON text.
SELECT TOP 1000 [Version]
,[OSType]
,[Online]
,[OnlineT]
FROM [ApplicationTest].[dbo].[table1]
for json auto
We can start with simple examples. In the following Transact-SQL code, we will define a text variable where we will put JSON text:
DECLARE @json NVARCHAR(4000)
SET @json =
N'{
"info":{
"type":1,
"address":{
"town":"Bristol",
"county":"Avon",
"country":"England"
},
"tags":["Sport", "Water polo"]
},
"type":"Basic"
}'
Now, we can extract values and objects from JSON text using the JSON_VALUE and JSON_QUERY functions:
SELECT JSON_VALUE(@json, '$.type') as type, JSON_VALUE(@json, '$.info.address.town') as town, JSON_QUERY(@json, '$.info.tags') as tags
This query will return “Basic”, “Bristol”, and ["Sport", "Water polo"] values. The JSON_VALUE function returns one scalar value from JSON text (e.g. strings, numbers, true/false) that is placed on a JSON path specified as the second parameter. JSON_QUERY returns an object or array (in this example an array of tags) on the JSON path. JSON built-in functions use JavaScript-like syntax to reference values and objects in JSON text via second parameter.
The OPENJSON function enables you to reference some array in JSON text and return elements from that array:
SELECT value
FROM OPENJSON(@json, '$.info.tags')
INSERT INTO Orders(Number, Date, Customer, Quantity)
SELECT Number, Date, Customer, Quantity
OPENJSON (@orders)
WITH (
Number varchar(200),
Date datetime,
Customer varchar(200),
Quantity int
) AS OrdersArray
Four columns in the result set that is returned by OPENJSON are defined in the WITH clause. OPENJSON will try to find the properties Number, Date, Customer, and Quantity in each JSON object and convert their values into columns in the result set. By default, NULL will be returned if the property is not found. The assumption in the query above is that the @orders variable contains the following JSON array:
'[
{"Number":1, "Date": "8/10/2012", "Customer": "Adventure works", "Quantity": 1200},
{"Number":4, "Date": "5/11/2012", "Customer": "Adventure works", "Quantity": 100},
{"Number":6, "Date": "1/3/2012", "Customer": "Adventure works", "Quantity": 250},
{"Number":8, "Date": "12/7/2012", "Customer": "Adventure works", "Quantity": 2200}
]'
As you can see, the transformation from a JSON text to a relational form is simple. You just need to specify column names and types and OPENJSON will find properties in JSON that match these columns. In this example, plain JSON is used; however, OPENJSON can handle any nested/hierarchical structure of JSON objects.
Also, OPENJSON can be used to combine relational and JSON data in the same query. If we assume that the JSON array shown in the previous example is stored in the Orders column, the following query can combine the columns and JSON fields:
SELECT Id, FirstName, LastName, Number, Date, Customer, Quantity
FROM Person
CROSS APPLY OPENJSON (OrdersJson)
WITH (
Number varchar(200),
Date datetime,
Customer varchar(200),
Quantity int ) AS OrdersArray
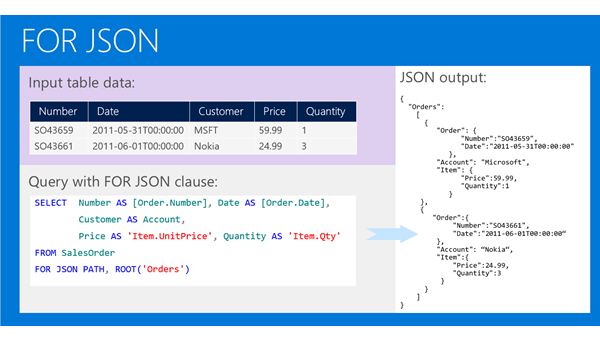
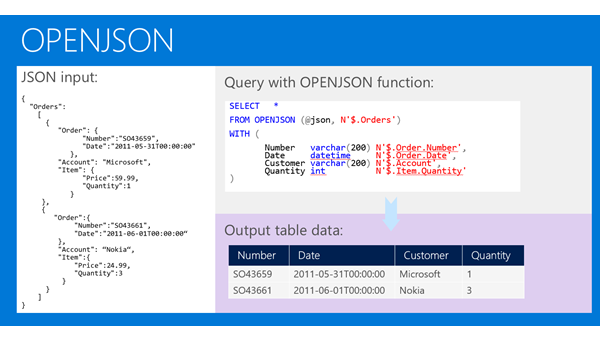
select * from [dbo].[table1] for json auto
declare @jsondata varchar(max)
set @jsondata=N'[{"Version":"2.1.1.1","OSType":1,"Online":1,"OnlineT":"on"},{"Version":"2.1.1.2","OSType":1,"Online":1,"OnlineT":"on"}]';
select Version
from openjson(@jsondata)
with(
Version varchar(50)
)
